CHEM 122 HW CH#10 ACIDS W14
advertisement
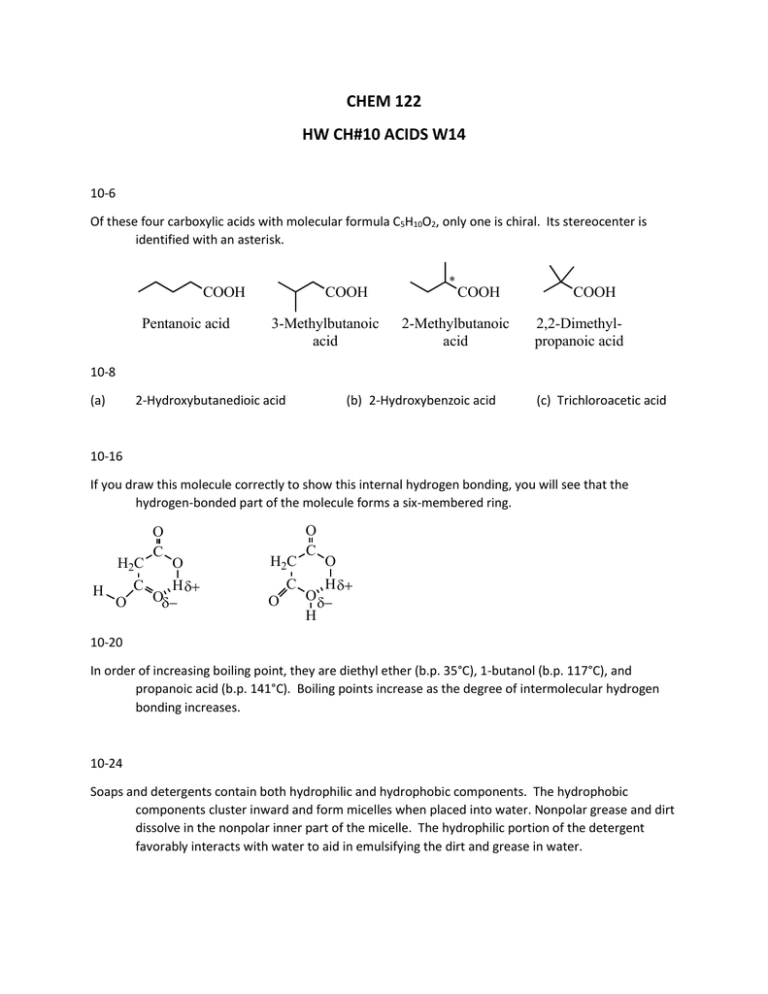
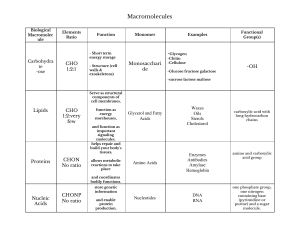
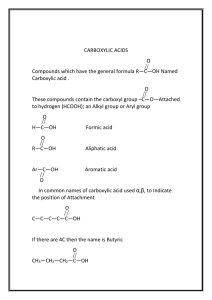
CHEM 122 HW CH#10 ACIDS W14 10-6 Of these four carboxylic acids with molecular formula C5H10O2, only one is chiral. Its stereocenter is identified with an asterisk. COOH Pentanoic acid COOH 3-Methylbutanoic acid * COOH 2-Methylbutanoic acid COOH 2,2-Dimethylpropanoic acid 10-8 (a) 2-Hydroxybutanedioic acid (b) 2-Hydroxybenzoic acid (c) Trichloroacetic acid 10-16 If you draw this molecule correctly to show this internal hydrogen bonding, you will see that the hydrogen-bonded part of the molecule forms a six-membered ring. H2C H C O O C O H O H2C C O O C O H O H 10-20 In order of increasing boiling point, they are diethyl ether (b.p. 35°C), 1-butanol (b.p. 117°C), and propanoic acid (b.p. 141°C). Boiling points increase as the degree of intermolecular hydrogen bonding increases. 10-24 Soaps and detergents contain both hydrophilic and hydrophobic components. The hydrophobic components cluster inward and form micelles when placed into water. Nonpolar grease and dirt dissolve in the nonpolar inner part of the micelle. The hydrophilic portion of the detergent favorably interacts with water to aid in emulsifying the dirt and grease in water. ionic, hydrophilic Cl N H3C CH3 nonpolar, hydrophobic polar, hydrophilic HO CH2 polar, hydrophilic O HO CH2 C CH2 O C (CH2)14CH3 HO CH2 nonpolar, hydrophobic 10-36 The pKa of ascorbic acid is 4.10. At this pH, ascorbic acid is present 50% as ascorbic acid and 50% as ascorbate ion. At pH 7.35 to 7.45, which is more basic than pH 4.10, ascorbic acid would be present as ascorbate ion. 10-38 CH3CH2NH2 is the stronger base. The electron lone pair on the less electronegative nitrogen is more basic relative to the electrons stabilized by resonance in the carboxylate anion. 10-40 Fischer esterification is the process of forming an ester by treating a carboxylic acid with an alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst, commonly sulfuric acid. An example is the formation of ethyl acetate from acetic acid and ethanol. O CH3C-OH + HOCH2CH3 Acetic acid Ethanol H2SO4 O CH3COCH2CH3 + H2O Ethyl acetate 10-44 Cinnamic acid reacts with the following reagents to accomplish the following syntheses: O H2 Ni OH 1. LiAlH4 2. H2O OH O OH CH3CH2OH H+ O OCH2CH3