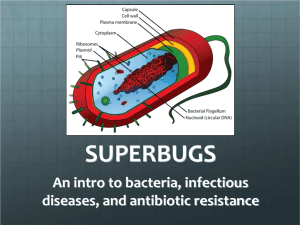
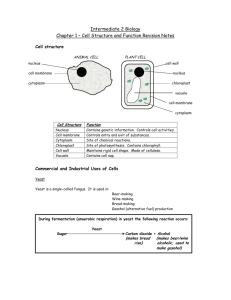
File
advertisement

Microbiology Technologies + Future Outlook Microbiology • Since we have started to harness the amazing power of bacteria, the field of microbiology has become much more prominent • As we previously learned, we are developing new ways to utilize bacteria to our advantage! – Detergents – Mining – Textiles – Food In the clinical lab • Most bacterial cultures are processed much like we did in this lab – Swab “infected” areas – Culture bacteria on growth media – Observe colonies – Perform culture tests* – Oxidase, indole* – Perform gram staining procedure – Identify organism – Perform Antibiotic susceptibility testing Microbiology Technologies •However, a clinical lab has access to more $$, and are designed to be more microbiology specific than our lab. •These are some of the interesting technologies used in clinical labs around the world today! Automated Laboratories Culturing Bacteria • Clinical labs now have access to a wide variety of Chromogenic Media – The chromogenic mixture contains chromogenic substrates as Salmon-GAL, X-Gal, X-glucuronide, etc. – Certain enzymes, produced by some bacteria, cleave these substrates, resulting in the different coloration of certain bacteria colonies. Bacterial Identification • Chromogenic Agar • Automated Identification systems – E.g. the Vitek system (bioMerieux) – Bacterial cultures are inserted into cards with a variety of different compounds, which when metabolized, will let the user know exactly what organism you are dealing with Bacterial Identification • MALDI-TOF system – Matrix Assisted Laser dissociated/ionized – Time of Flight – Essentially, a machine which zaps bacteria with a laser, causing all the proteins and cellular components of that bacteria to travel up a tube. – Mass spectrometer – complex machine which measures the mass of particles, and tells exactly what the bacteria is, in a matter of 2 minutes – Typically takes 4-5 days to confirm positive results Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing • First let’s look at a few key terms – Antibiotic – An antimicrobial agent, used to combat bacterial infections – Antiseptic – Antimicrobial agent applied to the surface of living tissue – Disinfectant – Antimicrobial agent that is applied to non-living surfaces for sterilization Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing • Bacteriocidal –Kills bacteria • Bacteriostatic –Stops bacteria from replicating, long enough so host immune system can fight off infection Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing • Automated Systems – The Vitek system , which we previously learned about can be used to give an antibacterial susceptibility background to a wide variety of organisms • Diffusion Systems – Etests – Kirby Bauer Disk Diffusion tests Etests • A strip of specialized paper, containing different concentrations of a specific antibiotic. • Where the bacteria stops growing tells the doctor what dose of antibiotic to give that patient (MIC – minimum inhibitory concentration) Kirby Bauer Disk Diffusion Test • Works by placing antibiotic disk on a cultured agar plate, and measuring the “zone of inhibition” size • Tells whether the bacteria is sensitive or resistant to the antibiotic, depending on the zone size So why is the study of microbiology important? • By now, hopefully we realize the importance of bacteria in our everyday lives… good or bad. • With a greater understanding of microbiology, more career opportunities open up into this exploration as well! Careers in Microbiology • Clinical Physician – Immunologist – Microbiologist – Pathologist • Laboratory Technician • Food & Drink – Any major food company hires microbiologists – Same with any brewing company as well… – Wine microbiology • Industry – Green movement in the 21st Century has opened the door to many microbial practices – Biomining, bioremediation, biofuels To Do Now • Use Kirby Bauer Disc diffusion sheet in front of you, to determine “your bacterias” zone of inhibition sizes to different types of antibiotics – Which antibiotic would you use to combat this infection? • NB. This is the hypothetical activity to replace the actual antibiotic test… it is possible these agents do not work against the organism you have found. – You must find your organism by deducing your Gram stain results + colony descriptions – Subsequently, determine which antibiotics are effective against that organism When you have finished • Continue to work on your Lab assignment, or continue review of Chapter 24.