How to Assess Working Capital Requirement
advertisement

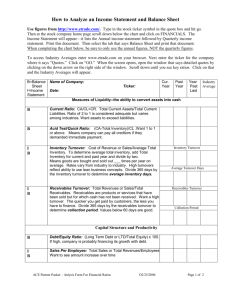
WORKING CAPITAL ASSESSMENT What is Working Capital ? Funds required to acquire current assets to enable business/industry to operate at the expected levels. CONCEPTS OF WORKING CAPITAL GROSS WORKING CAPITAL = CA These are in the system used/ consumed on a day to day basis. NET WORKING CAPITAL = CA – CL OR (SHF + TL) – (NFA + NCA) NWC is the entrepreneur's margin available in the system from Long term Funds What are Current Assets ? Assets which normally get converted into cash during the operating cycle of the firm. Cash & Bank balances Inventory Receivables Advances to suppliers/others Other Current assets What are Working Capital Sources? Own funds Bank borrowings Sundry Creditors Advances from customers Deposits due in a year Other current liabilities OPERATING CYCLE …...begins with acquisition of raw materials and ends with collection of receivables. Stages: 1) Raw materials (RM/RM consumption) 2) Work-in-process (WIP/COP) 3) Finished Goods (FG/COS) 4) Receivables (Debtors/Credit sales) Less: Creditors (creditors/purchases) Length of Operating Cycle Cash Cash Receivables Cash Receivables Raw Materia Service Trade Industry Finished Goods Receivables Stocks Semi Finished Goods FACTORS INFULENCING WORKING CAPITAL REQUIREMENT Nature of business – service/trade/manufacturing. Seasonality of operations – peak/non peak Production Policy – Constant/seasonal Market conditions- competition/credit terms Conditions of supply of RM/stores/spares etc. Quantum of production/Turnover(level of activity) Operating Cycle Current Assets to be maintained DATA TO BE OBTAINED Application. Financial Statements of Previous years Estimates/ Projections (with quantitative details) Working Capital Finance A) Fund Based Inventory finance and Bill Finance ( Post Sales Finance). B) Non Fund Based Letter of Credit (LC) Bank Guarantee. Assessment Methods Operating Cycle Method Service Sector Traders Manufacturing Activity. Drawing Power Method. Turnover Method. …. Assessment Methods MPBF method (II method of lending) for limits of Rs 6.00 crores and above Cash Budget method (Reason: Based on procurement and cash inflow) Seasonal Industries (Sugar/ Rice Mills/Textiles/Tea/Tobacco/Fertilizers) Contractors & Real Estate Developers Educational Institutions Operating Cycle Method Working capital requirement Operating expenses --------------------------------------No. of operating cycles in a year Operating Cycle Method A. Length of operating Cycle a. Procurment of Raw Material b. Conversion / Process time c. Average time of holding of FG d. Average Collection Period e.Operating Cycle (a+b+c+d) 30 days 15 days 15 days 30 days 90 days f. Operating Cycle in a year (365days/e) 4 cycle …..Operating Cycle Method B. Total Operating Expenses per Rs 60.00 lakhs Annum C. Total Turnover per Annum Rs 70.00 lakhs D. Working Capital Requirement = Total Operating Expenses (B)/ No. of operating Cycle (f as said earlier) Rs 15 lakhs Drawing Power Method (for units with small limits) (Rs.in lacs) Particulars Paid stocks (RM-Creditors) Semi Finished goods Finished goods Book debts Total Stock value Margin 4 25% 4 50% 4 25% 4 50% 16 DP 3 2 3 2 10 Turnover Method (originally suggested by Nayak Committee for SSI units) Applicable for limits upto Rs.6 crores A Sales Turnover B 25% of sales Turnover C 5% of Sales Turnover projected as margin D Actual NWC existing as per Last Financial Statement E B–C F B–D G MPBF (E or F whichever is less) H Additional margin to be brought in (C-D) MPBF Method Tandon’s II method of lending) A B C D Current Assets Current Liab. other than Bank Borrowings Working Capital gap (A-B) Minimum Stipulated NWC (25% of CA excluding export receivables) E F G H I Actual/projected NWC C–D C–E MPBF (F or G whichever is less) Excess borrowings/short fall in NWC (D-E) Justifications of the Performance Projection (Inventory/Receivable Norms – Comparison) Intra firm Comparison Comparison of estimates with previous years Actuals. For New Units Comparison of estimates with