Solutions for Problem Set #2
advertisement
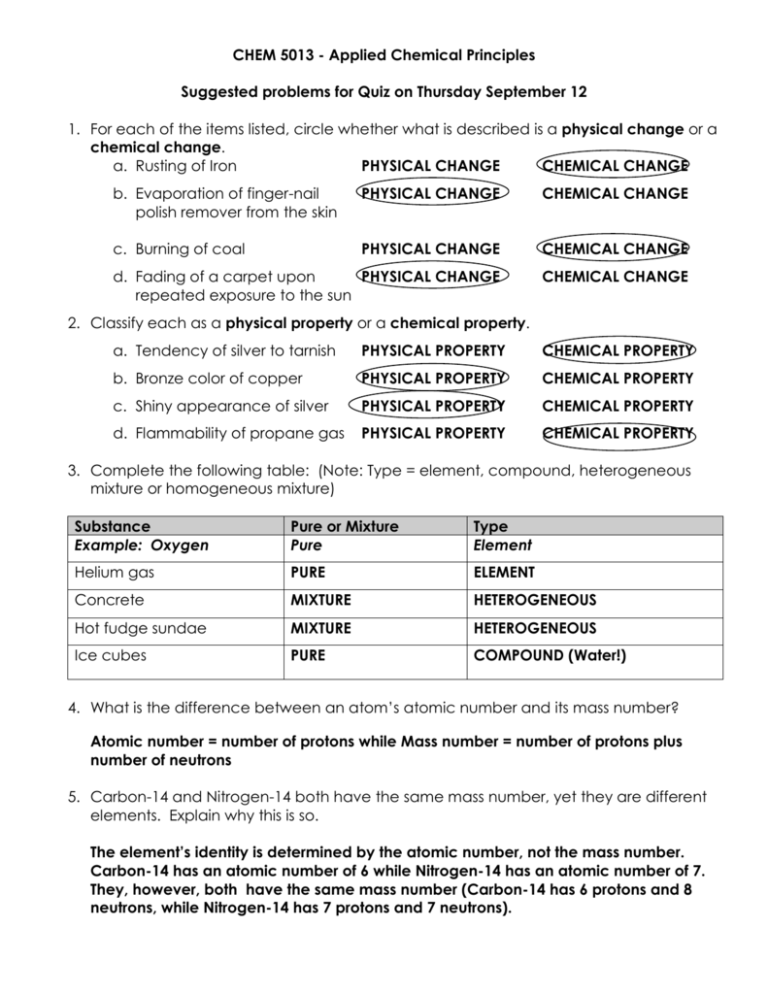
CHEM 5013 - Applied Chemical Principles Suggested problems for Quiz on Thursday September 12 1. For each of the items listed, circle whether what is described is a physical change or a chemical change. a. Rusting of Iron PHYSICAL CHANGE CHEMICAL CHANGE b. Evaporation of finger-nail polish remover from the skin PHYSICAL CHANGE CHEMICAL CHANGE c. Burning of coal PHYSICAL CHANGE CHEMICAL CHANGE d. Fading of a carpet upon PHYSICAL CHANGE repeated exposure to the sun CHEMICAL CHANGE 2. Classify each as a physical property or a chemical property. a. Tendency of silver to tarnish PHYSICAL PROPERTY CHEMICAL PROPERTY b. Bronze color of copper PHYSICAL PROPERTY CHEMICAL PROPERTY c. Shiny appearance of silver PHYSICAL PROPERTY CHEMICAL PROPERTY d. Flammability of propane gas PHYSICAL PROPERTY CHEMICAL PROPERTY 3. Complete the following table: (Note: Type = element, compound, heterogeneous mixture or homogeneous mixture) Substance Example: Oxygen Pure or Mixture Pure Type Element Helium gas PURE ELEMENT Concrete MIXTURE HETEROGENEOUS Hot fudge sundae MIXTURE HETEROGENEOUS Ice cubes PURE COMPOUND (Water!) 4. What is the difference between an atom’s atomic number and its mass number? Atomic number = number of protons while Mass number = number of protons plus number of neutrons 5. Carbon-14 and Nitrogen-14 both have the same mass number, yet they are different elements. Explain why this is so. The element’s identity is determined by the atomic number, not the mass number. Carbon-14 has an atomic number of 6 while Nitrogen-14 has an atomic number of 7. They, however, both have the same mass number (Carbon-14 has 6 protons and 8 neutrons, while Nitrogen-14 has 7 protons and 7 neutrons). 6. Provide the complete name for each of the following elements: a. Na b. Fe Sodium Iron c. S d. Cu Sulfur Copper 7. Provide the atomic symbol for each of the following elements: a. Helium b. Nitrogen He N c. Chlorine d. Phosphorus Cl P e. Mercury f. Gold Hg Au 8. Write the complete atomic symbol (nuclide symbol) for each of the following isotopes: a. Carbon -13 c. Sodium – 23 13C 23Na 6 11 9. Complete the following table: # protons # neutrons Aluminum-27 13 14 Mg 2+ ion # electrons 13 Overall Charge Neutral (0) 12 12 10 +2 Iron - 56 26 30 22 +4 Zirconium - 91 40 51 40 Neutral (0) 24 12 10. Identify the following elements by providing the FULL NAME of each: a. 24 X Magnesium b. 12 c. 104 X 46 58 X Nickel 28 Palladium d. 183 X Tungsten 74 11. The atomic mass of silver is 107.87 amu. There are only two isotopes of silver, 107Ag with an isotopic mass of 106.91 amu and 109Ag with an isotopic mass of 108.90 amu. Calculate the fractional abundance of each of the two isotopes of silver. 107.87 = 106.91(x) + 108.90(y) and x+y=1 or y=1-x 107Ag = 107.87 = 106.91(x) + 108.90(1-x) 0.518 (51.8%) 107.87 = 106.91(x) + 108.90 – 108.90 x 109Ag = -1.03 = -1.99 x 0.482 (48.2%) X = -1.03/-1.99 = 0.518 and y = 1-x = 1-.518 = 0.482 And X is the fractional abundance of Ag-107 while y is the frac. abund. Of Ag-109 12. The following table represents the percent abundances of the naturally occurring isotopes of an element. Isotopic mass (amu) Percent Abundance 23.985 78.99% 24.986 10.00% 25.982 11.01% a) Calculate the atomic mass of this element (23.985 x 0.7899) + (24.986 x .1000) + (25.982 x .1101) = 18.95 + 2.499 + 2.861 = 24.31 amu b) What is the identity of this element? (provide the full name) Name: Magnesium