Lesson 4 Student handout
advertisement

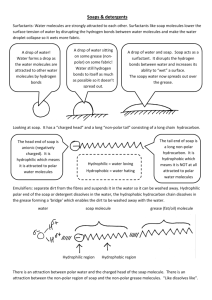
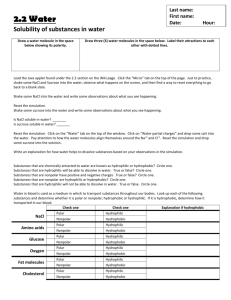
SBI4U: Biochemistry Lesson 4 - Polarity and Hydrophobic & Hydrophilic Molecules Learning Goals: I will be able to describe the properties of water that make it a good solvent for polar compounds I will explain the process of how soap works by using the terms hydrophobic and hydrophilic I will be able to describe what acids and bases are and how they compare to water What are we talking about? RECAP: Draw the shape of a water molecule above, and show the polar ends. How might 2 or more water molecules interact with each other? Solubility: How easily a substance dissolves • The general rule is "like dissolves like" • Polar substances dissolve polar substances • Non-polar substances dissolve non-polar substances • HYDROPHOBIC: • HYDROPHILIC: *Often, the subscript “(aq)” is visible - means that aqueous substances are soluble in water. H-Bonding Is Responsible for Density of Ice Being Less than Water • H-bonds lock into lattice structure in the solid state • Ice - Solid water is __________________ than liquid water, allowing it to float Water is the universal solvent • Water can dissolve many hydrophilic (water loving) substances Ionic compounds Other polar compounds • Any substance that dissolves in water is called a ____________. • Water, then, is a ____________. • Hydration is the process of water molecules surrounding ions to make “spheres of hydration” Q1: Can water dissolve non-polar oil? Why or why not? Q2: Can water pass freely through the cell membrane? • Some substances do not dissolve readily in water because they are ___________ solutes • Oil (fats or lipids) is an example of a hydrophobic – “water-fearing” - substance • Application: How does soap work to clean grease/oil from our dishes? How soap works: micelles • Soap can suspend oil/dirt in such a way that it can be removed. • Soap is an excellent cleanser • • • • Grease and oil are __________ and ____________ in HOH. When soap is added to oil-containing solution, the non-polar hydrocarbon portion of the soap attaches to the non-polar oil molecules. A ___________ then forms—with nonpolar solutes (grease/oil) in the centre. The outside of the micelle is polar (water soluble) and now the grease and oil can be washed away. • Isn’t our cell membrane made of fat? What happens when soap comes in contact with our cell membrane? Acids & Bases: • When 2 water molecules interact, one molecule gains a hydrogen (to become H3O+, hydronium ion) while the other loses a hydrogen (and becomes OH-, hydroxide ion). • ________ are defined as substances that increase the concentration of H+ (or H3O+) ions in solution. • ________ are defined as substances that increase the concentration of OH- ions in solution. • • When an acid is mixed with a base, the result is a _________________________. Neutralization reactions produce water and a salt. • • • A solution with a pH of 7 is considered _________(equal amounts of H3O+ and OH-). Solutions whose pH is less than 7 are ___________ (more H3O+). Solutions whose pH is greater than 7 are ___________ (more OH-). H.W. Read pgs. 16-23, Do Q’s #7, 8, 13, 14, 15, 16 and questions on the back.