Introduction to acids and bases
advertisement
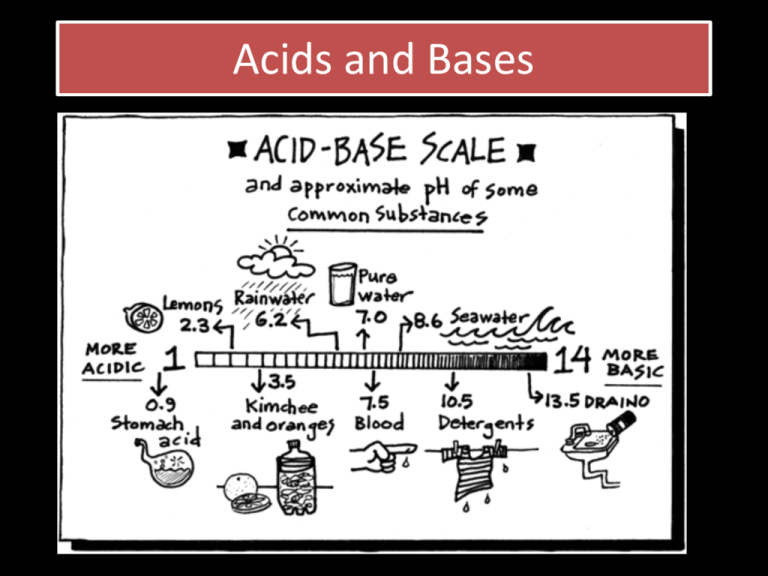
Acids and Bases • You should already know quite a lot about acids and bases: • Acids are corrosive chemicals with a characteristic sour taste. • They form solutions with a pH < 7 • More about pH later! • All acids react in similar ways: • Write balanced equations for the following: a) Iron with dilute sulfuric acid b) Lead carbonate with nitric acid c) Zinc oxide with hydrochloric acid d) Calcium hydroxide with nitric acid e) Sodium hydrogen carbonate with sulfuric acid f) Potassium hydroxide with hydrochloric acid (write an ionic equation!) a) Fe(s) + H2SO4(aq) FeSO4(aq) + H2(g) b) PbCO3(s) + 2HNO3(aq) Pb(NO3)2(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) c) ZnO(s) + 2HCl(aq) ZnCl2(aq) + H2O(l) d) Ca(OH)2 + 2HNO3(aq) Ca(NO3)2(aq) + 2H2O(l) e) 2NaHCO3(s) + H2SO4(aq) Na2SO4(aq) + 2CO2(g) +2H2O(l) f) OH-(aq) + H+(aq) H2O(l) • When equal volumes of 2 mol dm-3 sulfuric acid and 2 mol dm-3 aqueous sodium hydroxide are mixed, how can you tell they react? a) A gas is evolved b) The mixture becomes warm c) The solution changes colour d) A solid precipitate is formed • When equal volumes of 2 mol dm-3 sulfuric acid and 2 mol dm-3 aqueous sodium hydroxide are mixed, how can you tell they react? a) A gas is evolved b) The mixture becomes warm c) The solution changes colour d) A solid precipitate is formed All neutralisation reactions are exothermic! Definitions of acids and bases • • • • • • • • • • What’s the formula of sulfuric acid H2SO4 Hydrochloric acid? HCl Nitric acid? HNO3 Ethanoic acid? CH3COOH Carbonic acid? H2CO3 • What do they all have in common? • The most basic definition of an acid is the Arrhenius definition. • An acid is a substance that splits up in water to give a hydrogen ion and an anion • E.g. • HCl(aq) H+(aq) + Cl-(aq) • The (aq) bit is important • Acids do not show acidic properties in many nonaqueous solvents. • We can emphasise the importance of water: • HCl(aq) + H2O(l) H3O+(aq) + Cl-(aq) • H3O+ is known as a hydronium ion (or sometimes a hydroxonium ion). • We don’t usually bother showing this! • Because of the importance of the hydrogen ion in acidic reactions, we often omit the spectator ions • (the ions which don’t change during a reaction) • You did lots of examples of this at IGCSE • E.g. • Mg + 2HCl MgCl2 + H2 • Write it as ions: • Mg + 2H+ + 2Cl- Mg2+ +2Cl- + H2 • Remove any ions which are the same on both sides: • Mg + 2H+ + 2Cl- Mg2+ +2Cl- + H2 • Remove any ions which are the same on both sides: • Mg + 2H+ + 2Cl- Mg2+ +2Cl- + H2 • Leaving the ionic equation: • Mg + 2H+ Mg2+ + H2 How do we define a base? • A base is a substance which reacts with an acid to form water. • i.e. undergoes neutralisation!!! • What’s the difference between an alkali and a base? • An alkali is soluble in water. • This fits in much better with the Arrhenius definition for an acid . . . • An alkali is a substance which gives OH-(aq) ions in water. • E.g. • NaOH(aq) Na+(aq) + OH-(aq) A puzzle: • Name a common alkali gas • Ammonia (there is only one) • How does ammonia give hydroxide ions in water? • NH3(aq) + H2O(l) NH4+(aq) + OH-(aq) • Carbonates and hydrogen carbonates act in a similar way. Bronsted – Lowry Acids • This is just a different way of defining an acid. • An acid is a substance that acts as a proton donor. • • • • Why “proton” ? A hydrogen atom has 1 proton and 1 electron To make a H+ ion we take away the electron So a H+ ion is JUST a single proton • A base is a proton acceptor • [ there is a slight technical difference between the B-L definition and Arrhenius’ definition. In the B-L definition we don’t need to have H+(aq) present at any time – so we can talk about acids and bases without needing an aqueous solvent] • If an acid can donate one proton it is monoprotic • If it can donate 2 protons it is diprotic • 3 is triprotic • Many is polyprotic • A few species can either donate a proton or accept a proton. • These are known as amphiprotic • E.g. • H2SO4 HSO4- SO42- • E.g. • H2SO4 HSO4- SO42- Accept a proton • E.g. • H2SO4 HSO4- SO42- • Donate a proton