similar units in the area of operation. Higher projections shall be justified. MPBF Method Tandon’s II method of lending) Excess borrowing ( short fall in NWC ) shall be ensured by additional funds to be brought in by the applicant or by additional bank finance over MPBF. Important Aspects of MPBF method Production/Sales estimates Profitability estimates Inventory/receivables norms Build up of Net Working Capital Cash Budget Statement showing forecast of cash receipts, cash payments and net cash balance over a period of time Months-> 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Cash Receipts Cash Payments Surplus/deficit Cash credit – OB Cash credit - CB Peak deficit is financed and drawings regulated by monthly budgets Cash Budget Advantages: •Suitable for seasonal industries, contractors, software exporters etc. Limitations: •Will not reflect changes in various current assets and liabilities. •Will it give a clue whether a company is earning •profit or not. Funds flow statement is required to detect any diversion of funds. BIFURCATION OF FUND BASED LIMITS Inventory: OCC/KCC/PC/COD/SOD Bills : CBP/DBP/SBP/FBP CUBD/DUBD/FUBD Inventory Limit A. Total Inventory B. Creditors C. Margin D. Paid Inventory (A-B) E. Inventory Limit ( D-C) (Cont…) ….BIFURCATION OF FUND BASED LIMITS Bills /Book Debts Limit A. Receivables/ Sundry Debtors B. Margin C. Bills Limit ( A-B). Loan delivery system (FB W/C limits of Rs.10 crores & above from banking system) Cash Credit - 20% Demand Loan – 80% Loan Delivery System Objectives Loan delivery system (FB W/C limits of Rs.10 crores & above from banking system) Cash Credit - 20% Demand Loan – 80% Domestic Credit portion to be bifurcated into loan component and Cash Credit Relaxation. Bill Finance -Post Sales Finance (For Genuine Trade & Manufacturing Transactions) A. A. B. C. DBPs : Bills of Exchange accompanied with ; I) Invoice and ii) Documents of title of the Goods - LRS/RRS DUBD : Invoice /LRS / RRS – Maximum Tenor 180 days CUBD : Bill of Exchange / Promissory Notes. - Eligibility Carved out of MPBF Export Bills : FBP/FUBD - Security – Export Documents drawn against confirmed orders / LCs. …Bill Finance -Post Sales Finance (For Genuine Trade & Manufacturing Transactions) A. Book Debts Finance : A. Service Industry / Contractors B. Margin 50% C. Age not more than 90 days D. Collateral Security – 200% Urban / Semi Urban Security. Non Fund Based Limits Letter of credit ILC/FLC Usance/Sight Bank Guarantee Performance Financial – Bid Bonds/Security Deposits/ Mobilisation advance/retention money Deferred Payment Guarantee LC Assessment 1 Annual purchase/import 2 3 4 5 6 7 Out of (1) on credit basis Out of (2) on usance LC basis Average of (3) per month Lead time (no. of months) Usance period (no. of months) Usance LC requirement (5+6) X (4) FLC/ILC Guidelines to be followed For constituents borrowers with regular sanctioned credit facilities for genuine transactions. LCs shall not be opened with clause without recourse to drawer. Bank Guarantees: Performance and Financial Guarantees Purpose / Difference Security: Cash Margin +Counter Guarantee +Collateral Security (Immovable / Liquid Security) Restrictive Clause. Important Ratios Current Ratio (CA/CL) (norm – 1.15 upto Rs.6 crores/1.33 for above) Adjusted Current Ratio (reduce export bills discounted from BB & CA) Total debt equity (TOL/TNW) (Maximum norm : 6) Gearing Ratio (for NFB Limits) Maximum Norm: 10 Total Outside Liabilities + 100% of NFB Limits --------------------------------------------------------------------------- Net Worth – (NCA+Investments in associate concerns) Notes: TOL (excluding Sundry creditors representing stocks procured under LC/BG and mobilisation advance outstanding against BGs) NW (excluding Intangible Assets) NCA (excluding advances given for capital goods for business purpose) Exposure Norms for some Categories Category Constructions contractors Ceiling on borrowings FB + NFB limits shall not exceed 15 times net owned funds Housing Finance Borrowings shall be restricted to 3 times Institutions the net owned funds