THE EYE
advertisement

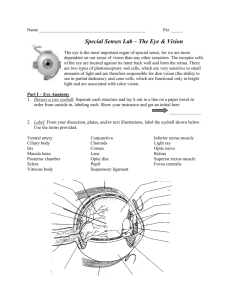
THE EYE CHAPTER 8 PAGES 272-284 COLOR CODE – PLATE 137 Sclera – orange fovea centralis – light green Cornea – green optic disc - tan Choroid – brown posterior chamber - peach Iris – blue Retina – purple Vitreous body – light blue Aqueous humor – yellow Lens – gray Pupil – black Conjunctiva – pink Optic nerve - red COLOR CODE – PLATE 139 Superior rectus – red Inferior rectus – pink Lateral rectus – blue Medial rectus – light blue Superior oblique – green Inferior oblique – light green Ciliary – orange Sphincter pupillae – yellow Dilator pupillae – peach Visual object – aqua Light waves - gray Retina – purple Optic nerve – brown Visual cortex - tan I. PARTS OF THE EYE (page 275/276) Sclerotic layer (sclera) 1. white, tough, outer layer 2. functions: provides shape of eyeball protection B. Choroid layer 1. contains blood vessels 2. function: nourishing eyeball A. C. Retina 1. inner layer 2. contains specialized cells that function in forming the image a. rods – sensitive to dim light form a shaded image b. cones – sensitive to bright light responsible for color vision D. Fovea 1. focal point of the retina 2. vision is clearest at this point 3. where cones are > #ous E. Optic Nerve 1. connects eyeball to brain 2. carries nerve messages to/from the brain 3. controls vision F. Blind Spot (pg.277) 1. where optic nerve joins the eyeball 2. where retina lacks rods & cones 3. no vision @ this point G. Cornea 1. clear bulge of the sclerotic layer 2. in front portion of eyeball 3. clear, to allow passage of light rays H. Iris 1. colored portion of eyeball 2. posterior to cornea 3. regulates the amt. of light entering the eye I. Pupil 1. opening in the iris 2. allows light to pass on to the retina 3. changes shape to optimize amt. of light a. dilates – gets larger in dim light b. constricts – gets smaller in bright light 4. must adjust when changing from dim to bright light and vise-versa J. Lens (pg. 280) 1. a convex, crystalline (glassy) structure 2. posterior to the pupil & iris 3. focuses light rays on the retina 4. changes thickness when focusing close vs. @ a distance K. Ligaments 1. attaches lens to muscles wh/ support the lens 2. regulates the shape of the lens from thin to flat in order to view objects close & @ a distance L. Aqueous humor 1. H2O-y fluid b/t cornea & iris 2. helps to maintain shape of cornea M. Vitreous humor 1. jelly-like substance in the inner part of the eyeball 2. maintains shape of the entire eyeball N. Lacrimal glands 1. located on the inner lining of the eyeball 2. secretes tear fluid wh/ moisten & washes the eyeball O. Eyelids protect & moisten eyeball P. Conjunctiva 1. lines the eyelids & covers part of outer surface of the eyeball 2. secretes mucus wh/ helps to lubricate eyeball & keep it moist II. Diseases/Conditions . . . . . . . . A. color blindness 1. lack of 1 or more types of cones 2. lack of 1 type partial color blindness 3. lack of all 3 types total color bldnss. 4. sex-linked trait almost exclusively in males B. conjunctivitis 1. commonly called pinkeye 2. inflammation of the conjunctiva 3. causes red, irritated, itchy eyes 4. highly contagious (bacterial/viral) C. cataracts 1. lens b/c hard & opaque 2. causes vision to be hazy blindness 3. treatments: a. surgical removal of lens & replacement w/ lens implant b. special cataract glasses c. laser surgery to remove hardened area of lens D. Glaucoma 1. pressure w/i the eye increases dramatically due to blocked drainage of aqueous humor 2. compresses retina & optic nerve 3. causes pain & possible blindness 4. symptoms: a. seeing halos around lights b. headaches c. blurred vision 5. treatments: a. eyedrops wh/ increase drainage rate b. surgical enlargement of drainage channel