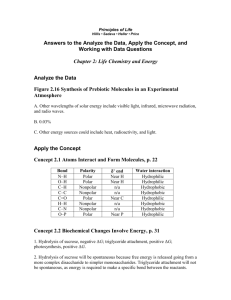
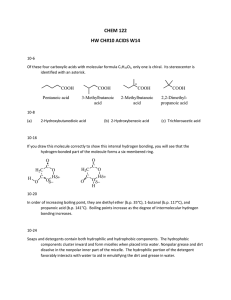
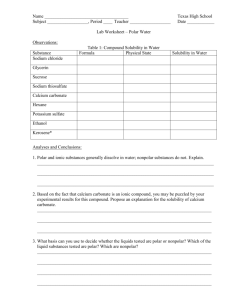
2.2 Solubility of substances in water
advertisement
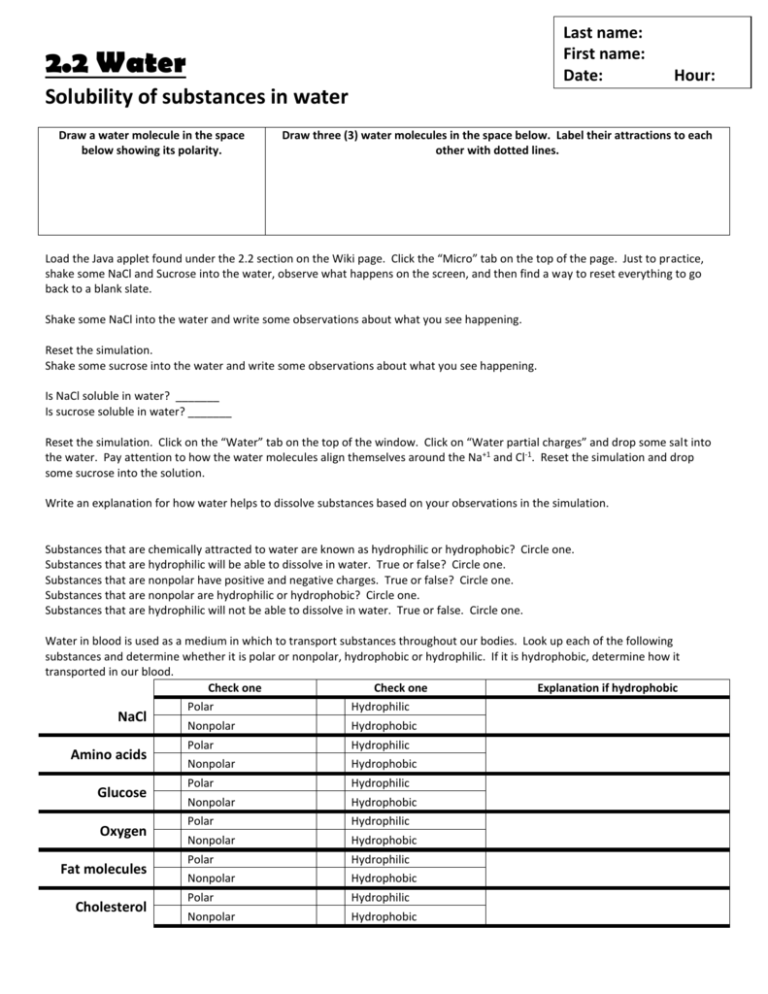
Last name: First name: Date: 2.2 Water Hour: Solubility of substances in water Draw a water molecule in the space below showing its polarity. Draw three (3) water molecules in the space below. Label their attractions to each other with dotted lines. Load the Java applet found under the 2.2 section on the Wiki page. Click the “Micro” tab on the top of the page. Just to practice, shake some NaCl and Sucrose into the water, observe what happens on the screen, and then find a way to reset everything to go back to a blank slate. Shake some NaCl into the water and write some observations about what you see happening. Reset the simulation. Shake some sucrose into the water and write some observations about what you see happening. Is NaCl soluble in water? _______ Is sucrose soluble in water? _______ Reset the simulation. Click on the “Water” tab on the top of the window. Click on “Water partial charges” and drop some salt into the water. Pay attention to how the water molecules align themselves around the Na+1 and Cl-1. Reset the simulation and drop some sucrose into the solution. Write an explanation for how water helps to dissolve substances based on your observations in the simulation. Substances that are chemically attracted to water are known as hydrophilic or hydrophobic? Circle one. Substances that are hydrophilic will be able to dissolve in water. True or false? Circle one. Substances that are nonpolar have positive and negative charges. True or false? Circle one. Substances that are nonpolar are hydrophilic or hydrophobic? Circle one. Substances that are hydrophilic will not be able to dissolve in water. True or false. Circle one. Water in blood is used as a medium in which to transport substances throughout our bodies. Look up each of the following substances and determine whether it is polar or nonpolar, hydrophobic or hydrophilic. If it is hydrophobic, determine how it transported in our blood. Check one Check one Explanation if hydrophobic NaCl Amino acids Glucose Oxygen Fat molecules Cholesterol Polar Hydrophilic Nonpolar Hydrophobic Polar Hydrophilic Nonpolar Hydrophobic Polar Hydrophilic Nonpolar Hydrophobic Polar Hydrophilic Nonpolar Hydrophobic Polar Hydrophilic Nonpolar Hydrophobic Polar Hydrophilic Nonpolar Hydrophobic