Ch. 25
advertisement

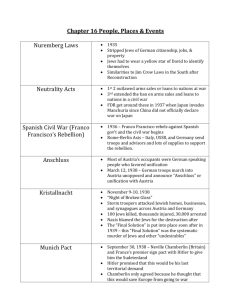
CHAPTER 25 WWII NATIONALISM AND THE GOOD NEIGHBOR POLICY “No state has the right to intervene in the internal or external affairs of another.” U.S. withdraws troops from Haiti and the Dominican Renounce the Platt Amendment Reduce role in Panamanian affairs Provide indirect aid to Batista in Cuban revolt Lower a tariff on sugar cane and RISE OF AGGRESSIVE STATES Mussolini Ethiopia Hitler Conscription and military buildup The Rhineland Austrian Anchluss Munich Pact Sudetenland Imperial Japan Manchuria China proper THE AMERICAN MOOD: NO MORE WAR Nye Committee and the “merchants of death” Proposed War Referendum Amendment (Louis Ludlow of Indiana) Neutrality Acts (1935, 1937) No weapons sold to belligerents No Americans on belligerents ships No loans to belligerents 1936 Olympics – Owens wins four golds 1938 – Joe Louis defeats Max Schmeling THE GATHERING STORM: 1938-39 Munich Pact was a disaster 1939 – Soviet-German Non-Aggression Pact After Czechoslovakia falls All action “short of war” Asks Hitler and Mussolini not to invade any more FDR asks Congress for $300 million in military appropriations 20,000 plans in the Army Air Corps 1939 budget - $1.3 billion for defense AMERICA AND THE JEWISH REFUGEES Nuremberg Laws of 1935 Outlaws marriage and sexual intercourse between Jews and non-Jews Jews stripped of German citizenship Restrictions on Jews in education, social, and political life 1938 – Kristallnacht Refugees – Though many came and benefited the U.S. in the field of science many were turned away St. Louis was turned back THE EUROPEAN WAR Germany demanded the Danzig and the Polish Corridor Invaded Poland FDR did not ask Americans to be impartial in thought or deed Amending of the Neutrality Acts Cash and Carry FROM ISOLATION TO INTERVENTION FDR wins reelection Appoints republicans as Sec. of War (Henry Stimson) and Sec. of Navy (Frank Knox) Signs the Selective Service and Training Act – America’s first peacetime draft Bases for Destroyers deal with Britain Lend Lease Program approved (even to USSR) America creates a “great arsenal of democracy” US convoys assist the British in the Atlantic Atlantic Charter and the “Four Freedoms” and the post war goals Reuben James and the arming of merchant ships and their entry to belligerent ports in war zones http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DrZjJsIA1EI PEARL HARBOR AND THE COMING OF WAR Japan seeks a Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere U.S. attitudes towards the Japanese – years of the “yellow peril” U.S. bans the sale of aviation fuel and scrap metal to the Japanese The Dutch and French can’t hold on to there Asian possessions U.S. freezes Japanese assets and places an all-out trade embargo on Japan Dec. 7, 1941 20 ships; 350 aircraft 2,400+ dead; 1,200 wounded The awakening of a sleeping giant http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3e99lfmmDN0 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mQm_I3GpaGM ORGANIZING FOR VICTORY FDR forms the Joint Chiefs of Staff Office of Strategic Services is created War Production Board allocates materials, limits production and distributes contracts War Manpower Commission supervises the mobilization of men and women National War Labor Board mediates disputes Office of Price Administration rations scare product and imposes price controls Office of War Mobilization coordinates the production, procurement, transportation and distribution of civilian and military supplies Industry conversions and new technologies Auto manufacturers make tanks 50 new synthetic rubber plants are created Alliance between the defense industry and the military 10 biggest companies got a third of the war contracts Dr. New Deal becomes Dr. Win the War THE WAR ECONOMY U.S. spent $320 billion to defeat the Axis Powers (10x more than in WWI) 17 million new jobs; increased corporate after-tax profits by 70%; raised purchasing power of industrial workers by 50% $40 billion went to the West (California got 10% of the funds) South’s industrial capacity increased by 40% Middle-class nation was emerging Factories hired the deaf and dwarfs Large-scale commercial farmers prospered due to higher consumer prices and increased productivity Labor union membership leaped from 9 million to almost 15 million in five years NWLB’s “maintenance-of –membership” rule Only a tiny minority of workers broke the no strike rule – wildcat strikes The Smith-Connally War Labor Disputes Act of 1943 allowed the President to take over any facility where strikes interrupted the war effort OPA institutes rationing Revenue Act of 1942 raised top income tax rate from 60 to 94% and imposed taxes on the middle class and lower income Americans for the first time In 1943 payroll deductions automatically withheld taxes from wages and salaries A WIZARD WAR The importance of wartime scientific and technological development Office of Scientific Research and Development (OSRD) – spent $1 billion to generate sonar and radar devices, rocket weapons, and bomb fuses: helps create lasers, transistors and semiconductors Earliest computers are created: Mark I and ENIAC Improvements in blood transfusions, heart and lung surgeries, and synthetic drugs; antibiotics produced like crazy MASH units Manhattan Project – University of Chicago; Oak Ridge, TN; Hanford, WA; Los Alamos, NM Used 120,000 people and $2 billion July 16, 1945 – it works! PROPAGANDA AND POLITICS Office of Censorship – examined letters A year passed before death and damage figures were released concerning Pearl Harbor Govt. banned publication of photographs of American war dead until 1943 Office of War Information (OWI) – employed artists, writers and advertising specialists to promote the war