chap 1 (Repaired) - Swapnil Patni's Classes
advertisement
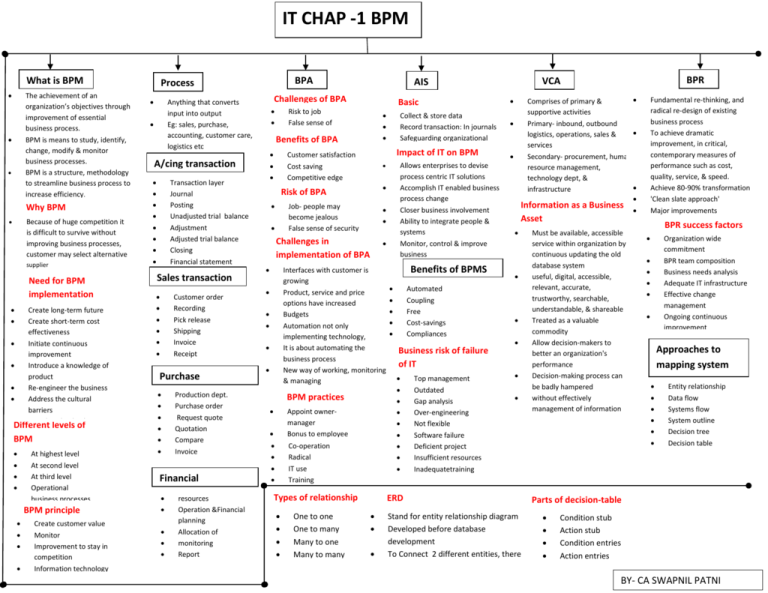
IT CHAP -1 BPM What is BPM The achievement of an organization’s objectives through improvement of essential business process. BPM is means to study, identify, change, modify & monitor business processes. BPM is a structure, methodology to streamline business process to increase efficiency. Why BPM Because of huge competition it is difficult to survive without improving business processes, customer may select alternative supplier Journal Posting Unadjusted trial balance Adjustment Adjusted trial balance Closing Financial statement Create customer value Monitor Improvement to stay in competition Information technology Recording Pick release Shipping Invoice Receipt Reconciliation Purchase cycle transaction Production dept. Purchase order Request quote Quotation Compare Invoice Receipt payment Financial Transaction cycle resources Operation &Financial planning Allocation of monitoring Report Risk to job False sense of security Customer satisfaction Cost saving Competitive edge Benefits of BPA A/cing transaction cycle Transaction layer Create long-term future Create short-term cost effectiveness Initiate continuous improvement Introduce a knowledge of product Re-engineer the business Address the cultural barriers Introduce leadership At highest level At second level At third level Operational business processes Challenges in implementation of BPA Interfaces with customer is growing Product, service and price options have increased Budgets Automation not only implementing technology, It is about automating the business process New way of working, monitoring & managing BPM practices Appoint ownermanager Bonus to employee Bottoms-up Co-operationapproach Radical IT use Training Types of relationship One to one One to many Many to one Many to many Allows enterprises to devise process centric IT solutions Accomplish IT enabled business process change Closer business involvement Ability to integrate people & systems Monitor, control & improve business Job- people may become jealous False sense of security Record transaction: In journals Safeguarding organizational assets Impact of IT on BPM Risk of BPA Basic Collect & store data functions Benefits of BPMS Automated Coupling Free Cost-savings Compliances Business risk of failure of IT Top management Outdated Gap analysis Over-engineering Not flexible Software failure Deficient project Insufficient resources Inadequatetraining Comprises of primary & supportive activities Primary- inbound, outbound logistics, operations, sales & services Secondary- procurement, human resource management, technology dept, & infrastructure Information as a Business Fundamental re-thinking, and radical re-design of existing business process To achieve dramatic improvement, in critical, contemporary measures of performance such as cost, quality, service, & speed. Achieve 80-90% transformation 'Clean slate approach' Major improvements Asset ERD BPR VCA AIS Challenges of BPA Anything that converts input into output Eg: sales, purchase, accounting, customer care, logistics etc Sales transaction cycle Customer order BPM principle Need for BPM implementation Different levels of BPM BPA Process Stand for entity relationship diagram Developed before database development To Connect 2 different entities, there is a need of relationship Must be available, accessible service within organization by continuous updating the old database system useful, digital, accessible, relevant, accurate, trustworthy, searchable, understandable, & shareable Treated as a valuable commodity Allow decision-makers to better an organization's performance Decision-making process can be badly hampered without effectively management of information BPR success factors Organization wide commitment BPR team composition Business needs analysis Adequate IT infrastructure Effective change management Ongoing continuous improvement Approaches to mapping system Entity relationship Data flow Systems flow System outline Decision tree Decision table Parts of decision-table Condition stub Action stub Condition entries Action entries BY- CA SWAPNIL PATNI