Motor Proteins and Movement (PowerPoint) Mountain West 2013
advertisement

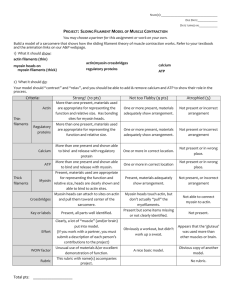
Move Me Mountain West Summer Institute 2013 David Aguilar, University of California San Diego Lisa Gallegos, Otero Junior College Richard Gomer, Texas A&M University Warren McClure, Otero Junior College Kathryn Ryan, Texas A&M University • Unit Goal – Understand how motor proteins interact with cytoskeleton components to direct movement. • Context – General Biology or Human Anatomy & Physiology – Freshman/Sophomore – Tidbit will be in the middle of a 1-2 week unit. Tidbit may be followed by discussion of neutrophil movement and/or cytokinesis. Next class will cover other molecular motors. • Prior Knowledge – Three main types of cytoskeletal proteins – ATP as an energy source – Components and arrangement of sarcomeres in skeletal muscle – Introduction to the Sliding Filament Theory • Tidbit Goal Know how ATP binding and hydrolysis regulate the interaction of actin and myosin • Teachable tidbit intended learning outcomes – Describe the molecular structure and functional features of a myosin molecule. – Dramatize the interaction of myosin and actin during the ATP cycle. – Discuss how the physical features of myosin allow it to function as a motor protein. – Recall ATP hydrolysis causes the high energy configuration of the myosin head. – Explain how actin and myosin interact to contract a muscle. – Predict what happens if there is no ATP. What is Rigor Mortis? Interactive Physiology Muscle Contraction • http://www.interactivephysiology.com/ip10/ muscular/slidflmt/topic28.html Sequential Events of Contraction – Cross Bridge Cycle Myosin head (high-energy configuration) 3 Actin Filament ADP and Pi (inorganic phosphate) released Myosin Filament 2 4 Myosin head (low-energy configuration) 1 Adapted from ©Pearson 2013 Elaine N. Marieb et al Human Anatomy and Physiolgy 9th Ed. Sequential Events of Contraction – Cross Bridge Cycle Myosin head (high-energy configuration) 3 Myosin head attaches to the actin myofilament Actin filament Myosin filament 2 4 Cocking of the myosin head occurs Power stroke—the myosin head pivots and bends as it pulls on the actin filament Myosin head (low-energy configuration) 1 The myosin head detaches the cross bridge is lost Figure 9.11 Clicker Question : Myosin head (high-energy configuration) 3 Myosin head attaches to the actin myofilament Actin filament Myosin filament 2 4 Cocking of the myosin head occurs Where would you predict ATP is interacting with myosin in this cycle? A. Position 1 B. Position 2 C. Position 3 D. Position 4 E. Multiple locations. Power stroke—the myosin head pivots and bends as it pulls on the actin filament Myosin head (low-energy configuration) 1 The myosin head detaches the cross bridge is lost Figure 9.11 Sequential Events of Contraction – Cross Bridge Cycle Myosin head (high-energy configuration) 3 Myosin cross bridge attaches to the actin myofilament Actin filament ADP and Pi (inorganic phosphate) released Myosin filament 2 As ATP is split into ADP and Pi, cocking of the myosin head occurs 4 Power stroke—the myosin head pivots and bends as it pulls on the actin filament, sliding it toward the M line Myosin head (low-energy configuration) 1 As new ATP attaches to the myosin head, the cross bridge detaches Figure 9.11 Clicker Question In rigor mortis, predict the stage where this cycle would stop? B C A D Defend your answer to your neighbor. B C A D Clicker Question In rigor mortis, predict the stage where this cycle would stop? B C A D Summative Questions – What is the consequence of taking cyanide which disrupts cell respiration? Explain in terms of molecular motors. – Sketch or arrange the interaction of myosin and actin during the ATP cycle. Alignment – Group 6 – Move Me Learning Objective Assessment Active learning Low Order/ High Order Know how ATP binding and hydrolysis regulate the interaction of actin and myosin Formative: Strip sequence Summative: Exam Question - Predict would happen in the absence of ATP and justify your answer Strip sequence and placement of ATP and ADP Formative Part 1 Recall – Low Dramatization of the actin myosin movement Part 2 Predict – High Summative Predict – High Know the physical movement of the myosin and how it functions as a motor. Formative: Dramatization of the actin myosin movement Summative: Exam question - Predict properties of various myosin dysfunction s ie. Mutated ATP binding site Diversity All students participate in the activity. There is a diversity of learning styles: visual, auditory, and kinesthetic.