Meningitis fact sheet
advertisement

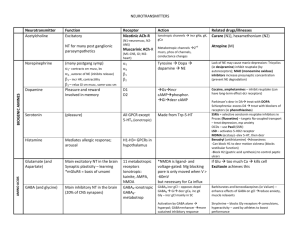
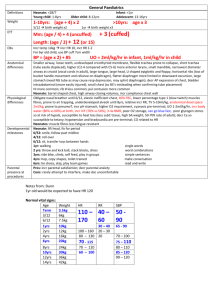
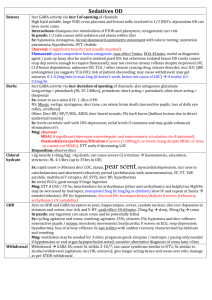
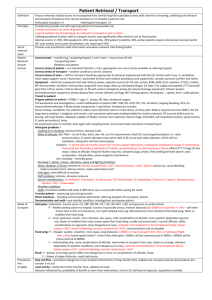
Meningitis Epidemiology Patho-genesis 20-100/100,000 neonates; 5/100,000 1/12 – 4yrs; 90% occur <5yrs; 90% mortality untreated (10% treated if meningococcus or Hib; 30% treated if pneumococcus); 30% survivors have long term sequelae In paeds: 4.5% mortality; 10-20% intellectual / auditory complications; asymptomatic N meningitidis nasal carriage in 10%; meningococcal sepsis bimodal (0-4yrs, 15-25yrs); <3/12 + febrile = 1% incidence Encephalitis: mortality HSV 60% without trt, 30% with trt Usually haematogenous spread, sometimes direct; damage from inflamm response Strep pneumoniae (60%): G+ive diplococci; more indolent course; FND prominent; 50% also have pneumonia; 25% resistant to penicillin, 9% resistant to cefotaxime; if resistance, use vanc + rifampicin N meningitidis (16%): G-ive aerobic diplococci; use benpen 45mg/kg Q4h IV for 3-5/7, or cefotaxime/ceftriaxone if allergy; 13 serogroups; C>B in Aussie (usually other way round in developed countries); reservoir in NP; aerosol transmission; sudden onset headache, fever, true rigors, neck stiffness, N+V, photophobia, altered LOC, AP, limb pain, arthritis, rash (in 40%, may take 6-12hrs to develop; haemorrhagic, petechial, purpuric; may blanch initially); may be fatal in 12hrs (mortality 1-5% - up to 40% if invasive meningococcal disease); assoc with Waterhouse Friedrichsen syndrome (acute adrenal haemorrhage) Grp B strep (14%), E coli: if <3/12; Grp B strep use benpen 60mg/kg Q4h IV for 14-21/7 Hib (7%): if non-vaccinated; use cefotaxime / ceftriaxone Listeria (2%): if neonate and immunocomp; use benpen or ampicillin Staph: if CNS shunt, open wound, neurosurg Viral: mumps, coxsackie, enterovirus, herpes, EBV, echovirus, HIV, CMV Other bacterial: M TB, mycoplasma, borrelia, treponema pallidum, brucella Fungi and parasites: cryptococcus neoformans (use amphotericin + flucytosine), toxoplasma gondii, cysticercosis Drugs: NSAIDS, bactrim Other: sarcoid, SLE, Wegener’s Assessment Investigation Encephalitis: HSV (temporal + frontal psych, memory, aphasia), HZV, EBV, CMV, enterovirus, adenovirus, rabies, vector-borne; post-viral (eg. Influenza, measles, rubella, varicella, HIV); bacterial (rickettsia, leptospirosis, amoebic) Brain abscess: haematogenous (30%; multiple, polymicrobial, often anaerobes/strep), local (30%; eg ear bacteroides temporal or cerebellar; eg. Sinus and dental anaerobes, strep frontal), unknown (20%), neurosurg (10%; staph and G-ive rods); trt with cefotaxime and metronidazole Hx: 25% bacterial present within 24hrs, viral present day 1-7 (5% within 24hrs); classic Sx absent in infants and elderly; fever in 80% bacterial (3040% viral); seizures in 30-40% children, 20-30% adults; confusion in 85% bacterial (25-50% viral); photophobia in 80% bacterial (60-70% viral); headache + fever + neck stiffness present in 50% (2 present in nearly 100%) OE: isolated CN lesion in 10-20%; look for shock; Kernig’s (passive knee extension