bio 342 human physiology
advertisement

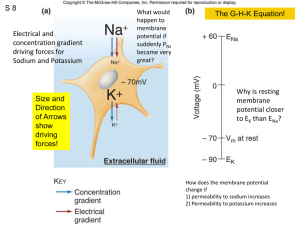
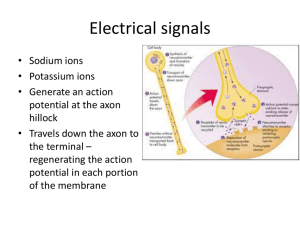
30 September 2011 Section B: Membrane Potentials Section C: Synapses Test Monday: Turn in Take-Home Portion at beginning. All personal materials on floor at front of room. At least one vacant seat to nearest neighbor. Coverage up to and including Ch 6 B Check your Multiple Choice Grade on Moodle Site Tuesday Wednesday 1QQ on Synapses. 1QQ # 11 for 8:30 class 1. Why doesn’t an action potential reach + 60 mV? a) b) c) d) Voltage- gated Na+ channels open and spontaneously close quickly Voltage-gated K+ channels open a little later than the Na+ channels Na+ K+ ATPase quickly pumps out the Na+ that enters during an AP As the membrane approaches +60 mV, the driving force for Na+ entry is weaker e) Na+ is not the only permeable ion. 2. Which are the accurate statements regarding V-gated K+ channels? a) The more the membrane is depolarized, the more K+ channels will open, and the membrane will depolarize even more, generating a positive feedback cycle. b) These channels inactive after a short open time and can only reopen if the membrane potential returns to negative values. c) These channels are “blocked” by lidocaine, xylocaine, and novocaine. d) These channels close as the membrane repolarizes. 1QQ # 11 for 9:30 class 1. Why doesn’t an action potential reach + 60 mV? a) b) c) d) Voltage- gated Na+ channels would be forced “shut” at + 60 mV Voltage-gated K+ channels open a little sooner than the Na+ channels. Na+ K+ ATPase quickly pumps out the Na+ that enters during an AP As the membrane approaches +60 mV, the driving force for Na+ entry is weaker e) Na+ channels open only briefly and then quickly inactivate. 2. Which are the accurate statements regarding V-gated K+ channels? a) The more the membrane is depolarized, the more K+ channels will open, and K+ will leave the cell, contributing to repolarization. b) These channels inactive after a short open time and can only reopen if the membrane potential returns to negative values. c) These channels are “blocked” by lidocaine, xylocaine, and novocaine. d) These channels open shortly after the V-gated Na+ channels open. S1 The Questions: How does an action potential move along the axon? Why doesn’t the amplitude get smaller with distance? Why is the conduction of an action potential unidirectional? Axon Hillock of interneuron or efferent neuron Axon Trigger Zone of Sensory Neuron S2 In unmyelinated axons, action potential must be generated at each point along the membrane, a relatively slow process that involves influx of Na+ which sets up positive feedback cycle. In myelinated axons, action potential must be generated only at the nodes of Ranvier, which allows AP to be conducted much faster and with fewer ions moving, and thus less energetically expensive. S3 Saltatory Conduction Figure 6.23 AP CV (up to 100 m/s) Reminder: influx of Na+ is very quickly followed by efflux Location of channels of K+ (not shown above) Energy Requirements Axon diameter Clustering of V-gated channels at Nodes of Ranvier What’s at the end of an axon? S4 Section C: Synapses and Synaptic Transmission Figure 6.24 S5 Anatomy of an Electrical S 8 Synapse (aka Gap Junction) Comparison to Chemical Synapses • Directionality • Response time • Sign inversion? Uncommon in human CNS. Common in cardiac muscle and some smooth muscle. S6 Anatomy of a Chemical Synapse Presynaptic cell Postsynaptic cell S7 Most neurotransmitters are synthesized in the axon terminal. Exceptions: Peptide NTs originate in cell body, move in vesicles by fast orthograde axonal transport to axon terminal. Figure 6.27 Vesicle release proportional to Ca++ influx (High f AP leads to residual Ca++ in terminal) Tetanus toxin & Botulinum toxin disrupt SNARE function. Fates of neurotransmitters: 1) Bind to receptor on Postsynaptic cell 2) Diffusion away from synapse 3) Enzymatic degradation e.g. Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and Monoamine Oxidase (MAO) 4) Uptake by astrocytes 5) Reuptake into presynaptic terminal (e.g. SSR) S8 Presynaptic Facilitation Presynaptic Inhibition Mechanism: vary Ca++ entry in presynaptic terminal B. Size of PSP is Variable! Figure 6.33 Who Cares?