Cell Cycle - WordPress.com
advertisement

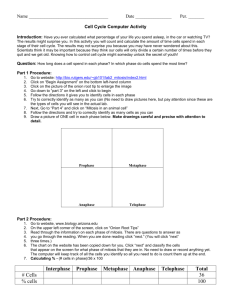
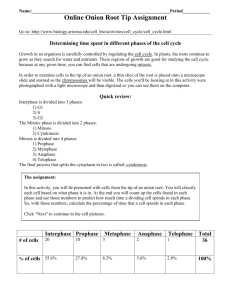
Cell Cycle Stages and division of cell http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/00 72495855/student_view0/chapter2/animat ion__how_the_cell_cycle_works.html 1. Which of the following represents the correct order of the phases of the cell cycle? A)G1 -> G2 -> S -> M Quiz B)G1 -> G2 -> M -> S C)G1 -> S -> G2 -> M D)G1 -> S -> M -> G2 E)G1 -> M -> G2 -> S 2. The division of the cytoplasm is called A)synapsis.B)mitosis.C)meiosis.D)cytokinesis.E)cytogenetics. 3. Which of the following represents the correct order of the phases of mitosis? A)prophase -> anaphase -> metaphase -> telophase B)prophase -> metaphase -> anaphase -> telophase C)prophase -> metaphase -> telophase -> anaphase D)metaphase -> prophase -> telophase -> anaphase E)metaphase -> prophase -> anaphase -> telophase 4. DNA replication occurs in mitosis.A)TrueB)False 5. Mitosis and cytoplasmic division result in the formation of two genetically identical Answers 1. C 2. D 3. B 4. B 5. A The cell cycle is an ordered set of events, culminating in cell growth and division into two daughter cells. Non-dividing cells not considered to be in the cell cycle. Sequence of cell cycle is G1-S-G2-M. T he G1 stage stands for "GAP 1". The S stage stands for "Synthesis". This is the stage when DNA replication occurs. The G2 stage stands for "GAP 2". The M stage stands for "mitosis", and is when nuclear (chromosomes separate) and cytoplasmic (cytokinesis) division occur. Mitosis is further divided into 4 phases. Regulation of Cell Cycle How cell division (and thus tissue growth) is controlled is very complex. The following terms are some of the features that are important in regulation, and places where errors can lead to cancer. Cancer is a disease where regulation of the cell cycle goes awry and normal cell growth and behavior is lost. Cdk (cyclin dependent kinase, adds phosphate to a protein), along with cyclins, are major control switches for the cell cycle, causing the cell to move from G1 to S or G2 to M. MPF (Maturation Promoting Factor) includes the CdK and cyclins that triggers progression through the cell cycle. p53 is a protein that functions to block the cell cycle if the DNA is damaged. If the damage is severe this protein can cause apoptosis (cell death). p53 levels are increased in damaged cells. This allows time to repair DNA by blocking the cell cycle. A p53 mutation is the most frequent mutation leading to cancer. An extreme case of this is Li Fraumeni syndrome, where a genetic a defect in p53 leads to a high frequency of cancer in affected individuals. p27 is a protein that binds to cyclin and cdk blocking entry into S phase. Recent research (Nature Medicine 3, 152 (1997)) suggests that breast cancer prognosis is determined by p27 levels. Reduced levels of p27 predict a poor outcome for breast cancer patients. In mammalian cells, different Cyclin-CDK (Cyclin-Dependent Kinases) complexes are involved in regulating different cell cycle transitions: Cyclin-D -CDK4/6 for G1 progression, Cyclin-E -CDK2 for the G1-S transition, Cyclin-A -CDK2 for Sphase progression, and Cyclin-A/B-CDC2 for entry into M-phase.