File - Chemistry from AZ
advertisement

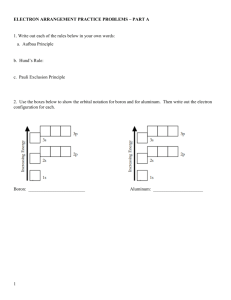
Name: ____________________ THE BOHR ATOM In 1913, Niels Bohr (student of Ernest Rutherford) from Denmark proposed his model of the atom. He agreed with the atom as having a dense, positively charged nucleus and negatively charged electrons outside the nucleus. But, he believed these electrons traveled in specific spherical paths known as orbits. PRINCIPAL ENERGY LEVEL Electrons move in principal energy levels or “shells” around the nucleus. principal energy level (“shell”) is a region of discreet energy levels. principal quantum number (n) is the number of the shell or principal energy level. For example, when n=2 this refers to second shell. the Each principle energy level (“shell”) can hold a certain amount of electrons, as shown in the table below. Principal Energy Levels (n) n=1 n=2 n=3 n=4 n=5 Maximum # of Electrons (e-) Write out the ground state electron configuration for the following elements: Element 7N 17Cl 13Al Ground State Electron Configuration Ground State: ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ _________________________________ 1 Infer: What can you conclude about all the elements on the periodic table and their electron configurations? Exited State: ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ Photon: ________________________________________ Nitrogen Ground State Electron Configuration Excited State Electron Configuration ____________________ ____________________ Practice: Complete the following table. Element Numbe r of e- Ground State electron configuration Possible Excited State electron configuration 17Cl 13Al From Ground State to Excited State Back to Ground State 2 He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics 1922 "for his services in the investigation of the structure of atoms and of the radiation emanating from them". During World War II, Bohr fearing arrest by the Germans, escaped to Britain from where he went to the US to work on the Manhattan Project at the Los Alamos laboratory in New Mexico. The Manhattan Project led to the development of the first atom bomb. Emission Spectrum of Hydrogen When an electric current is passed through a glass tube that contains hydrogen gas at low pressure the tube gives off blue light. When this light is passed through a prism four narrow bands of bright light is observed against a black background. These narrow bands have the characteristic wavelengths and colors shown in the table below. If an electron falls from the 3-level to the 2-level, red light is seen. Wavelength Color 656.2 nm 486.1 nm 434.0 nm 410.0 nm red blue-green blue-violet violet Bright-light spectrum: ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ______________________ 3 ________________________________________________________________ ___________ How can a bright-line spectrum be useful in studying stars? ________________________________ ________________________________ ________________________________ ________________________________ 1. When an excited electron in an atom moves to the ground state, the electron (1) absorbs energy as it moves to a higher energy state (2) absorbs energy as it moves to a lower energy state (3) emits energy as it moves to a higher energy state (4) emits energy as it moves to a lower energy state 2. Which electron configuration represents the electrons in an atom of Ga in an excited state? (1) 2-8-17-3 (2) 2-8-17-4 (3) 2-8-18-3 (4) 2-8-18-4 3. During a flame test, a lithium salt produces a characteristic red flame. This red color is produced when electrons in excited lithium atoms (1) are lost by the atoms (2) are gained by the atoms (3) return to lower energy states within the atoms (4) move to higher energy states within the atoms 4. The diagram below represents the bright-line spectra of four elements and a bright-line spectrum produced by a mixture of three of these elements. 4 Which element is not present in the mixture? (1) A (2) D (3) X (4) Z 5. The bright-line spectrum of an element in the gaseous phase is produced as (1) protons move from lower energy states to higher energy states (2) protons move from higher energy states to lower energy states (3) electrons move from lower energy states to higher energy states (4) electrons move from higher energy states to lower energy states Name: __________________________________ The Electron Cloud Model/ Wave Mechanical Model Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle: ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ______________________ SUBLEVELS: 5 ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ______________________ E N E R G Y ORBITALS: ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________ Each sublevel has one or more orbitals. The number of orbitals is always the same regardless of the shell. s has _____________ orbital p has _____________ orbitals d has _____________ orbitals f has ______________ orbitals ** Each orbital holds a maximum of 2 electrons. ELECTRON PAIR SPIN: An orbital pair of electrons must have opposite spins. The notation for an electron pair is ↑↓ SUMMARY Principal energy level “n” Sublevels orbitals present s present in each p sublevel f Maximum number of electrons d 6 1 2 3 4 5 Hund’s Rule: ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ _________________________________ Levels of Representation I. Electron configuration: This notation shows the number of electrons in each energy level. Will always be found on the periodic table and represents the ground state. Element Number of Electrons Electron Configuration 17Cl 7N 20Ca 7 II. Representative configuration: Expands the electron configuration to include principal energy levels, sublevels and number of electrons using the following notation… 1s22s22p6 Element Number of Electrons Representative Configuration 17Cl 7N 20Ca III. Orbital notation: uses up and down arrows to show the electron pairs occupying each orbital. Element 17Cl 7N 20Ca Orbital notation ____ 1s ____ 2s ____ ____ ____ 2p ____ 3s ____ ____ ____ 3p ____ 1s ____ 2s ____ ____ ____ 2p ____ 3s ____ ____ ____ 3p ____ ____ _____ 1s 2s 4s ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 2p 3s 3p Question: Look at the calcium representative and orbital configuration. Why aren’t there any electrons in the 3d sublevel? IV. Electron dot diagram (Lewis Dot Diagram): Diagrams only the valence electrons as dots around the element’s symbol that represents the kernel of the atom. 8 Cl N Ca 9