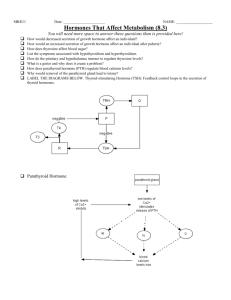
The second messenger
advertisement

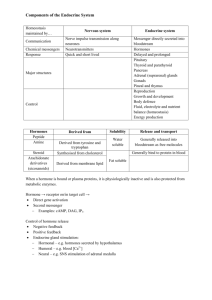
Biokimia Hormon Susila Sastri Hormon • Hormone : chemical entity that is secreted or produced by specific glands or cells and that acts as a chemical messenger or signal molecule • Hormones circulate as signaling substances in the blood at very low concentrations (10– 12 to between 10–7 mol L–1). The four primary areas of hormone action Growth & Development Reproduction Hormones Maintenance of internal environment Energy production, utilization & storage Cell Communication GAS MOLECULE Generalized Signal Transduction Pathway Simple Intracellular & Extracelluler Signaling Receptor Receptors: specific membrane proteins, which are able to recognize and bind to corresponding ligand molecules, become activated, and transduce signal to next signaling molecules: A. Membran B. Intra Sel Glycoprotein or Lipoprotein Properties of binding of Hormon and Receptor • highly specificity • highly affinity • saturation • reversible binding • special function model Control of receptor activity • Phosphorylation or dephosphorylation of R • Phospholipid of membrane • Enzyme catalyzed hydrolysis • G protein regulation Function of receptor (1) Recognize the special ligand (2) Binding to special ligand (3) Signal transduction biological effect Koolman, Color Atlas of Biochemistry, 2nd edition © 2005 Thieme Hypothalamus Releasing hormones Anterior pituitary Nervous Posterior pituitary Thyrotropin Somatotropin FSH Vasopressin Prolactin LH Oxytocin ACTH Adrenal Thyroid Cortex Pancreas Ovary T3 Testis Cortisol Insulin, Estradiol Testosterone aldosterone glucagon, somatostatin Muscles liver Tissues Liver, muscles Adrenal Medulla Epinephrine Reproductive Mammary organs glands Struktur Kimia Hormon 1. Derived from amino acids (Hydrophilic) Amino acid derivatives thyroxine Histamine, serotonin, melatonin, and the catecholamines, dopa, dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine are known as “biogenic amines.” Tripeptides TRH Small peptides VP (ADH), somatostatin Intermediate-size insulin, parathyroid hormone peptides Complex polypeptides gonadotropins, TSH and glycoproteins A. Signaling substances derived from amino acids B. Examples of peptide hormones and proteohormones 2. Derived from lipid precursors Cholesterol derivatives cortisol, testosterone, vitamin D , estradiol Fatty acid derivatives prostaglandins, leukotrienes Phospholipid derivative platelet-activating factor Lipophilic hormones Steroid hormones Calcitriol (vitamin D hormone) is also included in this group, although it has a modified steroid structure.The most important steroid hormone in invertebrates is ecdysone. 3. Derived from other chemicals (mediator) adenosine Purines nitric oxide Gases Pituitary hormones and the hypothalamic factors controlling their secretion Classification of hormones: mechanism of action. • Hormones that bind to intracellular receptors • Hormones that bind to cell surface receptors – The second messenger is cAMP – The second messenger is cGMP • The second messenger : calcium or phosphatidylinositols (or both) • The second messenger : a kinase or phosphatase cascade I. Hormones that bind to intracellular receptors • • • • • • • • Androgens Calcitriol (1,25[OH]2-D3) Estrogens Glucocorticoids Mineralocorticoids Progestins Retinoic acid Thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) II. Hormones that bind to cell surface receptors A. The second messenger is cAMP: B. The second messenger is cGMP: • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • α2-Adrenergic catecholamines β-Adrenergic catecholamines Adrenocorticotropic hormone Antidiuretic hormone Calcitonin Chorionic gonadotropin, human Corticotropin-releasing hormone Follicle-stimulating hormone Glucagon Lipotropin Luteinizing hormone Melanocyte-stimulating hormone Parathyroid hormone Somatostatin Thyroid-stimulating hormone Atrial natriuretic factor Nitric oxide II. Hormones that ….. C. The second messenger is calcium or phosphatidylinositols (or both): • • • • • • • • • • • Acetylcholine (muscarinic) α1-Adrenergic catecholamines Angiotensin II Antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) Cholecystokinin Gastrin Gonadotropin-releasing hormone Oxytocin Platelet-derived growth factor Substance P Thyrotropin-releasing hormone D. The second messenger is a kinase or phosphatase cascade: • • • • • • • • • • Chorionic somatomammotropin Epidermal growth factor Erythropoietin Fibroblast growth factor Growth hormone Insulin Insulin-like growth factors I and II Nerve growth factor Platelet-derived growth factor Prolactin