Plants II
advertisement

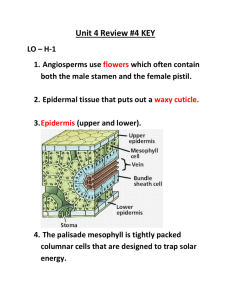
SEED PLANTS II The Flowering Plants (Anthophyta) Anthophyta Phylum Anthophyta (Angiosperms) Constitutes ~300,000 species (Gymno. 720 spp) Most recently evolved & most diverse group Divided into many groups: Basal Angiosperms Magnoliids (~8500) Eudicotyledones (dicot) Monocotyledones (monocot) Phylogeny of Angiosperms Basal angiosperms Fusion Fusion of Carpel secretion fusion From Endress & Igersheim, 2000 Characteristics of Angiosperms Double fertilization: egg + sperm produce zygote (2n) egg + 2nd sperm produce endosperm (3n) Mostly closed carpels: enclose ovule Reduced gametophytes (pollen grain, embryo sac) Sieve tubes and companion cells (phloem) Vessels (xylem) Stamens with 2 pairs of pollen sacs Chemical evolution! Refinements in vascular tissue, especially xylem, probably played a role in the enormous success of angiosperms in diverse terrestrial habitats. Like gymnosperms, angiosperms have long, tapered tracheids that function for support and water transport. Angiosperms also have fiber cells, specialized for support, and vessel elements (in most angiosperms) that develop into xylem vessels for efficient water transport. Amborella (Basal angiosperms) Fruit mailto:stephens@cats.ucsc. edu http://www.amborella.org/ Scott Zona Scott Zona The plant is dioecious. Female flowers with 5-6 carpels (a). Male flowers 10-25 stamens (b). Magnolia (Magnoliids) Fruit: aggregate follicle Tulip (Magnoliids) Differences Between Monocot & Eudicot EUDICOT MONOCOT Embryo with single cotyledon Embryo with two cotyledons Pollen with a single furrow or Pollen with three furrows or pores pore* Flower parts in multiples of four Flower parts in multiples of or five three Major leaf veins reticulate Major leaf veins parallel Stem vascular bundles in a Stem vascular bundles ring scattered Have taproots Have fibrous roots Secondary growth often present Secondary growth absent A Grass Pollen Pollen of Horse chestnut Flower: the main feature of angiosperms (= Carpel) The Flower Perianth: Sepals & petals collectively Androecium: stamens collectively Gynoecium: pistils collectively Types of Flowers Complete flower: has all 4 floral parts Incomplete flowers: missing a floral part(s) Perfect Flower: bisexual Imperfect flower: unisexual flowers Staminate flowers: have only the stamens Pistillate (carpellate) flowers: have only pistils Monoecious plants: separate staminate and pistillate flowers on the same plant Dioecious plants: either staminate or pistillate flowers Floral symmetry: Actinomorphic flower: floral parts are of similar shape & size (radially symmetrical) Zygomorphic: floral parts are different (bilaterally symmetrical) Inflorescence: A cluster of flowers with a definite arrangement Fertilization: the fusion of two gamete nuclei to produce a diploid zygote Pollination: transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma Pollen transferred within the same flower is called self- pollination, and the species is an in-breeder Pollen transferred to a different flower is called crosspollination and the species is out-breeder Example of Example ofMonocot Monocot Flower: Flower: Lilium sp. Lilium sp. Dicot Example of a Dicot Flower Hibiscus moscheutos Dicot Stamens Stigmas Hibiscus II Filament tube Style Ovary Ovules Angiosperm Life Cycle Embryo sac Egg Microspores Pollen Sperm Megaspores Meiosis 1n 2n Fertilization Zygote Sporophyte Development of Pollen Microsporogenesis: the development of microspore mother cell (microsporocyte) into microspores This involves meiosis Liliy Flower Microsporocytes Microsporocyte undergo Meiosis Tetrads of Microspores Pollen tetrads Microspores 4 microspores were produced by meiosis Microsporogenesis is complete Development of Pollen Microgametogenesis: the development of microspores into male gametophyte (pollen grain) This involves mitosis Mature Male gametophyte Microspores underwent mitosis to produce male gametophytes Mature Pollen grain Tube nucleus The tube nucleus produced the pollen tube The generative cell produced two sperm nuclei Development of Female Gametophyte Megasporogenesis: the megasporocyte (megaspore mother cell) develops into megaspores by meiosis Lilium Ovary Megasporocyte Before Meiosis Megasporocyte Two-nucleate Stage (formed by meiosis) Four-nucleate Stage (formed by meiosis) This survives others die Functional Megaspore Megasporogenesis is complete Development of Female Gametophyte Megagametogenesis: the megaspore develops into mature female gametophyte (embryo sac) by mitosis Three mitotic divisions follow First mitotic Division: 2-nucleate embryo sac 2nd Mitotic Division: 4-Nucleate embryo sac 3rd Mitotic Division: 8-Nucleate embryo sac 8-Nucleate embryo sac 2 of 4 Antipodals Egg & 2 synergids Pollination & Fertilization Pollen Tube Sperms Double Fertilization