UV-Vis Spectroscopy
advertisement

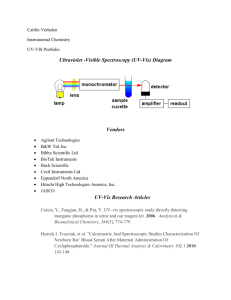
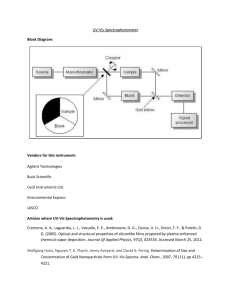
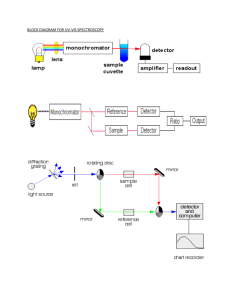
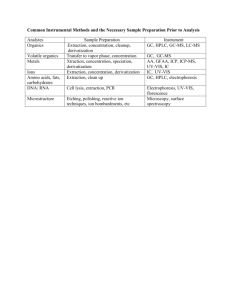
UV-Vis Spectroscopy By: Kimberly Lopez What is UV-Vis analysis? UV-Vis is fast, simple and inexpensive method to determine the concentration of an analyte in a solution. Used for relatively simple analysis, where the type of compound to be analyzed is known, to do quantitative analysis to determine the concentration of the analytes. Uses Used in a broad range of areas, mainly for routine measurements Hospitals Petrochemical industry Food industry Water quality control labs Chemical and biological plants Uses In laboratories UV-Vis can be used to monitor the separations in liquid chromatography If a mixture is separated in a column, UV-Vis can be used to detect the different compounds UV-Vis is relatively cheap and an easy detector compared to Mass spectrometry detectors How it works? In UV-Vis, a beam with a wavelength varying between 180nm-1100nm passes through a solution in a cuvette. The sample in the cuvette absorbs this UV or visible radiation. I₀ is the radiation coming in I is the radiation coming out How it works? The amount of light that is absorbed by the solution depends on: The concentration The path length of the light through the cuvette How well the analyte light absorbs at a certain wavelength Violet: 400 - 420 nm Indigo: 420 - 440 nm Blue: 440 - 490 nm Green: 490 - 570 nm Yellow: 570 - 585 nm Orange: 585 - 620 nm Red: 620 - 780 nm UV-Vis Spectrophotometer Double Beam UV-Vis Spectrophotometer The relation of absorbance to concentration is given by lambert-Beer’s law (Beer’s Law): A = ɛlc Absorbance Epsilon Path Length Molar absorption coefficient of the analyte for a certain wavelength Concentration of analyte UV-Vis Spectrophotometer 1st choice in most laboratories concerned with the identification and measurement of organic and inorganic compounds - in nucleic acids, proteins, foodstuffs, pharmaceuticals and fertilizers, in mineral oils and in paint. In every branch of molecular biology, medicine and the life sciences, the spectrophotometer is an essential aid to both research and routine control. What can be Analyzed? Analytes that can be dissolved in solvents like water, ethanol and hexane Analytes that absorb UV or Visible light Quantitative measurements with a single analyte in the solution or more if they do not interfere. Analyzing Mixtures Compounds that absorb UV or visible light have UVVis Spectrum Mixtures may be analyzed if the UV-Vis spectra of compounds differ sufficiently from each other In most cases, where there is more than one analyte, this is where Beer’s Law comes in What is shown? UV-Vis spectrum shows the absorbance of one or more sample components in the cuvette when scanned through various wavelengths Y-axis show the absorbance X-axis shows the wavelength Relevance to Forensics Screening methods in drug analysis and some applications in trace analysis Related to forensic pharmacology, color is due to the absorption of light by two nearby elements of a molecule, in other substances such as metals, color is due to unique absorption that is characteristic of that the element(s) present. In Spectrophotometry Cell length is controlled for, the Coefficient and Concentration for unknowns is not usually known in forensic analysis, therefore this method is not utilized often for dealing with unknowns. Hair samples UV-Vis spectrophotometer is used to analyze the dyes and pigments in both hairs and fibers. This is done by studying the absorbance and fluorescence spectra of these microscopic samples. Microspectrophotometers are also used to identify the polymers contained in man-made fibers. This is done by examination of the ultraviolet absorbance spectra to identify the polymer. Drug samples Since many illegal drugs contain aromatic groups that produce characteristic UV/Vis spectra. As the absorption peak depends on the nature of the aromatic group(s) in the drug compound, additional spectroscopic information regarding drug derivatives and their metabolites will be obtained. Food dyes Using a UV-visible spectrometer and a range of food dyes you will test how the absorbance wavelength value relates to the color of the solution. Safety Risk of burn. Before replacing the lamp, set the power switch off and cool down the lamp. Room temperature within the range of 15°C to 35°C. A position not exposed to direct sunlight. A position not subject to strong vibration, or any continuous (even weak) vibration. A position free from strong magnetic or electromagnetic fields. A location free from exposure to corrosive gas, or any organic or inorganic gas that has an absorption band in the UV region. A location substantially free dirt or dust. Before changing a fuse or the inlet voltage, turn off the power switch and disconnect the power cable. Advantages & Disadvantages Analyze substances quickly and they are not difficult to use UV-Vis spectrometers bring high-tech spectral analysis to the food industry, where they help laboratory technicians study food products These devices are used in fields as diverse as forensic analysis, research and medicine Dust or grim may coat the mirrors in a double-beam UV-Vis spectrometer, the device's performance will degrade Repair costs can also double because you can't replace one mirror if it needs fixing. Because they work as a pair, you must replace both mirrors. Stray light caused by faulty equipment design and other factors could decrease an instrument's linearity range and reduce the absorbency of the substance it measures Electronic components in the spectrometer or sample source may also generate noise that decreases measurement accuracy and reduces the device's sensitivity. Works Cited "UV/Vis Spectrometry Basics." - Chromedia. Web. 31 Mar. 2015. "Forensic Applications of UV-Vis Spec." Forensic Applications of UV-Vis Spec. Web. 31 Mar. 2015. "Analytical Forensic Pharmacology/UV-VIS Spectroscopy." Wikibooks, Open Books for an Open World. Web. 31 Mar. 2015. "CRAIC Technologies Mobile." Fiber and Hair Analysis. Web. 31 Mar. 2015. Lee, Kevin. "Advantages & Disadvantages of a UV-VIS Spectrometer." EHow. Demand Media, 4 May 2010. Web. 31 Mar. 2015. "10C: UV/Vis and IR Spectroscopy." - Chemwiki. Web. 31 Mar. 2015.