Superbugs
advertisement
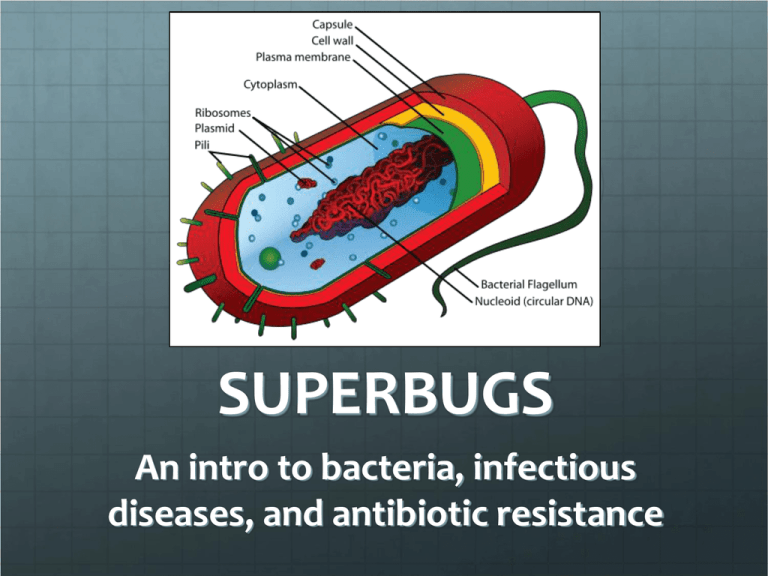
SUPERBUGS An intro to bacteria, infectious diseases, and antibiotic resistance What are bacteria? Single-celled organisms Prokaryotes: genetic material NOT contained in a nucleus Auto-trophs and hetero-trophs How abundant are bacteria? Bacterial Abundance Total bacteria on Earth Number of stars in the universe Age of the universe in seconds Bacteria in the human gut Global gross product ($/year) Cells in the human body Texts sent in 2009 People on Earth 5 x 1030 7 x 1022 4.4 x 1017 1 x 1014 7 x 1013 10X 1 x 1013 1.5 x 1012 6.9 x 109 All about bacteria… Help make yogurt, cheese, & wine Involved in environmental recycling and clean-up How many types of bacteria are there? Bacterial Distribution Insect Species Bacterial species in the soil Bacterial species in the air Bacterial species in the ocean Bird Species Bacterial species in the human mouth Bacterial Species in the human gut Pathogenic Species 1-10 million 4 million 4 million 2 million 10,000 600 500 55 Infectious Diseases Pathogen: a biological agent that causes disease Can be a virus, bacteria, fungi, protozoa, or parasite Infectious diseases are communicable or transmissible from one person to another Virus: Influenza (H1N1) Protist: Malaria (Plasmodium) Fungi: Plant pathogen (Rigidoporus laetus) Staph Infection: Staphylococcus aureus Mycobacterium tuberculosis Salmonella typhimurium Antibiotics Compounds that kill bacteria or inhibit their growth Naturally produced by microorganisms to kill others Now many are made synthetically Antibiotics Susceptible vs. Resistant Antibiotic Clearing Lawn Why is resistance bad? Because you can’t treat the disease! The patient will remain sick How do you get resistance? Usually from mutation in DNA Genetic mutations can be passed to offspring… Leads to evolution! Genetic Mutation Susceptible + Antibiotic Antibiotic Resistant What can you do to help? Follow the directions! Take antibiotics only when necessary