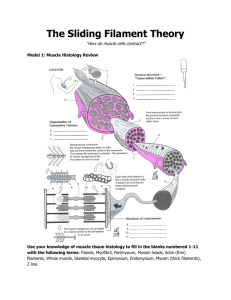
The Muscular System: Sliding Filament Theory 1. a. The thick
advertisement

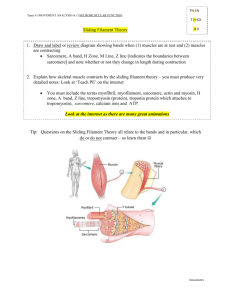
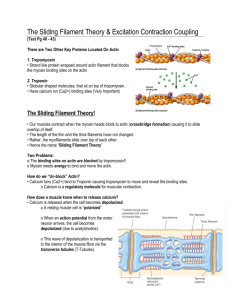
The Muscular System: Sliding Filament Theory 1. a. The thick filament is composed of what molecule? MYOSIN b. Flexing the head of this molecule provides what is known as the POWER STROKE. 2. The myosin head contains binding sites for what two molecules? a. ATP b. ACTIN 3. Three molecules make up the thin filament. a. Which molecule has a binding site for myosin heads? ACTIN b. Which molecule covers this binding site? TROPOMYOSIN c. Which molecule has a binding site for calcium ions? TROPONIN 4. What molecule must bind to the myosin head in order for it to disconnect with Actin? ATP 5. Hydrolysis of the molecule in question 4 returns the myosin molecule to the HIGH ENERGY confirmation. 6. Binding of the myosin heads sequentially prevents CROSS BRIDGE BINDING of the thin filament. (PULLING THEM TOWARD THE CENTER OF THE SARCOMERE BUT THEN ACTIN (ON THIN FILAMENTS) RELEASES THE ADP AND P SO THAT MYOSIN HEAD IS RELEASED AND CAN BIND AGAIN) 7. Name three roles for ATP in the contraction of muscle. a. PROVIDE THE ENERGY FOR THE POWER STROKE (MYOSIN HEAD BENDS) b. DISCONNECTING THE MYOSIN HEAD FROM ACTIN c. ACTIVELY TRANSPORTING CA++ OUT TO THE SARCOPLASMIC RETICULUM 8. What molecule is connected to the Z line? THIN FILAMENTS 9. Which of the following shorten during contraction? (may be more than one) a. Thin filament DOES NOT b. Sarcomere SHORTENS c. H zone SHORTENS d. Thick filament DOES NOT 10. What is the name of the condition in which muscles become rigid after death? RIGOR MORTIS b. What is this condition due to? Lack of ATP leads to the inability of the cells to actively pump calcium back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum and the myosin heads are unable to detach from the actin.