Food Chains and Food webs
advertisement

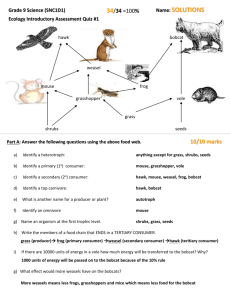
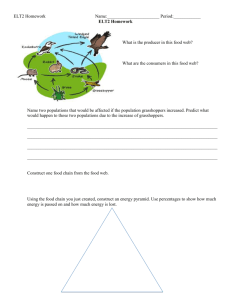
FOOD CHAINS and FOOD WEBS FOOD CHAINS Are designed to show the direction that energy flows from producers to top carnivores, in a simplified single pathway. ENERGY IN FOOD CHAINS energy passed to consumer Producer 10% Primary consumer 10% 90% 2o consumer 90% energy used to live 10% Rule: only 10% of the energy in an organism is passed on to the next trophic level 1 unit 100 units 10 units 10 units 100 units 1000 units FOOD WEBS & TROPHIC LEVELS 1. TROPHIC LEVEL - the place in a food chain that an organism feeds a. FIRST TROPHIC LEVEL - producers or autotrophs that feed themselves *Any organisms found at the second trophic level or higher are considered to be heterotrophs i.e. they do not produce their own food b. SECOND TROPHIC LEVEL - herbivores or primary [1o] consumers that eat producers c. THIRD TROPHIC LEVEL – carnivores or secondary [2o] consumers that eat herbivores d. FOURTH TROPHIC LEVEL – carnivore or tertiary [3o] consumers that eat other carnivores 2. FOOD WEB - a series of interconnected food chains We will use this simpler food web to answer a series of questions HAWK BOBCAT WEASEL FROG MOUSE GRASSHOPPER SEEDS VOLE GRASS FALLEN LEAVES HAWK BOBCAT WEASEL FROG MOUSE GRASSHOPPER SEEDS Identify an autotroph VOLE GRASS FALLEN LEAVES produces its own food Identify a primary consumer eats a producer HAWK BOBCAT WEASEL FROG MOUSE GRASSHOPPER SEEDS producer 2o consumer VOLE GRASS Identify a secondary consumer a carnivore that eats herbivores 3o consumer 1o consumer FALLEN LEAVES 1o Consumer Identify a tertiary consumer a carnivore that eats other carnivores HAWK BOBCAT WEASEL FROG MOUSE GRASSHOPPER SEEDS VOLE GRASS FALLEN LEAVES Identify an organism at the fourth trophic level [show how it is at this level] HAWK BOBCAT WEASEL FROG MOUSE GRASSHOPPER SEEDS Identify a decomposer Identify an omnivore VOLE GRASS FALLEN LEAVES something that eats dead things something that eats both plants & animals HAWK BOBCAT WEASEL FROG MOUSE GRASSHOPPER SEEDS VOLE GRASS FALLEN LEAVES Explain, what would be the effect on grasshoppers if fewer leaves fewer fallen leaves means less food for voles voles now eat more grass voles eat more grass less grass for grasshoppers to eat fewer grasshoppers as they leave area as less food Over a longer time less food means some voles leave fewer voles means less food for bobcat bobcats now eat more frogs fewer frogs means weasels eat more grasshoppers fewer grasshoppers HAWK BOBCAT WEASEL FROG MOUSE GRASSHOPPER SEEDS VOLE GRASS FALLEN LEAVES Explain what would be the effect on bobcats if fewer grasshoppers Fewer grasshoppers means less grass & seeds being eaten and less food for frog, weasels & mice Less food for frogs means frogs leave If fewer frogs, less food for bobcats fewer bobcats Over a longer time If more grass, more food for voles If more voles, more food for bobcats more bobcats HAWK BOBCAT WEASEL FROG MOUSE GRASSHOPPER SEEDS VOLE GRASS FALLEN LEAVES Explain what would be the effect on hawk if fewer bobcats. Fewer bobcats means more voles and frogs Over a longer time more frogs means more grasshoppers eaten More voles eat more grass Fewer grasshoppers means less food for mice & weasels [although weasels can eat frogs] Less grass for grasshoppers & mice Overall, less food for hawks fewer hawks Fewer grasshoppers & mice, less food for hawks fewer hawks HAWK BOBCAT WEASEL FROG MOUSE GRASSHOPPER SEEDS VOLE GRASS FALLEN LEAVES Explain what would be the effect on voles if fewer hawks Fewer hawks means more weasels and more mice More mice & weasels eat more grasshoppers So now fewer grasshoppers so they eat less grass Now more grass, so more food for voles more voles References • Investigating Science – Pearson • A. Dercho