File - Ms. Diggs' Honors US History
advertisement
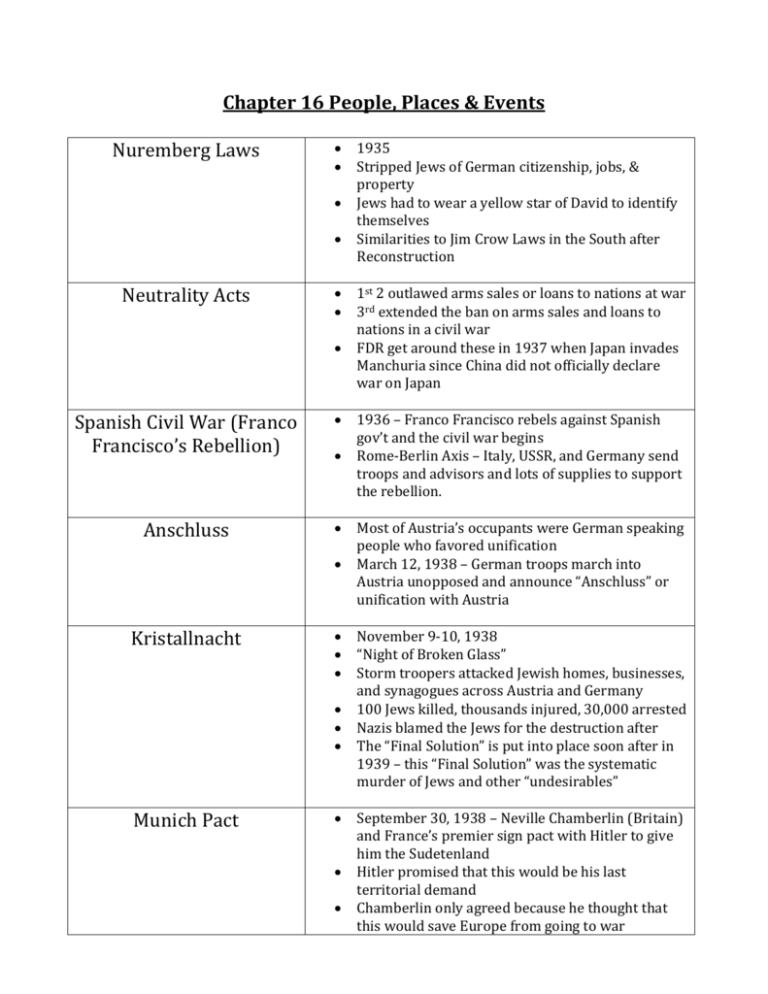
Chapter 16 People, Places & Events Nuremberg Laws Neutrality Acts Spanish Civil War (Franco Francisco’s Rebellion) Anschluss Kristallnacht Munich Pact 1935 Stripped Jews of German citizenship, jobs, & property Jews had to wear a yellow star of David to identify themselves Similarities to Jim Crow Laws in the South after Reconstruction 1st 2 outlawed arms sales or loans to nations at war 3rd extended the ban on arms sales and loans to nations in a civil war FDR get around these in 1937 when Japan invades Manchuria since China did not officially declare war on Japan 1936 – Franco Francisco rebels against Spanish gov’t and the civil war begins Rome-Berlin Axis – Italy, USSR, and Germany send troops and advisors and lots of supplies to support the rebellion. Most of Austria’s occupants were German speaking people who favored unification March 12, 1938 – German troops march into Austria unopposed and announce “Anschluss” or unification with Austria November 9-10, 1938 “Night of Broken Glass” Storm troopers attacked Jewish homes, businesses, and synagogues across Austria and Germany 100 Jews killed, thousands injured, 30,000 arrested Nazis blamed the Jews for the destruction after The “Final Solution” is put into place soon after in 1939 – this “Final Solution” was the systematic murder of Jews and other “undesirables” September 30, 1938 – Neville Chamberlin (Britain) and France’s premier sign pact with Hitler to give him the Sudetenland Hitler promised that this would be his last territorial demand Chamberlin only agreed because he thought that this would save Europe from going to war Nonaggression Pact Blitzkrieg Cash Carry Provision The Ardennes Vichy Government The British were happy but Churchill thought war was inevitable and the pact was dishonorable Broke pact on March 15, 1939 – invaded Czechoslovakia Between USSR and Germany on August 23, 1939 USSR said that they would not interfere with Germany’s invasion of Poland Spilt Poland between the two of them Said they would not fight one another Danger of 2 front war is eliminated for Germany Strategy used when Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939 “Lightning War” – take enemy by surprise and and quickly crush all opposition with overwhelming force Two days later France and G.B. declare war on Germany Major fighting in Poland was over within a couple weeks, though. GB and France couldn’t mobilize in time to help. September 1939 Warring nations can buy arms with cash as long as they use their own ships to transport the goods French – Maignot Line / German – Siegfried Line “Phony War” – both sitting waiting for something to happen April 9, 1940 – Hitler starts surprise attack on France through the forest French soldiers fled across the English channel Italy attacks France from the South at the same time June 22, 1940 – The French surrender The Vichy government, which is a Nazi controlled puppet government, is set up in the South and the North is occupied by the Nazis (both which were terms in Hitler’s surrender agreement with the French) Charles de Gaulle flees to England and sets up a government in exile for