The 20th Century - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
advertisement

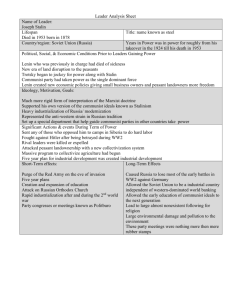
The 20th Century Mexican, Russian, and Chinese Revolutions Mexican Revolution Causes • • • • The need for political and land reforms, education, and nationalism World War I affects - Economic recession caused by the U.S.'s limited purchasing of Latin American products led to an unhappy population Foreigners controlled large amounts of the economy Large land amounts under the hacienda system were mainly controlled by the elite (Economic unbalance) Consequences • Overthrew dictator Porfirio Diaz • Created the Modern Mexican state • Mexican Constitution of 1917- Promised land reform, - Limited foreign land and resource ownership - Offered rights to workers - Limited churches ability to own land - Allowed for educational reforms • National confederation formed to represent workers in workers • Party of the Institutionalized Revolution formed into a powerful political force Politics and Culture in Mexico Political • • • • • • Porfirio Diaz's regime was in control Corruption in the government and political opponents were exiled Government oppressed workers who disagreed with the land distribution or forced labor Rigged elections kept Diaz in power Marxist socialism grew among the intellectuals US intervened Cultural • • • • • Nationalism grew (ex. Secular schools that focused on Mexican heritage) Diego Rivera and Jose Orozco painted murals and designed public buildings that "informed, convinced, and entertained" Novelists analyzed and wrote about past events and heroes The Catholic church opposed secularization and education reforms Peasant movement supported by the church occurred in 1920 (Cristeros fought against secularization) Mexican Revolution Key Players • Francisco Madero- Democratic reformer in Mexico that proposed moderate reforms in 1910 o Believed in moderate democratic reforms to relieve social tension wiothout limiting economic growth o Arrested by Porfirio Diaz and began the revolution against him when released from prison o Temporarily gained power but assassinated 1913 • Porfirio Diaz- A Mexican president from 1876-1911 (35 years officially and unofficially) o Imposed strong central government o Under his rule Mexico modernized: Built mines, plantations, telegraph lines and railroads Modernization brought wealth to the nation-- Most wealth was maintained within a few families Many lower classes were repressed and participated in forced labor More Key Players • Victoriano Huerta-Attempted to reestablish the central dictatorship in Mexico following the removal of Madero in 1913 o Forced from power in 1914 by: Emiliano Zapata- A peasant leader who hoped rebellion would bring • land reform Pancho Villa- Mexican revolutionary and military leader in northern Mexico along with Zapata Alvaro Obregon-Emerged as leader of the Mexican government in 1915 and became president in 1920 I must-ache you a question, who are these people? Francisco Madero Emiliano Zapata Porfirio Diaz Victoriano Huerta Alvero Obregon Pancho Villa Russian Revolution Causes • • • • • • Attempts to incorporate Lenin's version of Communism Economic strains from World War I Many men joined the armies leaving farms unattended causing food shortages (famine) Workers rebelled due to poor working conditions and they wanted higher pay Government was corrupt and oppressive -Tsar refused to initiate reforms The rise of radical socialist parties who wanted to overthrow tsarism and capitalism (Mostly among the intelligentsia and educated) Consequences • • • • • • • • • • Ends tsarist rule in Russia Creates the first Communist state Withdrawal of Russia from World War I Industrial growth and organization of economy on five-year plans Lenin redistributes land Formation of Soviet Union Russia eventually evolves into a world power Communism spreads and the world begins to pick sides (communists versus capitalists---ex. Cold War) Rapid spread of education Comintern (International office of communism) developed Russian Stabilization • • • • • Leon Trotsky develops a new Red Army that used lower classes and peasants to build a successful army that is loyal to the government Lenin develops a New Economic Policy which promised some freedom to small business and landowners Food production began to recover under new economic policies A new constitution set up a system of socialist republics U.S.S.R.- The federal system of socialist republics established in 1923 in various ethnic regions of Russia and was dissolved in 1991 o Controlled by Communists o Diminished nationalities protest under the Bolsheviks o Had mixed impacts-- it preserved ethnic Russians but did little to impact minority groups like Jews o Supreme Soviet developed which acted as a parliament but was controlled by communists o Comintern-Encourages the formation of communist parties elsewhere o Overall: Communists take over with authoritarian rule and make it more efficient than the last form of government, even enforced a political police Key Players • Vladimir Lenin- Russian founder of the Bolsheviks and leader of the Russian Revolution o First head of the U.S.S.R o Communist radical o Supported his New Economic Policy (combined capitalism with socialism), redistributed land, and nationalized banks and industry • Joseph Stalin- Successor to Lenin as head of the U.S.S.R. and led them through World War II o Fought for position by crushing his opponents o Strong nationalist view of communism o Represented the anti-Western strain on Russian tradition o Established a series of five year plans to replace the New Economic Policy o Pushed agricultural collectivization o Furthered Cold War with the U.S. o Comintern developed- International office of communism More mustaches... Vladimir Lenin Joseph Stalin "Have you signed up as a volunteer?" -Red Army" Chinese Revolution Problems After the Fall of the Qing • • • • • • • • Power struggle between warlords, students, politicians, and secret societies Japanese intruders Communist movements Internal divisions and foreign influences Military commanders or warlords held the most power and that often led to domination in politics New ideologies developed Poor/Weak military = DEFENSELESS Western powers continuously intervened Chinese Revolution Causes • • • • • • • • Western Interference Unfair treatment of peasants Communism's spread Weak rulers and warlord domination Wish to unify China under a single government Wish for social reforms to solve poverty problems Japan's thirst for expansion and imperialistic conquering in China Chinese thinkers and younger generations wanted to modernize China (Women's rights, education, literacy, and Westernstyle culture) Consequences • • • • End of the final Chinese dynasty Internal fighting over power -Marxist and Communist Marxist Study Club developed Communist Party for China develops, which offers a solution to the void left from the Qing Guomindang forms as a Nationalist party Communist Alliance forms between the Soviet Union and China -Whampoa Military Academy is founded Events • Long March • May Fourth Movement: Attempt at making China a liberal democracy • • Chinese Revolution Key Players • • Yuan Shikai- A warlord in northern China after the fall of the Qing Dynasty o Hoped to seize the imperial throne o President of China after 1912 o Resigned due to the Japanese invasion of 1916 Sun Yat-Sen- Head of the Revolutionary Alliance organization that led 1911 revolt against the Qing Dynasty o Briefly elected president in 1911 before Yuan o Created the Guomindang in 1919: A Nationalist party in China Drew support from local warlords and Chinese criminals Initially forged an alliance with communists in 1924 until the civil war More Key Players... • Chinese Marxists o Li Dazhao-Chinese intellectual who gave attention to Marxist philosophy Headed a study circle at the University of Beijing Saw peasants as the leaders of revolutionary communism o Mao Zedong- Communist leader Advocated the rural reform and the role of peasants in the revolution Led Communist action against the Guomindang Long March of 1934- Communist escape from Hunan province during the civil war with the Guomindang ( Mao becomes the head of the Communist Party Seized control of all mainland China by 1949 Initiated the Great Leap Forward in 1958 Conclusion: Mustaches = Power Yuan Shikai Sun Yat-sen Li Dazhao Mao Zedong