Sheep Eye Dissection Lab
advertisement

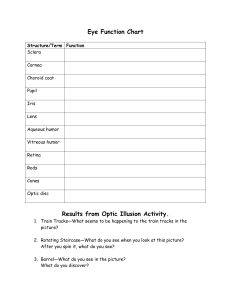
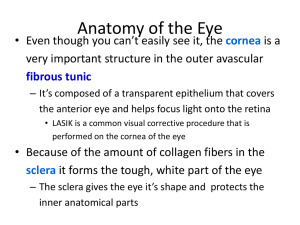
Heading Sheep Eye Dissection Lab Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to dissect a sheep eye, which is similar to the eyes of all mammals including humans, to gain a better understanding of the structure and function of the parts of the eye. Hypothesis: Materials: Procedure: 1. Locate these external structures and record your observations in the results section. Optic nerve Sclera Cornea Iris Pupil Muscles Fat Eyelids 2. Have the eye facing up towards you. Puncture the sclera with the tip of your scissors (or a scalpel) about 1cm outside the edge of the iris. 3. Being careful not to squeeze the liquid out of the eye, use the scissors to cut a circle around the eye, staying 1 cm from the iris. Pull the cut portion away from the sclera and lay it face down on your tray. 4. Carefully remove the lens and the vitreous and aqueous humors from the eye, notice the difference between the aqueous and the vitreous humor. 5. Examine the lens carefully. Attached to it are the fine ciliary muscle fibers that controlled the shape of the lens. In a fresh or living eye the lens would be clear, but once preserved they become cloudy. Using your probe and forceps to gently lift and work around the edges of the lens. 6. Next examine the back portion of the eye. You will see a thin, wrinkled white layer of tissue that is the retina. It will be attached to the optic nerve at the blind spot. Use your forceps and scissors to cut away the retina. 7. At the very back of the eye is a bluish layer called the tapetum. This layer is a reflective surface found only in some animals with good night vision. Heading 8. Identify these internal structures and record your observations in the results section. Vitreous humor Aqueous humor Iris Pupil Lens Ciliary muscles Retina Blind spot Tapetum 9. Dispose of all materials according to the teacher’s directions and clean your work area. Results: External Observations What does it look like? What is its function? Optic Nerve Sclera Cornea Iria Pupil Muscles Fat Eyelids Internal Observations What does it look like? Vitreous humor What is its function? Heading Aqueous humor Iris Pupil Lens Ciliary Muscles Retina Blind Spot Tapetum Analysis Questions: 1. What parts were easy to locate and which were difficult to identify? 2. Number these in the order in which light passes through them to form an image inside the eye. ______ cornea ______ lens ______ optic nerve ______ pupil ______ retina ______ vitreous humor ______ aqueous humor 3. Describe the path light travels through the eye to reach the brain. 4. Where are the photoreceptors found in the eye? 5. What are the two types of photo receptors? 6. What surprised you most about this dissection?