Ecology Quiz #1 - Answers
advertisement
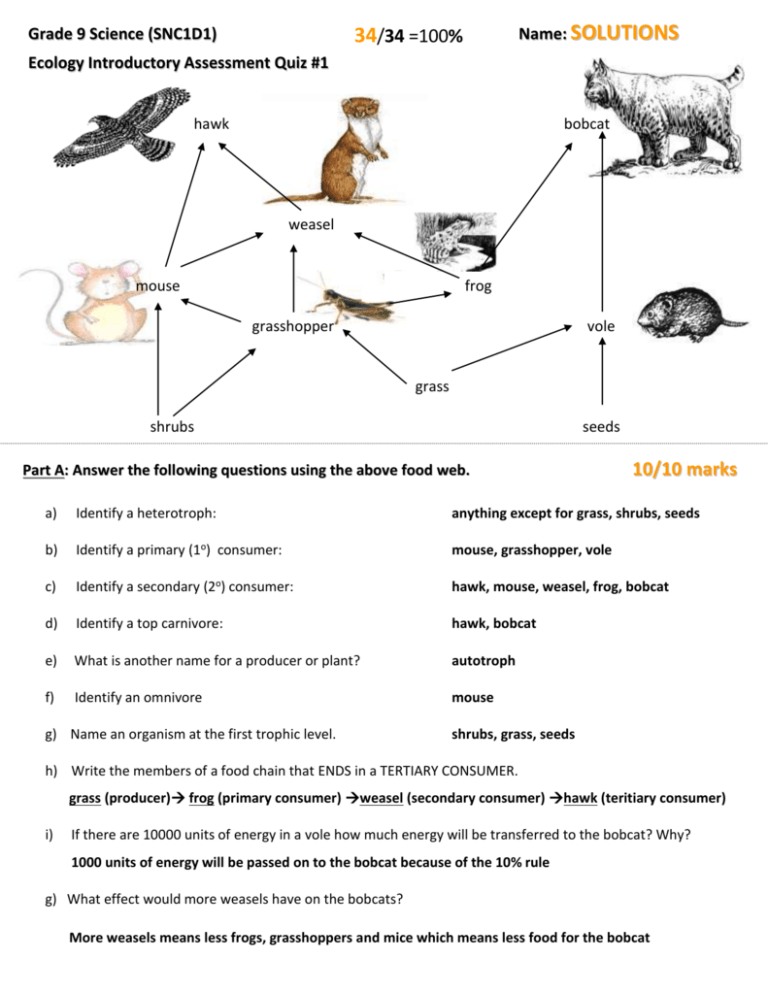
Name: SOLUTIONS 34/34 =100% Grade 9 Science (SNC1D1) Ecology Introductory Assessment Quiz #1 hawk bobcat weasel mouse frog grasshopper vole grass shrubs seeds Part A: Answer the following questions using the above food web. 10/10 marks a) Identify a heterotroph: anything except for grass, shrubs, seeds b) Identify a primary (1o) consumer: mouse, grasshopper, vole c) Identify a secondary (2o) consumer: hawk, mouse, weasel, frog, bobcat d) Identify a top carnivore: hawk, bobcat e) What is another name for a producer or plant? autotroph f) Identify an omnivore mouse g) Name an organism at the first trophic level. shrubs, grass, seeds h) Write the members of a food chain that ENDS in a TERTIARY CONSUMER. grass (producer) frog (primary consumer) weasel (secondary consumer) hawk (teritiary consumer) i) If there are 10000 units of energy in a vole how much energy will be transferred to the bobcat? Why? 1000 units of energy will be passed on to the bobcat because of the 10% rule g) What effect would more weasels have on the bobcats? More weasels means less frogs, grasshoppers and mice which means less food for the bobcat 5/5 marks Part B: Multiple Choice - Circle the best answer. 1. Which group can best be described as a population? a) all the honeybees in an orchard c) the life in Earth's atmosphere d) the living and nonliving factors in a meadow b) all the plants and animals in a forest 2. All of Earth's water, land, and atmosphere within which life exists is known as a) community b) biodiversity c) population d) biosphere 3. A student measured some abiotic factors present in an aquarium in a biology laboratory. Which data did the student most likely record? a) the size and number of each species of fish b) the temperature and oxygen content of the water c) the number of each type of green plant and each type of snail 4. Human activities are impacting a) animals b) plants e) all of the previous answers c) protists, fungi, and moneran organism d) climate, land, water, air 5. Which ecological term refers to all the organisms shown in the diagram? a) heterotrophic b) community c) population d) lithosphere Part C: Calculations 1. Calculate the relative abundance of the japanese beetle, crow, milkweed bug and red tailed hawk 4/4 marks Total Number of Organisms found in 25 m x 25 m Square Area of Grassland species # individuals red tailed hawk 2 coyote crow 1 10 opossum raccoon grasshoppers japanese beetle 7 9 56 72 milkweed bug 64 Total 221 relative abundance 2/221 = 0.9% 10/221 = 4.5% 72/221 = 64/221 = 34% 29% 2. Indicate the species richness. 8 1/1 mark 2/2 marks 3. Calculate the biodiversity index….Show the formula and your work!! biodiversity index = # of different species = total # of individuals 8 221 = 0.036 4. What is the name of the sampling method that was used to gather the above data? Why? (e.g. canopy fogging, quadrat sampling, transect sampling, netting) quadrat sampling because the data was collect from a square area 2/2 marks 5. Circle the negative trait associated with each species. Write the number in the bottom row. species X Y Z size large large small diet herbivore carnivore herbivore biotic potential very low low high range species small small large range individual small large small human interactions few many few 3 6 0 # of negative traits 5/5 marks a) Which species is most likely to be classified as endangered? species Y b) Which species is most like to be classified as vulnerable? species X or Z 7. The sightings of the eastern cougar are very rare in all areas in which it is found. What term would describe the eastern cougar’s current status? endangered 1/1 mark 8. The grizzly bear is no longer found in Manitoba and Saskatchewan but can still be found roaming the mountains of Alberta and British Columbia. What term would describe the grizzly bear’s current status? extirpated 9. Define biodiversity: 1/1 mark 1 /1 mark the variety and number of different life forms on our planet 10. Explain two activities that threaten biodiversity. 1. deforestation 2. urbanization 2/2 marks











