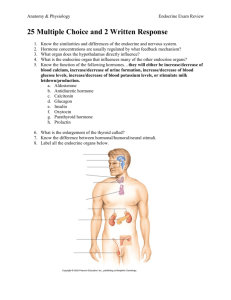
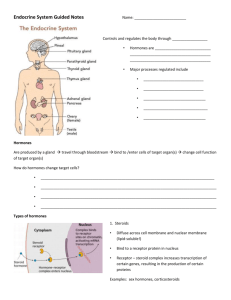
Communication in Living Things is normally not covered in the 10th
advertisement

Communication in Living Things is normally not covered in the 10th grade biology curriculum. Because of this, you should take the time to examine this topic. Chapter 45: Hormones and the Endocrine System is our 3rd step in understanding this idea. In this outline you will find the AP Bio curriculum that is addressed in chapter 45 and some questions that will guide you so that you can begin to understand this topic. Big Idea 3: Living systems, store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information essential to life processes o o Essential Knowledge 3.D.2 Cells communicate with each other through direct contact with other cells or from a distance via chemical signaling (11.1, 11.2, 45.1, 45.2) Signals released by one cell type can travel long distances to target cells of another cell type Endocrine signals are produced by endocrine cells that release signaling molecules into the blood stream that reach all body parts o Insulin o Human growth hormone o Thyroid hormones o testosterone o estrogen Essential Knowledge 3.D.4 Changes in signal transduction pathways can alter cellular responses Blocked or defective pathways = deleterious, preventative or prophylactic Diabetes Use the information from chapter 45 (page 974) to answer the following questions. 1. What is a hormone? 2. Why does a hormone elicit a response only with target cells? 3. The body has two long-distance regulating systems. Which involves chemical signals by hormones? 4. Several types of secreted signaling molecules are discussed in this chapter. Compare the action of each of the following and give an example. Signaling Molecule Hormones Action Example Local Regulators Neurotransmitters Pheromones 5. Recall that target cells have receptors for specific hormones. Where are the receptors for lipidsoluble hormones found? 6. Where are the receptors for the water-soluble proteins? Explain this difference for two types of hormones. 7. Carefully read the section of Cellular Response Pathways, and use that information to complete this table. Hormone type Method of Secretion Mode of Travel in Bloodstream Location of Receptors Examples Water –Soluble Lipid-Soluble 8. On the AP Biology exam, you will be expected to understand the process of positive feedback. How is oxytocin an example of a hormone that is under positive regulation (positive feedback system)? 9. Complete the following chart for this pair of antagonistic hormones. Hormone Insulin Secreted by Action Glucagon 10. On the AP Biology exam, you will be expected to explain a feedback loop. Use figure 45.13 (page 982) to examine the control of blood glucose by insulin and glucagon. This is a commonly used example and one you should know. 11. What occurs in diabetes mellitus? 12. Distinguish between type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes. 13. Which type of diabetes is correlated with obesity? 14. You will find it useful to be able to link hormones with the tissue that secretes them and know their functions. Pull together the information from this chapter to complete the following chart. Hormone Growth Hormone Secreted by Action and/or Effect of Hypo- or Hypersecretion Thyroxine Calcitonin Testosterone Estradiol 15. What two hormones are antagonistic controllers of blood calcium levels? 16. Why are gluccocorticoids effective in treating arthritis? What is the problem with their longterm use?