neuro3toend
advertisement

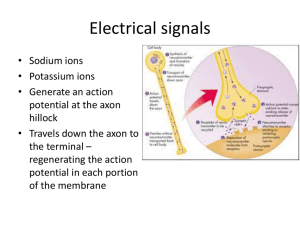
S8 Electrical and concentration gradient driving forces for Sodium and Potassium Size and Direction of Arrows show driving forces! What would happen to membrane potential if suddenly PNa became very great? The G-H-K Equation! Why is resting membrane potential closer to EK than ENa? How does the membrane potential change if 1) permeability to sodium increases 2) Permeability to potassium increases S9 The Goldman Hodgkin Katz Equation • If you know the concentrations of ALL permeable ions and their relative permeabilities, you can calculate the membrane potential using the GHK Equation. S 10 At RMP, some Na+ leaks in, some K+ leaks out. S 14 Which ion moving in which direction (into or out of cell) is responsible for depolarization and overshoot? Which ion moving in which direction (into or out of cell) is responsible for repolarization and hyperpolarization? Increase PNa+ Can the membrane potential go more negative than -90 mV? Increase PK+ Increase PK+ How do ions get across the membrane? Ion channels! S 15 Leak Channels Gated Channels ….. Ligand-gated ….. Mechanically-gated ….. Voltage-gated Electrogenic SodiumPotassium ATP-ase maintains concentrations across membrane Graded potentials are conducted decrementally for only a few millimeters, die out over distance and time, and are proportional to the size of the stimulus. 3 Na+ 2K+ S 17 Graded potentials are conducted no more than 2mm Insect bites foot (stimulus). Sensory neuron produces graded potential in proportion to intensity of the stimulus. How is signal conducted to the brain? S3 Types and locations of Ion Channels Sensory neuron Leak Channels Gated Channels ….. Ligand-gated ….. Mechanically-gated ….. Voltage-gated w/ LGCs and MGCs Intracellular Recording Electrode or Stimulating Electrode Interneurons & Motoneurons w/ LGCs w/ VGCs S4 Expanded on next slide What happens when the membrane is depolarized by more than about 15 mV? Action potentials are all or nothing. Analogy of shutter release pressure on a camera, either trips shutter or not. How is the intensity of a stimulus encoded by action potential if all action potentials have the same size (amplitude)? S5 Relevance of the GHK equation Changes in membrane permeability produce changes in membrane potential via the opening and closing of ion channels! S6 To reset from inactivated state to closed state, membrane must repolarize. Open at -55 mV Membrane must repolarize to “reset” Na+ Channels to be capable of opening again. Compare and contrast voltagegated Na and K channels based on time to open and duration of open time. S7 Voltage-gated Na+ channel Tetrodotoxin from ovary of Puffer fish, used in Japanese sushi (fugu) scienceblogs.com/.../upload/2006/03/channel.jpg S8 What types of ion-channels are labeled in this neuron in red? TTX with red fluorescent marker S9 Rising Phase Falling Phase Relative permeabilities Duration of AP Refractory periods absolute RP relative RP Why does the peak of the action potential not reach ENa? Properties of V-gated Na+ and K+ channels account for the shape of the action potential and the refractory periods. S 10 S 11 Natural ways to Initate an Action Potential Graded depolarization in cell body reach threshold at axon hillock Graded depolarization in in receptive membranes of sensory neurons reach threshold for AP at trigger zone. i.e. nociceptors and stretch receptors. Unstable membrane potential cycles: pacemaker potentials in pacemaker cells of heart, smooth muscles of gut, and medullary neurons for respiratory rhythm. S 12 Who Cares? Novacaine, lydocaine, xylocaine, All block voltage-gated Na+ channels Prevent action potentials, so stimulus does not result in an action potential in sensory neurons which would convey that information to the brain where person would be conscious of the stimulus! S 13 Questions About Action Potential Conduction: How does an action potential move along the axon? Why doesn’t the amplitude get smaller with distance? Why is the conduction of an action potential unidirectional? What is the absolute refractory period and what is going on with voltage gated sodium channels that accounts for the absolute refractory period? What is the relative refractory period and what is going on with voltage gated sodium channels that accounts for the relative refractory period? Axon Hillock Axon S 14 In unmyelinated axons, action potential must be generated at each point along the membrane, a relatively slow process that involves influx of Na+ which sets up positive feedback cycle. In myelinated axons, action potential must be generated only at the nodes of Ranvier, which allows AP to be conducted much faster and with fewer ions moving, and thus less energetically expensive. S1 The Questions: How does an action potential move along the axon? Why doesn’t the amplitude get smaller with distance? Why is the conduction of an action potential unidirectional? Axon Hillock of interneuron or efferent neuron Axon Trigger Zone of Sensory Neuron S3 Saltatory Conduction Figure 6.23 AP CV (up to 100 m/s) Reminder: influx of Na+ is very quickly followed by efflux Location of channels of K+ (not shown above) Energy Requirements Axon diameter Clustering of V-gated channels at Nodes of Ranvier What’s at the end of an axon? S4 Section C: Synapses and Synaptic Transmission Figure 6.24 S5 Anatomy of an Electrical SynapseS 8 (aka Gap Junction) Comparison to Chemical Synapses • Directionality • Response time • Sign inversion? Uncommon in human CNS. Common in cardiac muscle and some smooth muscle. S6 Anatomy of a Chemical Synapse Presynaptic cell Postsynaptic cell S7 Most neurotransmitters are synthesized in the axon terminal. Exceptions: Peptide NTs originate in cell body, move in vesicles by fast orthograde axonal transport to axon terminal. Figure 6.27 Vesicle release proportional to Ca++ influx (High f AP leads to residual Ca++ in terminal) Tetanus toxin & Botulinum toxin disrupt SNARE function. Fates of neurotransmitters: 1) Bind to receptor on Postsynaptic cell 2) Diffusion away from synapse 3) Enzymatic degradation e.g. Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and Monoamine Oxidase (MAO) 4) Uptake by astrocytes 5) Reuptake into presynaptic terminal (e.g. SSR) S8 Presynaptic Facilitation Presynaptic Inhibition Mechanism: vary Ca++ entry in presynaptic terminal B. Size of PSP is Variable! Figure 6.33 Who Cares? S1 Unidirectional Release, diffusion, binding, Post-synaptic Receptor Types: Inotropic or Metabotropic Figure 6.25 Classification: Excitatory (closer to threshold for AP) Or Inhibitory (stabilizes or hyperpolarizes) S2 Types of Ligand-Gated Receptors = ACH = Acetylcholine Inotropic receptor Metabotropic receptor Agonist = Nicotine Agonist = Muscarine Antagonist = Curare Antagonist = Atropine Types of Acetylcholine Receptors so named for agonist: Nicotinic AChR and Muscarinic AChR S3 Priority by proximity To axon hillock! S4 Figure 6.28 EPSPs :which ion moving in which direction? Duration of PSP vs AP Synaptic delay Some ion Channels that allow flux of Na+ and K+ simultaneously e.g. nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor (nAChR) S5 Figure 6.29 IPSPs :which ion moving in which direction? Some IPSPs result in no change in membrane potential by opening Chloride channels that stabilize membrane potential at resting value (Nernst Potential for Cl- = -70mV) or in cells that actively transport Cl- out. EK+ S6 Figure 6.31 Summation and Synaptic Integration Different times Different locations Challenge question: Suppose each IPSP hyperpolarizes by 5 mV and each EPSP depolarizes by 5 mV. If 4 inhibitory synapses are active at the same time, how many excitatory synapses must be active simultaneously to exceed threshold (-55 mV) if the resting membrane potential is -70mV? S7 Synapses named for NT used: -ergic Examples: Cholinergic Adrenergic Serotonergic GABAergic Peptidergic S 11 Pharmacological agents intended to act in brain must be able to cross blood-brain barrier. Who Cares? Parkinsons Disease Treatments for Parkinsonism: a) tablets of L-Dopa (which crosses the BBB) unlike Dopamine (which would have widespread effects) b) neuronal transplants (self, fetal, stem cell, pig), c) electrical stimulation NIH Stem Cell Information S3 Touch, pain, temperature, proprioception Vessel stretch, O2, CO2, etc. 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves Vision, taste, smell, hearing, equilibrium Skeletal Muscle Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Glands Tracts, pathways, commissures Nuclei Nerves & Ganglia Control of digestive functions in quadraplegics via enteric nervous system. S4 Figure 6.38 S5 Components of gray matter Figure 6.39 Amygdala & Hippocampus S6 How do we know the functions of various brain regions? Analogy: experiments to discover the function of a battery in a car. a) Correlations of deficits of stroke victims with brain regions affected. b) Selective ablations. c) Selective electrical and chemical microstimulation i) Dr. Hettes’s experiments on rats ii) Neurologist Wilder Penfield & Epilepsy S7 S8 Homunculus = representation of body parts S9 Dorsal roots = sensory (afferent) Ventral roots = motor (efferent, both somatic and autonomic) Gray matter regions of brain and spinal cord “Pinched nerves” and bulging discs Ascending and descending axonal tracts in white matter not anatomically delineated. Atlanta-Boston flight Origin-Destination Naming of white matter tracts….. S 10 Explanation for Cervical and lumbar enlargements of spinal cord. Spinal nerves named for vertebral level. 8 12 5 5 1 Using patient’s localization of symptoms with knowledge of dermatomes to determine which spinal nerve is affected by damage. Epidural injections into region of cauda equina of Lidocaine-like agents to block action potentials in sensory and motor axons without risk of damage to spinal cord. S1 Homunculus = representation of body parts Somatotopy = adjacent regions of the body are represented by adjacent regions in the cerebral cortex. S3 Dermatomes Who cares? Surgery for chronic back pain How might this information be clinically useful? S4 Cranial Nerves Challenge: Identify the deficits associated with damage to a given cranial nerve. S5 On Old Olympus’ Vision Treeless Top A Fat Hearing & Equilibrium !!! Spinal S6 Figure 6.43 ACh & mAChR Locations of neuronal cell bodies, ganglia, pharmacology of the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) at skeletal muscle (nAChR) Diagram of NMJ compared to synaptic varicosities characteristic of autonomic postganglionic axons. Locations and proximities of target cells and distributions of receptors on target cells. Somatic = excitatory only at NMJ (ex. Reduced muscle tone) Autonomic= exitatory or inhibitory depending on NTs and their receptors. Sympathetic (thoraco-lumbar) division Parasympathetic (cranio-sacral) division) S7 Figure 6.44 S8 Why activation of the sympathetic division has widespread effects. S8 Antagonist = Curare Figure 6.46 Antagonist = Atropine Adrenal medulla is modified sympathetic ganglion that secretes mainly EPI S9 S 10 mAChR Table 6.11 Emotional Thermoregulatory