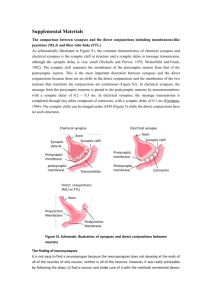
neurotransmitters
advertisement

Electrical signals • Sodium ions • Potassium ions • Generate an action potential at the axon hillock • Travels down the axon to the terminal – regenerating the action potential in each portion of the membrane synapse neurotransmitters • Chemical signals released by presynaptic neurons • Bind to receptors on postsynaptic neuron or effector cells • Stimulate or inhibit them • 50+ different molecules have been identified • Classified chemically and functionally Other examples • • • • • Histamine GABA Glutamate Glycine Endorphins Postsynaptic membrane receptor • Receive neurotransmitter • Specialized to open/close ion channels • Produces graded local change to membrane potential/voltage according to amount of NTM released and time it sticks around Types of synapses • Where the axon synapses with the postsynaptic cell • Graded potentials dissipate in strength as spread – most effective type of synapse? Effects Excitatory Synapses • Depolarization (more +) of postsynaptic membrane • Channels allow Na+ and K+ ions to diffuse simultaneously • Local graded depolarization = EXCITATORY POSTSYNAPTIC POTENTIAL (EPSP) • Helps trigger an action potential Inhibitory Synapses • Induce hyperpolarization (more -) of postsynaptic membrane • More permeable to K+, Clor both • Less likely to “fire” an action potential, or requires a larger depolarizing current • INHIBITORY POSTSYNAPTIC POTENTIAL (IPSP) Neural integration • Reflects sum of all incoming neural information received • Both stimulatory and inhibitory inputs • Axon hillock keeps a running account of all the signals it receives modeling • Seekers: must find the right message • Neuron chain, standing hand to hand – once stimulated, must pass the message from one person to the next until reaches axon hillock. • Axon hillock: keeps a running total of the charge Problem solve: how do you get your message to “win”? • Must adhere to the same rules…but can alter everything else Summation: add together to influence activity of post-synaptic neuron temporal • 1 or more presynaptic neurons transmit impulses in rapid-fire order • Quick succession, before signal dissipates spatial • Postsynaptic neuron stimulated by a large number of terminals from same or different neurons at the same time • Large number of receptors bind neurotransmitters