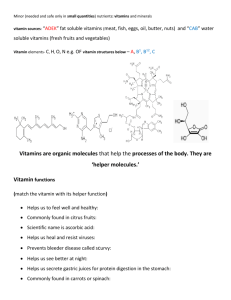
Food Sources for Vitamin A
advertisement

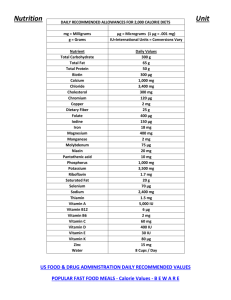
• Nutrition: It’s the study of how your body uses the nutrients in the foods you eat. •Malnutrition: the lack of the right proportions of nutrients over an extended period of time. * NUTRIENTS The chemical substances obtained from food during digestion that are used by your body to keep it going. * The saying, “You are what you eat” is true in many ways. Research has shown over the test of time just how important the foods you eat are for your health and well-being. In Spring 2011, research revealed that the foods a child eats the first 5 years of life sets the stage for the types of illnesses he/she will develop as an adult. In Fall 2011, research also found a link between certain health ailments of children based upon the foods the mother ate while pregnant. * Nutrients 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Needed Daily Protein Carbohydrates Fats Minerals Vitamins Water Pie Can/not Fix My Various Worries The foods we eat give: 1. Our bodies building materials 2. Energy to do things 3. Health protection PROTEIN Helps build & repair body tissue. When in excess supply, protein can be used for energy (or when we don’t eat enough carbs or fat). Protein is found in EVERY cell of your body from hair to finger nails and muscles. Protein Food Sources meat, poultry, milk products, eggs, dried beans, peas, lentils, peanuts, peanut butter and other nuts, tofu Carbohydrates Major source of energy for body activities Give us heat energy for maintenance of body temperature If we don’t eat enough carbohydrates, our body will burn protein instead. Simple Carbohydrates: (produce instant, but short term energy) sugar, honey, molasses, syrups, jams, jellies, and candy Complex Carbohydrates: (produce longer term energy for endurance) from the starch in cereals, pasta, rice, grains and vegetables, such as potatoes & corn. Provide us with that “satisfied” feeling after eating. Fats have 9 calories per gram, which take longer to burn than proteins and carbohydrates Source of stored energy and the carrier of essential fatty acids and vitamins Provide protection for internal organs Excess fat intake is stored as body fat, which forms a cushion around the body for padding, as well as insulation from hot and cold temperatures. Type of Fats Saturated Fats: come from animals (the ‘bad” kind of fat with cholesterol) Animal fat is solid at room temperature. Think about what happens to bacon fat when it cools? Unsaturated Fats: come from vegetables (the healthy fat). Healthy vegetable fats are liquid at room temperature MINERALS Furnish building materials and help regulate body functions. It’s similar to needing oil in a car—it makes the parts move smoothly and freely. **Minerals= Calcium, Phosphorus, Iron, Iodine** Remember “MIPIC” (“my/me pic”) CALCIUM Necessary for strong bones and teeth Also needed for blood clot formation to form a scab to heal wounds Important for maintaining normal muscle and nerve functions Milk and dairy products, broccoli, dark green leafy vegetables (especially spinach), salmon, sardines and enriched breads, cereals, and grains. Works along with calcium Important for development of nerve tissue Food Sources: liver, meat, fish, poultry, eggs, milk, cheese, whole grain bread and cereals, nuts. Necessary for the formation of hemoglobin (protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen) in the blood You will become anemic if you don’t have enough iron, causing you to feel very weak and tired, and possibly cause the whites of your eyes to turn yellow. Food Sources of Iron red meats, liver, kidneys, egg yolks, oysters, dried beans, whole grains and enriched breads and cereals, dark green leafy vegetables, raisins, dried apricots, and other dried fruit Helps thyroid gland to function properly Deficiency causes goiter—the thyroid gland tries so hard to absorb iodine in the foods you eat, it enlarges and creates a tumor that has to be removed. Food Sources: Iodized salt and Seafood Help regulate the chemical processes in your body Help your body store and use energy for growth and development Needed for general health maintenance *VITAMINS* Classifications of Vitamins Fat Soluble Vitamins: A, D, E, K These vitamins will only dissolve in fat in order for our body to absorb them. Water Soluble Vitamins: B & C These vitamins will only dissolve in water in order for our body to absorb them. How Vitamins are Absorbed Fat Soluble Vitamins Water Soluble Vitamins Used by Body Excess excreted in Urine Excess Intake Wasteful Excess stored In Liver Excess intakes