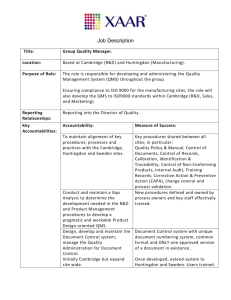
The Need for a Quality Management System
advertisement

Quality Management System “ NURSING EDUCATION ASSOCIATION CONFERENCE 2006 PORT ELIZABETH Vernon Pillay Nursing Education Manager Life College of Learning "Quality is never an accident; it is always the result of high intention, sincere effort, intelligent direction and skillful execution; it represents the wise choice of many alternatives." William A. Foster Workshop Introduction to Quality The Need for a Quality Management System Everybody Powered by Quality Designing a Quality Management System Provider Quality Commitment Power Teams & Processes Managing the Quality Management System Better our best Provider Quality Commitment Outcomes At the end of this section participants will be able to: Link the QMS to the vision and mission. Understand why quality is part of every provider’s “reason for existence”. Understand the Quality Principles and how these impact on each learner and facilitator Identify a suitable definition for Quality in the organization in which you work Definition of Quality Quality can be approached from 5 Philosophical points of view: The Transcendent approach The product –based approach The user opinion/ preference based approach The manufacturing- based approach The value-based approach Quality as seen by the Customer The word quality means different things to different customers Criteria to define quality include: Appearance Function Cost Customer Orientation Satisfying stated and implied needs meeting customer expectations: specific measurable parameters, or by expectations as perceived. It is crucial that the requirements for quality fully reflect the stated and implied needs of the customer Quality Management Is the result of the so-called “quality circles” of the 1980’s Isolating and analyzing the process/ part of the process Lesson learn’t QMS cannot be added into an Organization at the end of the process Entrenched in the value system A strategic choice made before implementation QMS IS THEREFORE All the coordinated activities of the overall management function of an organization that determine its quality policy, objectives, and responsibilities and its implementation by means of a quality management system QMS consists of 3 fundamental structures: POLICY MANAGEMENT “Doing the right things ” FUNDAMENTAL STRUCTURES OF QMS PERFORMANCE IMPROVEMENT “Doing things right the first time” PROCESS MANAGEMENT “Keeping things right” The typical vision statement: We know where we are going and why We have pride of ownership in our jobs We continuously improve everything we do We set the standards We provide excellent value Quality Principles Education Enlightening Excellence Energy Empowerment lifelong learning new information exceeding expectations a passion for life the power to act Exercise 1 Instructions In your groups, identify practical ways in which you can demonstrate the quality principles in the work you do. Principles will be assigned to your group. Write your suggestions on the flipchart paper provided. You will be required to give feedback to the larger group. The Need for a Quality Management System Outcomes At the end of this section participants will be able to: Understand the transformation of education and training as captured by the SAQA Act and the Skills Development Act Discuss different views of quality Discuss the factors that drive the need for quality management in education & training Explain the Quality Assurance cycle THE NQF & SAQA NQF – monitor qualifications and assure quality According to framework SAQA was formed To register SA Qualifications To Assure the quality of all SA Qualifications To put the following bodies in place: NSB’s & ETQA’s SGB QUALITY IN EDUCATION SAQA’s QUALITY CYCLE SAQA Registers Standards Qualifications Learning Outcomes Moderation Requirements STANDARD SETTING QUALITY ASSURANCE 12 NSB’s ETQA’s SGB’s Accredits ETQA’s Accredits Providers Accredits courses Registers PROVIDERS Assessors Skills Development Ensuring quality learning in the workplace Employees are skilled to perform their jobs competently Learning must contribute to the development of the worker Credits versus attendance courses SETAs quality assure training in the workplace Different Views of Quality Conforming to some external standard (centres of excellence) Peer validation (moderation by external agencies) Quality is also relative Notions of Quality ISO 9000 approach “Value for money” has a focus on performance indicators “Quest for zero defect” – against pre set standards Fitness for purpose – evaluation of an organization’s policies against national standards Transformative Quality in Education Enhancing the participant’s performance and development- to succeed Empowering the participant to influence their own transformation Quality Assurance Cycle Plan detailed action resources, timeframes & indicators for improvement Plan objectives and outputs Decide what quality means (agreed features, standards, improvement targets Develop coherent QA systems to monitor actual performance against standards New Cycle Old Cycle Review Strategic Plan Write self assessment reports, summarizing the analysis, evaluation and priorities for action Follow self assessment procedures Exercise 2 Instructions Take the Quality Cycle and in your groups answer the following question: What are the benefits of the quality cycle and how does it impact on education? Record your answers on the flipchart paper. You will be required to give feedback to the larger group. Designing a Quality Management System Outcomes At the end of this section participants will be able to: Apply the general process to develop a quality management system for the provision of education, training & development Quality Management Principles Customer Focus Leadership Involvement of people Process approach System approach to management Continuous Improvement Factual approach to decision making Mutually beneficial supplier relationships A Successful, Cost effective QMS is one in which Quality policies and objectives are well defined Everyone is motivated to achieve quality Responsibilities are clearly delegated in the organization for activities influencing quality Communication is good Instructions are simple, clear and available Meaningful records are kept Training is available at all levels The system is regularly monitored Process to Establish a QMS Define the scope of QMS Define Quality Policy and Objectives Identify key processes and Organizational structure Plan to establish a QMS Define Key Processes Design Quality Manual Training on QMS Model of Process-based QMS Continuous improvement of the QMS Management Responsibility Interested Parties Resource Management Measurement, analysis and improvement Input Requirements Product realization Interested Parties Output Satisfaction Product Total Quality Management Teams Culture Communication Process Tools System Commitment Exercise 3 Instructions In your groups, draw an educational process you are familiar with, in the form of a flowchart. Draw your flowchart on the flipchart paper provided. You will be required to give feedback to the larger group. Managing the Quality Management System Outcomes At the end of this section participants will be able to: Monitor a quality assurance system Evaluate a quality assurance system Report and make recommendations QMS Reviews – Quality Audit System audits Process audits Product/service audits Internal audits External audits Audits have to be planned and performed as part of the quality management activities Exercise 4 Instructions In your groups, discuss one quality audit initiative, you would use to enhance quality in your institution. Write it up on the flipchart paper provided. You will be required to give feedback to the larger group Summary Quality is relative Vision & Mission statements are about quality Monitor and review quality Legislation supports quality Policies, Processes & procedures are essential Everybody is responsible for quality Understand the Principles of Quality Continuous Quality Improvements “Quality, quality, quality: never waver from it, even when you don't see how you can afford to keep it up. When you compromise, you become a commodity and then you die.” Gary Hirshberg (founder of Stonyfield Farm Yogurt) THANK YOU