the French Battle of Britain Tripartite Act Lend Lease Act Summer 1940 2,600 German planes at Hitler’s disposal London is bombed consistently for 2 months The British Royal Air Force (RAF) fight back and use new technology (radar) in order to win the battle Because of the time and supplies lost, Hitler gives up on conquering Great Britain September 27, 1940 Italy, Germany, and Japan all form a formal alliance Officially become the Axis powers This was done to keep the United States out of the war If the US declared war on any of the 3 countries then the other two would automatically declare war on the US, so the US would immediately begin fighting a two-front war March 1941 Great Britain has no more cash to give the US for supplies under the Cash/Carry provision Congress puts into effect the Lend Lease Act which allows the US to lend and lease arms and supplies to countries whose “defense was vital to the United State’s” FDR said that it was like “lending a garden hose to a neighbor whose house is on fire” Soon after this act was put into place Hitler goes back on the nonaggression pact and attacks the Soviet Union FDR starts lending to the USSR because of this Selective Training & Service Act Wolf Packs Hitler send submarines or U-boats to patrol the Atlantic so that Lend/Lease ships could not get to the USSR or Great Britain As many as 40 U-boats would patrol at a time, these large numbers of submarines all patrolling at the same time were called “wolfpacks” Congress boosts defense spending and institutes the first peacetime military draft Men 21-35 were registered Atlantic Charter June 1941 – FDR says that US ships are allowed to attack U-boats in self defense 350,000 tons of supplies could be gone in a months time Finally with the use of radar and air attacks the wolf packs were under control in 1943 Roosevelt and Churchill’s secret meeting Churchill tried to convince FDR to go to Congress and try to get them to declare war FDR said that he could not do that since there had been no attack on the US Did agree that “security, disarmament, selfdetermination, economic cooperation, and freedom of the seas” were all in both of the countries’ best interest These mutual factors all became the blue print for the “United Nations” or Allies (which included 26 different nations) and was signed soon after Tojo (Japanese dictator) begins taking over French bases in Indochina (Vietnam, Cambodia, & Laos) U.S. cuts trade with Japan in order to show disapproval of these acts (this trade cut also cuts oil which the Japanese need desperately) Because the Japanese need oil so badly, peace talks between the Japanese and US begin On Nov. 5, 1941 the US deciphers a message that Tojo had sent to his men that told the navy to prepare an attack of the US Peace talks continue through the month, but FDR warns generals On Dec. 6, 1941 the US deciphers a message from Tojo to his men to reject all peace proposals from the US Early on Dec. 7, 1941 the Japanese attack Pearl Harbor, kill over 2,000 men, and destroy much of the United State’s navy On Dec. 8 the US declares war on Japan with full isolationist support Italy and Germany declare war on the US a few days later Pearl Harbor











