click - Uplift Education
advertisement

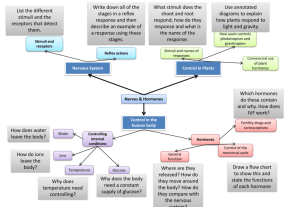
Endocrine System Guided Notes Name: _________________________ Controls and regulates the body through _________________ • Hormones are ___________________________ _______________________________________ _______________________________________ • Major processes regulated include • _____________________________ • _____________________________ • ______________________________ • _______________________________ • ______________________________ Hormones Are produced by a gland travel through bloodstream bind to /enter cells of target organ(s) change cell function of target organ(s) How do hormones change target cells? • ____________________________________________________________________________________ • _____________________________________________________________________________________ • _____________________________________________________________________________________ • _____________________________________________________________________________________ Types of hormones 1. Steroids • Diffuse across cell membrane and nuclear membrane (lipid-soluble!) • Bind to a receptor protein in nucleus • Receptor – steroid complex increases transcription of certain genes, resulting in the production of certain proteins Examples: sex hormones, corticosteroids 2. Amino-acid based (amines, peptides, and proteins) • Bind to a receptor protein on cell membrane • Receptor starts a series of events that produce a specific change in the function of the cell Examples: insulin, oxytocin, GH, melatonin, calcitonin, etc. Non-steroidal hormones always use second messenger molecules – molecules that are produced within the target cell as a result of the binding of the hormone with the receptor Quick Review 1. What are the two types of hormones, and what is the major difference between them? 2. Which type of hormone produces second messenger molecules? 3. Which of the following is NOT one of the major processes controlled by hormones? a. b. c. d. Body coordination Growth and development Electrolyte balance Cellular metabolism 4. Which of the following is NOT a typical effect of hormones on target cells? a. b. c. d. Mitosis is stimulated Enzymes are activated Proteins are synthesized Cellular mutations develop The control of hormone release Hormones regulate body functions by producing specific effects in target cells. Disorders can develop if too much or too little hormone is secreted. How does the body determine when/how much hormones to release? The release of nearly all hormones is controlled by ____________________________________________. Review: Compare and Contrast Negative and Positive Feedback Loops Example: Blood sugar regulation Example: Blood Calcium Regulation Stimulus of Hormone Release Even when glands are part of a negative feedback loop, there must be some stimulus that triggers the release of hormones. What was stimulus in the previous two examples? There are three basic types of stimuli that cause the release of hormones. 1. Humoral stimuli (non-hormone chemicals in the blood and body fluids) 2. 3. Often there is just one stimulus that a gland responds to. Occasionally there are multiple stimuli (ex: release of aldosterol by adrenal glands) Example of multiple stimuli: aldosterone release Diabetes mellitus Diabetes is a disorder characterized by abnormally ____________________________________________ Facts • • • • 347 people world-wide have diabetes. 7th leading cause of death in the US Leading cause of kidney failure, non-traumatic limb amputation, and adult-onset blindness in US Major contributor to heart attack and stroke Major Types of Diabetes Type I (juvenile-onset) • Occurs when the immune system attacks the insulin-producing cells of the pancreas, which means that _________________________________________________ can be produced • Genetic risk factors and environmental triggers • ~5% of cases Type II (adult-onset) • Too little insulin is produced and/or cells become _____________________________ • Obesity and inactivity are major risk factors, but genetics also play a role • ~90% of cases