Basic Computer Concepts - Woodland Hills School District
advertisement

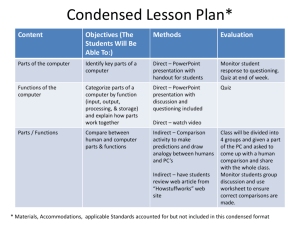
Basic Computer Concepts Mrs. Sheila M. Thompson Woodland Hills High School http://videos.howstuffworks.com/podtech-networks/2485-mythbustersguys-talk-computer-history-video.htm 1 What Is a Computer? An electronic device that can perform tasks and calculations based on the instruction it has been given. • • • • • Microprocessor Internal Memory Auxiliary Storage Input Units Output Units How Computer Works • Accept inputs from a person or another outside source • Interpret and process the input data • Display the results or perform an action based on the input data or command Types of Software • System software – which controls the way the computer parts work together. • Application software – tells the computer how to perform a specific task. Any Computer System Memory Central processing unit (CPU) Input Output Auxiliary Storage Disk Disk Types of Computers • Personal Computer (PC) • most common used in homes, offices and schools • Small, relatively inexpensive, individual user. Types of Computers • Minicomputers - Server • Smaller than a mainframe and larger than a microcomputer. • Medium-sized companies – accounting, advertising, and manufacturing firms Types of Computers • Supercomputer • Largest, fastest; 50–1,500 times faster than PCs • Cost prohibitive – used by largest firms, government agencies and universities. http://videos.howstuffworks.com/medialink/2253-a-decade-of-supercomputing-video.htm Types of Computers • Mainframe computers • Larger, more powerful than microcomputers • Large capacity to store & manipulate data • 10 – 40 times faster, but $100,000-$2,000,000 Internal Memory (RAM) • Temporary (erased when power turned off) • Measured in bytes • 1 Byte = 1 character (8 bits) • 1 Kilobyte = 210 (~1,000 bytes) • 1 Megabyte = 220 (~1,000,000 bytes) • 1 Gigabyte = 230 (~1,000,000,000 bytes) • Need 128Mb of RAM • Keep multiple programs & data files in memory • Graphic-intensive programs demand a lot of memory Read-only Memory (ROM) • Computer memory on which data has been recorded on a ROM chip • Can be read, but cannot be deleted • Preserves its contents even when the computer is shut down • Stores critical programs – needed for system start-up The System Unit Box-like case that contains computer’s electronic components v Sometimes called the chassis v The System What are common components inside the system unit? • Processor • Memory • Expansion Card • • • • Sound Card Modem Video Card Network interface Card Back of the Computer • Cooling Fan • Power Supply • Keyboard Connector • Mouse Connector • Parallel Printer Port • Video Connector Inside the Computer • • • • • • • • CD-ROM CPU Expansion slots Floppy drive Hard disk Memory chip Motherboard Power supply http://computer.howstuffworks.com/pc.htm Central Processing Unit (CPU) Interprets and carries out basic instructions that operate a computer Also called the processor Motherboard Main circuit board in system unit a contains chips, integrated circuits, and transistors also called system board Microprocessor • Brain of the computer • Current chips for PC • Intel (Celeron, Pentium III, and soon-to-be announced Pentium IV) • AMD (K-6 and Athlon) • Which do I buy? • Pentium or Athlon for graphic-intensive programs • K-6 or Celeron for business and Internet browsing http://videos.howstuffworks.com/podtech-networks/2480-how-the-newestmicroprocessors-work-video.htm Hard Disks hard disk installed in system unit • High Capacity Storage • Consist of several inflexible, circular platters that store items electronically • Components enclosed in airtight, sealed case for protection Input Devices • Feed data into computer • Keyboard - most commonly used input device. • Mouse, pointing stick, trackball, light pen, puck and touch pad • Opitical Character Recognition – OCR – scans printed pages and translates characters and images into a file that can be edited using word processing. • Scanner – a device that can read text or illustrations and transmit into digital format Input Devices • Digital Camera – captures images in memory storage without using film. • Microphone – accepts voice input to enter data or execute commands. Output Devices • Printers – devices that print text or graphic onto paper. • Impact printer – uses a device that strikes a ribbon • Non-impact printers – use laser and ink-jet technology. • Speakers are input and out put devices Monitor Size and Resolution • Monitors come in different sizes: 17,” 19,” and 21” • Resolution is expressed in pixels (such as 800 x 600 or 1024 x 768) • The higher the resolution, the more you can see. Larger monitors let you run at higher resolutions: e.g., 19” to run 1024 x 768 comfortably • A graphics card (video display adapter) speeds processing Storage Devices • Hard Drive – an internal storage device, also known as a fixed disk. • Flash drives – durable, rewritable hard drives, can easily fit in a pocket or on a chain. • Jump drives • Thumb drives • Digital Audio Tape – standard magnetic tape that resembles a basic audio cassette. Auxiliary Storage (Permanent) • High Capacity Removable Storage • Zip disks (100 or 250Mb) • Jazz Disks (1 or 2Gb) • Hard (Fixed) Disk • Most common are 10 –30Gb Auxiliary Storage (Continued) • CD-ROM 650Mb • Recordable devices also available • DVD drives 4.7Gb-17Gb • ROM and RAM • Higher capacity than CD • Tape Units • Used for large, unattended back-ups What is a CD-ROM? • Compact disc that uses same laser technology as audio CDs for recording music • Cannot erase or modify contents • Typical CD-ROM holds about 650 MB v Commonly used to distribute software and games CD-R and CD-RW What is a CD-RW (compact discrewritable)? v v Erasable disc you can write on multiple times Must have a CD-RW disc, CD-RW software, and CD-RW drive Purchasing Decisions • Local store versus mail order • Magazines • Internet • Use credit card to double warranty • 30-day price guarantee • Don’t forget the software • Windows XP, Windows Vista • Microsoft Office (check the version) http://videos.howstuffworks.com/howstuffworks/44-how-to-buy-a-laptopvideo.htm The PC Today • Main Components • 1Gb microprocessor • 1028 Mb RAM • 250 Gb hard drive • 1 floppy drive • Zip drive • DVD-ROM drive • 21” monitor • 64Mb graphics card • Other Components • Cable modem • CD-RW drive • Camera • Microphone • TV adapter • Sound card/speakers http://videos.howstuffworks.com/harvard-extension-schools-computer-science-e-1understand/1291-plugging-everything-in-video.htm Software • System Software • Microsoft Windows - Operating System • Home – Windows 98, Windows Me, windows XP Media Center, Windows XP Professional • Business – Windows NT, Windows 2000 • Antivirus and file compression is not built into Windows • Application Software • Microsoft Office • Word, Excel, Access, PowerPoint, Publisher, and Photodraw • Different editions contain different applications Purchasing on the Web • • • • • www.dell.com www.gateway.com www.ibm.com www.pcwarehouse.com www.microwarehouse.com Essential Computing Concepts: Getting 32