File
advertisement

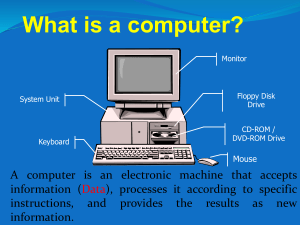
Condensed Lesson Plan* Content Objectives (The Students Will Be Able To:) Methods Evaluation Parts of the computer Identify key parts of a computer Direct – PowerPoint presentation with handout for students Monitor student response to questioning. Quiz at end of week. Functions of the computer Categorize parts of a computer by function (input, output, processing, & storage) and explain how parts work together Direct – PowerPoint presentation with discussion and questioning included Quiz Compare between human and computer parts & functions Indirect – Comparison activity to make predictions and draw analogy between humans and PC’s Parts / Functions Direct – watch video Indirect – have students review web article from “Howstuffworks” web site Class will be divided into 4 groups and given a part of the PC and asked to come up with a human comparison and share with the whole class. Monitor students group discussion and use worksheet to ensure correct comparisons are made. * Materials, Accommodations, applicable Standards accounted for but not included in this condensed format Four Functions of a Computer • • • • Input Process Storage Output In 4 assigned groups spend five minutes discussing what you think human function relates to your assigned function and computer examples Motherboard Contains: • CPU • Ports • Memory chips that control functions like video & networking •Connects to main power source Input • Gets information into the computer and translates to digital form. Comes from devices such as: – – – – – – Keyboard (Qwerty style from typewriters) Mouse Scanner Microphone Camera Graphic tablet • Texts, graphics, sounds, video, music, are all transformed into binary code. Letters, words, numbers, and even colors all use the universal ASCII language • ASCII – zeros and ones stand for electrical pulses (1 = +, 0 = neutral – Each zero or one is a bit and 8 bits = a byte – A byte is a single letter, number, symbol, or sound Human comparison – Ears, Eyes, Nose, Mouth Input Devices Process • CPU is main processing unit of a computer • It coordinates all of the actions of the machine by following instructions such as: – Perform calculations – Interact with other components to operate the computer • The microprocessor is the primary work area where information gets processed • Software (i.e. games or programs on the computer) are the sets of instructions that you give to the processor • Microprocessor primary steps are: – Fetch – Decode – Execute Human Comparison – Certain Sections of the Brain or Digestive System Storage • Computers have two types of storage – Temporary • RAM or Random Access Memory stores information as you use it • Constantly gets erased and rewritten as you open & close files – Long-term • • • • Hard Drives CD-ROMs Floppy disks Flash Drives – The capacity of these types of memory vary – but the more you have, generally the better Human Comparison – Brain (Different parts – long-term and short –term memory) Process and Storage All of these can store the same amount of information Output • Display the information the computer has been processing or retrieve the information or result of the instructions given earlier – Monitor – Printer – Speakers Human Comparison – Written work, speech, song, poem, painting, sculpture, repaired car Output Devices Parts of the Computer • Go to http://computer.howstuffworks.com/pc.htm Read the article from numbers 1 – 5 http://videos.howstuffworks.com/howstuffwork s/23-computer-tour-video.htm Reference: Intel.com Matching Worksheet on Quiz