in supine patient causes neck pain and hamstring resistance); Brudsinski’s (passive neck flexion or single hip flexion causes involuntary flexion of both hips) In children: 15% of neonates have physical findings (lethargy, seizures, poor feeding, fever, hypothermia, paradoxical crying, hypotonicity, bulging fontanelle late); meningisim not present until 18/12; focal signs in 15% all cases, 30% pneumococcal; seizures in 30% (with worse than expected mental status after); 15-20% decr LOC (more in pneumococcus); subdural effusion / empyema (30% in Hib, 20% in strep); may deteriorate after Abx (bacteriolysis inflamm); beware partially treated meningitis (more frequent V, longer duration of Sx); suspect encephalitis if seizures / altered LOC / behaviour Encephalitis: usually no motor/sensory Sx; psych, cognitive, seizure, mvmt disorder, LOC, confusion Bloods: FBC, coag, blood cultures, U+E, BSL; Ag testing if blood/urine not helpful; ?procalcitonin CT head: if papilloedema, altered LOC, FND, seizure, immunocomp, Ca, concern Re: SOL, history of CNS disease, seizure in week prior, >60yrs; CT may be normal despite incr ICP in 45%; CT features of incr ICP = changes ventricle size, decr basilar cistern size, narrowed sulci, transfalcine herniation, change in rate of grey/white matter CT head encephalitis: diffuse hypoattenuation in temporal lobe, sparing of lentiform nucleus; mass effect in 80%; maybe vesicular haemorrhage EEG in encephalitis: slowing of background rhythm or epileptiform; abnormal in 80% HSV CXR LP: do cell count, diff, glu, protein, Gram stain, culture, Ag (high sens and spec, esp Hib and neisseria), PCR; India ink if indicated (cryptococcal); use non-styleted needle in small infants Technique: SC ends at L1-2 (96%), T12 (2%), L3 (2%); lower in children; go L3-4; use USS if can’t feel IV spaces; avoid alcohol based skin preps; 2225G adult (12cm), 22-25G child (6cm), 2cm neonate; 20-30deg cephalad; replace stylet before removing; no evidence for immobilisation after; normal OP = 7-18cm in adults, up to 20cm in 8-18yrs, 1-10cm in young child (incr p in meningitis, Ca, abscess, ICH, benign intracranial HTN; decr in CSF leak, dehydration, hyperventilation) Cell counts: mycoplasma, listeria, spirochetes, syphilis, leptospira, borrelia have less marked CSF changes; partially trted picture seen if close to SA space (eg. Asbcess); LP within normal limits on cells in 2-3%; WCC >100 in 99% bacterial meningitis, >1000 in 90%; lymph >50% in 10% bacterial; nearly 100% mononuclear in viral (may be more polymorphs in 1st 48hrs); turbid if >400 RBC, >200 WBC; lymphocytes may predominate in listeria and neonates Protein incr 0.01g per 1000 RBC (also incr by alcoholism, abscess, Ca, haem, trauma, DM, epilepsy, disc herniation, MS, polio, incr Ur); Glu decr in mumps and sometimes in HZV/HSV; Ag tests: latex agglutination (rapid, high sens, 50-90% sens for neisseria, 50-100% for pneumococcus, 80% for Hib, 90% for cryptococcus, Grp B strep) PCR (for HSV, >95% sens, 100% spec; for TB, 80% sens, >95% spec) Xanthochromia: cause by blood >4hrs, extreme incr protein, incr carotin, severe jaundice