may Accumulate & Cause toxic effects Fat soluble vitamin Important for proper vision, especially in dim light. (helps your eyes adjust to darkness when you turn out the lights) Prevents night blindness Helps maintain smooth, healthy skin Necessary for growth and reproduction and normal bone development Food Sources for Vitamin A All foods that are yellow or orange, or were yellow or orange before ripening Liver, egg yolks, dark green and yellow vegetables, sweet potatoes, carrots, milk, butter, margarine, apricots, yellow-orange fruits Water soluble vitamin The 3 most important types of Vitamin B to prevent an assortment of types of malnutrition are: Thiamin (B1) Riboflavin (B2) Niacin (B3) Functions of Vitamin B Promotes the normal working of the central nervous system Aids in digestion and promotes healthy appetite Keep the eyes, skin and mouth healthy Food Sources for Vitamin B Meat, pork, fish, liver, dried beans, peas, whole grain and enriched breads and grains, & cereals, eggs, dark leafy veggies, peanuts Water soluble vitamin Necessary for strong body cell and blood vessel development and maintenance Important in healing wounds Offers protection and resistance to stress and illness Citrus fruits, strawberries, blueberries, cantaloupe, broccoli, cabbage, tomatoes, kiwi, green peppers, potatoes, & dark leafy vegetables Fat soluble vitamin Enables the body to use the minerals, calcium and phosphorus in a normal way in building sound bones and teeth. This is the only Vitamin our body can make. The body can convert the rays from the sun on your skin into Vitamin D. Sunshine on our skin, eggs, cheese, milk that has been fortified with Vitamin D, fish (tuna, mackerel, sardines), fish liver oils, boxed ready to eat cereals Fat Soluble Vitamin Serves as an antioxidant- protects cells from damage Vitamin E is put in many skin care products for healthier and more youthful looking skin by slowing down oxidation of the skin cells, so the face looks smoother and younger longer. Sources of Vitamin E Egg yolks, vegetable oil, whole grain bread and cereals, liver, leafy green vegetables Fat soluble vitamin needed for normal blood clotting. (Do you remember which other nutrient helps clot blood? Hint: C _ _ _ _ _ _ ). Food Sources: pork, liver, spinach, broccoli & other dark leafy veggies, egg yolks, cauliflower, brussel sprouts WATER Aids in regulating body temperature Carries nutrients to body cells and waste products away We need to drink 6 to 8 glasses of water a day. More than 80% of our body is made up of water Aids in digestion 92% of our blood is made up of water Cellulose Needed in our digestive track for roughage Food Sources: the little fibers in celery or leafy vegetables (When you break apart celery and other leafy vegetables, you can see the little strands of cellulose) Fiber Needed for roughage in colon and intestines Prevents colon cancer Food Sources: whole grains and brans, flax seed Calorie A measure of energy value in food (it tells you how much energy that can be generated from eating food items) Growth, breathing, and physical activity involve some sort of expenditure of energy. Weight is maintained by burning off the exact number of calories that you take in each day. Examples of Calorie Expenditures per Hour Bicycling, moderate Boxing Dressing & Undressing Driving a car Eating Lying still, awake Playing Ping Pong Playing video games/typing Playing a violin Rowing in a race Running Sewing at the sewing machine Skating Swimming (2 miles per hour) Vacuuming the rugs Walking (3 miles per hour) Walking (5.3 miles per hour) 175 798 49 63 28 7 308 70 42 1,120 490 28 245 553 189 140 581 Empty Calorie Food containing a very high calorie count with little or no nutritional value—foods we call junk foods. They are called empty calories, because even though we eat the food, our body is asking for nutrients, and getting nothing but calories. Large muffin (450 calories): 1 hour of jogging 20-ounce caffe mocha with whipped cream (400 calories): Slice cheese cake (700 calories): 40 minutes of swimming laps 3 hours of brisk walking Large chocolate chip cookie (400 calories): 40 minutes on stair machine Bagel with cream cheese (500 calories): 2 hours & 30 minutes of ballroom dancing Common Food Items & How Much Activity it takes to Burn them off Size of CD/DVD oPancakes Size of Tennis Ball (1/2 Cup) oCooked rice/pasta oCooked Veggies Size of Baseball (1 Cup) oYogurt oMilk oRaw leafy veggies Size of Computer Mouse o Sweet/Baked Potato Size of Deck of Cards (2-3 oz.) o Cooked meat (steak, pork chops) Size of Teaspoon o Butter/margarine o Fat and oil *1 Slice oBread *1 Whole Amount oWhole Fruit