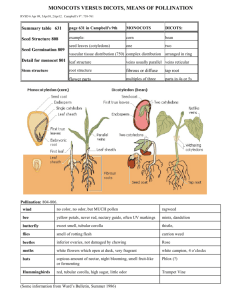
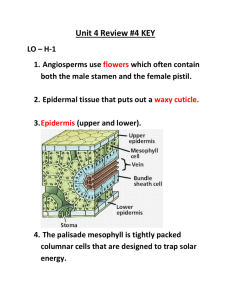
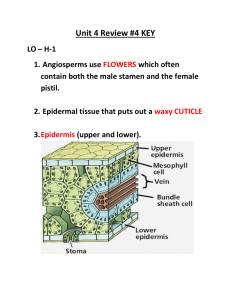
carry out photosynthesis
advertisement

Plant Overview and Reproduction Pre-AP Biology What Is a Plant? • Members of the kingdom Plantae • Plants are multicellular eukaryotes • Plants have cell walls made of cellulose. • Plants develop from multicellular embryos and carry out photosynthesis using the green pigments chlorophyll a and b 2 Overview of the Plant Kingdom • Botanists divide the plant kingdom into four groups based on three important features: 1. Water conducting tissues 2. Seeds 3. Flowers 3 4 5 The Plant Life Cycle • Characterized by alternation of generations: the two generations are the haploid (N) gametophyte, or gameteproducing plant, and the diploid (2N) sporophyte, or spore-producing plant. 6 7 Monocots and Dicots • Monocots and dicots are named for the number of seed leaves, or cotyledons, in the plant embryo. Monocots have one seed leaf, and dicots have two seed leafs 8 9 Reproduction of Seed Plants Chapters 24 Life Cycle of Gymnosperms • Reproduction in gymnosperms takes place in cones • Male cones produce – pollen grains • Female cones produce – ovules Flowers and Fruits • Angiosperms have unique reproductive organs known as flowers. Q: Why are flowers evolutionary adaptations? A: they attract animals that pollinate them 14 15 Structure of Flowers • Flowers are reproductive organs that are composed of 4 kinds of specialized leaves Sepals • Enclose the bud before it opens, leaf-like Petals • Brightly colored, attract insects to flower Stamen • Male reproductive structure of flower, made of 2 parts • Filament – long, thin, stalk that supports the anther • Anther – makes pollen grains Anther Filament Anther + Filament = Stamen Pistil • Female reproductive structure, made of 3 parts Stigma • where pollen grains land, sticky Style • Connects stigma to ovary Style Ovary • swollen base of the pistil where ovules are formed • Flowers contain ovaries, which surround and protect the seeds • After pollination, the ovary develops into a fruit, which protects the seed and aids in its dispersal. 28 Fruit • Ripened ovary, thick wall of tissue that surrounds the seed 29 Pollen Pollen Grain • Contains the male gamete 31 Pollination • The transfer of pollen from the male gametophyte to the female gametophyte 32 Seeds • An embryo of a plant that is encased in a protective covering and surrounded by a food supply 33 Embryo • Early development stage of a sporophyte plant • The seed’s food supply provides nutrients to the embryo as it grows 34 Seed Coat • Surrounds and protects the embryo and keeps the contents of the seed from drying out • Can be specialized for dispersal 35 36 Pollination • Most gymnosperms (some angiosperms) are wind pollinated • Most angiosperms are pollinated by animals • Insect pollination beneficial to insects and other animals: provides them with food • Plants also benefit: this method of pollination is more efficient Seed Dispersal • Animals • Wind and water Ultraviolet Flowers http://www.naturfotograf.com/UV_flowers_list.html