Traumatic tap: in 15%; RBC usually >400-1000; clearing SE: uncal/tentorial herniation (can occur up to 1hr post), post-LP headache (2-15%; 70% with 16-19G, 20-40% with 20-22G, 5-10% with 24-27G; keep bevel parallel to fibres to decr incidence by 50%; incr risk if young, thin, slim female; onset 24-48hr post-procedure, duration 4-8/7, worse on standing, suboccipital; best rest, fluid, analgesia, caffeine, blood patch), epidural haematoma (lac of ant/lat epidural venous plexus), epidermoid cyst, infection, paraparesis, nerve root inj CI: local sepsis, anticoag, bleeding diathesis, plt <50, incr ICP, SOL Opening p N neonate N child 5 1-10 WCC <30 N adult 7-18 Bacterial >30 <4 <2 0 0 >80% PMN (neut) <5 0 0 Up to 10,000 <5 <4 <20 Protein <0.8 <0.4 Glu Glu % serum RBC >2.5 50% <2 >2.5 2.5-3.5 >40% 60-80% <2 Gram Stain Culture Viral <30 Encephalitis Slightly high TB Fungal 30 Ca 20 <500 Up to 500 Up to 500 Up to 500 Up to 10,000 Up to 5000 Up to 1000 <5-10 %PMN MMN (lymph) Prtl trted <100 (10%) >1-2 <2.2 0.18-0.45 0 <50% >10-100 <100 N / Up 0.4 - 2 N / Low + in 20-50% + in 30-70% - ive - ive <50% >50% >50% High early >100 >100 >100 Normal/high <40% Normal/high If traumatic, subtract 1 WBC per 1000 RBC + in 60-80% + <100 <50% High late 0.4 - 2 N >2 Low late <30% - ive + late >2 <2.2 >2 <2.2 <40% <40% . -ive –ive -ive -ive Bacterial Ag + in 80% + in 70% - ive - ive –ive -ive A+B C: if shocked give IVF; SIADH in 30% children so use 50% maintenance after resus Supportive: seizure control, analgesia, fever control, BSL Steroids: IV dex 10mg (0.2mg/kg) Q6h for 4/7 if >1/12; give at least 15-30mins before Abx; give within 30mins; decr host response to Mng bacteria; decr deafness; in children halves incidence of audio / neuro sequelae (but >70% had Hib infections); in adults decr risk of adverse outcome and mortality; benefit best in pneumococcal (adult) and Hib (children) Antibiotics: give within 30mins (give before LP if there will be >20min delay to LP); once sens available, see above <3/12: amoxicillin 50mg/kg QID (TDS if <1/52) + cefotaxime 50mg/kg QID (BD if <1/52) (give 100mg/kg loading dose if >1/12) + vancomycin 15mg/kg QID (if suspect pneumococcus, G+ive diplococci seen, Ag +ive) >3/12: cefotaxime 100mg/kg loading dose 50mg/kg QID (max 2g) or ceftriaxone IM 100mg/kg loading dose 80-100mg/kg OD (max 4g) (if no IV access) + amoxicillin 50mg/kg QID IV (max 2g) (if suspect Listeria) + vancomycin 12.5mg/kg QID IV (max 500mg) (if suspect pneumococcus, G+ive diplococci seen, Ag +ive) In adults: MCQ says ceftriaxone 2g + benpen 1.8g Contact prophylaxis: meningococcus / Hib – give rifampicin 10mg/kg BD x4 (CI’ed in pregnancy and liver disease; ceftriaxone IM or Complications ciprofloxacin PO if CI’ed); contact = family and household contacts, those exposed to oral secretions, sexual partners Encephalitis: aciclovir 10mg/kg TDS IV for HSV; ganciclovir for CMV Seizures (30%), SIADH (30%), cerebral herniation, infarction, oedema, venous/sinus thrombosis, hydrocephalus, shock (10%), DIC, empyema (30% Hib, 20% pneumococcal) Notes from: Dunn, Cameron (adult and child), TinTin, Starship Guidelines . .