Electron Configuration
advertisement
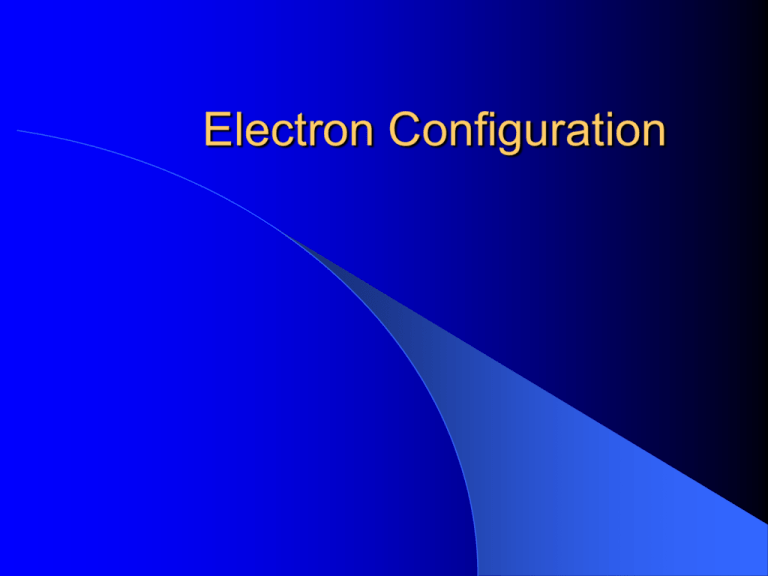
Electron Configuration Quantum Number Number that specifies the properties of the atomic orbitals Tells us the distance from the nucleus and the shape of the orbital Principal Quantum Number Main level or shell These are the Bohr energy levels n = 1, n = 2, n = 3 As n increases, the distance from the nucleus increases Sublevel Each main level is divided into sublevels Four types of sublevels s p d f S orbitals Spherical P orbitals Dumbell shaped One dumbell in each axis P Orbitals D orbitals F orbitals Orbital Each sublevel is made of orbitals Every orbital can hold 2 electrons s – 1 orbital – 2 electrons p – 3 orbitals – 6 electrons d – 5 orbitals – 10 electrons f – 7 orbitals – 14 electrons Main Level Sublevel # orbitals # e in sublevel Total e Electron Configuration Arrangement of electrons in an atom Aufbau Principle – electrons fill into an atom starting with the lowest energy levels Electron Configuration Polka F:\Documents\electron configuration.avi Electron Spin Way which the electrons rotate on their axis Pauli Exclusion Principle – in order for two electrons to occupy the same orbital, they must have opposite spin Write configuration for C S Higher Order There are exceptions to the order of filling as you move to higher levels Br Valence Electrons Electrons in the last main energy level These are the electrons involved in chemical reactions There are a maximum of 8 valence electrons How to find valence e Write configuration and count electrons in last main energy level Examples: Find valence electrons for C Fe Cl Draw Dot Structure C Fe Cl Periodic Table Demitri Mendeleev First to publish a chart of the elements Arranged by increasing atomic mass with similar elements in columns Moseley’s Table He suggested that the elements are arranged by atomic number rather than atomic mass Periodic Law – chemical and physical properties are periodic functions of their atomic numbers Table Properties Horizontal Rows are called Periods Vertical Columns are called Groups or Families For every group or family, the electron arrangement is the same Configuration from the Table Group tells end configuration, period tells tells the highest energy level Ca in group 2 period 4 so it ends in 4s2 Blocks Chart is broken into blocks based on the orbitals they fill last Groups 1 and 2 fill s last – called s block Groups 3 –12 called d block Groups 13 – 18 called p block Bottom two rows are the f block Name the element with the following end configuration 5s1 2s22p3 4s23d6 3s23p6 6s25d9 http://modelscience.com/PeriodicTable.html