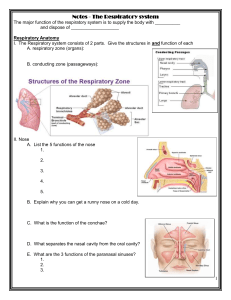
Respiratory System: Functions, Organs, and Cellular Respiration
advertisement

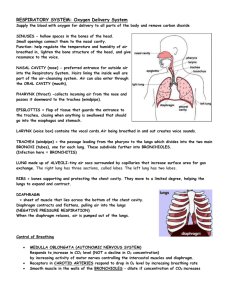
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM WHAT IS CELLULAR RESPIRATION? • Cellular respiration is a chemical reaction that happens in all cells. • It uses glucose (sugar) and oxygen to release energy for the cell. • The cell uses the energy to grow and reproduce. • The chemical equation for this reaction is… C6H12O6 + 6O2 = 6H2O + 6CO2 + energy CELLULAR RESPIRATION AND THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM • How do cells get the oxygen they need to carry out cellular respiration? – The respiratory and circulatory systems! • How do cells get rid of the carbon dioxide waste gas that results from cellular respiration? – The respiratory and circulatory systems! WHAT ARE THE FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM? • Brings in the oxygen needed for the chemical reaction called cellular respiration • Removes the carbon dioxide waste gas that results from the reaction • Allows for speech ORGAN SYSTEM - Respiratory System ORGANS • Lungs (Main Organs) • Nose and Nasal Cavity • Pharynx • Larynx • Trachea • Bronchi • Alveoli • Diaphragm TISSUES • Epithelial Tissue – Makes mucous – Has Cilia • Cartilage • Connective Tissue • Smooth Muscle Tissue CELLS • Epithelial Cells • Sensory Receptor Cells (in the nose) • Smooth Muscle cells • Pneumocytes Nose and Nasal Cavity • Receives odors, sense organ • Warms and moistens incoming air • Filters air through hairs and traps dust in mucus-lined passageways Pharynx • Region at back of mouth • Passage-way for air and food Larynx • Voice box or Adam’s apple • Contains vocal cords – elastic ligaments along the edge of larynx that vibrate to produce sound • Watch! • http://tinyurl.com /2a765hk Trachea Cilia • Windpipe • Muscular tube that acts as a passage way leading from larynx to lungs • Held open by Cshaped cartilage rings • Walls inside are lined with cilia to move mucus Bronchi • Two tubes leading from the trachea • One leads to each lung • Bring air to and from lungs Lungs – External • Right lung larger – 3 lobed • Left lung smaller – 2 lobed • Thin pleural membrane protects and covers surface Lungs - Internal • Bronchioles – tiny tubes that branch throughout lung • End in small sacs called alveoli- the site of gas exchange – Oxygen leaves air sacs and enters bloodstream – Carbon dioxide leaves bloodstream and enters lungs SPECIAL STRUCTURES ALVEOLI Diaphragm The flat muscle beneath the lungs that contracts and relaxes to help move oxygen into the lungs and carbon dioxide out of the lungs THE PATH OF AIR • WATCH THIS! http://www.lung.org/your-lungs/howlungs-work/ INTERACTIONS WITH OTHER BODY SYSTEMS • The respiratory system interacts with the circulatory system because blood carries oxygen gas needed by all cells from the lungs to the rest of the body. When cells use the oxygen and glucose in the mitochondria to release energy, the waste gas carbon dioxide is produced. The blood carries the waste gas to the heart where it is pumped to the lungs and is exchanged for oxygen. This circulation between the heart and lungs is called pulmonary circulation. INTERACTIONS WITH OTHER BODY SYSTEMS • The respiratory system interacts with the muscular system because the process of bringing air into the lungs or inhalation and the process of sending carbon dioxide out of the lungs or exhalation is controlled by an involuntary, smooth muscle called the diaphragm. INHALING AND EXHALING INHALE = CONTRACTING MUSCLES EXHALE = RELAXED MUSCLES INHALING AND EXHALING • During inhalation, the muscles surrounding the rib cage that protects the lungs contract and enlarge the chest cavity. At the same time, the diaphragm contracts and flattens out, also increasing the volume of the chest cavity. Air rushes in to fill the increased volume. • During exhalation, the muscles in the rib cage and the diaphragm relax, decreasing the volume of the chest cavity and forcing air out. Thought Question • What is the main function of the respiratory system? – To bring oxygen into the body that can be delivered by the blood to the body cells Thought Question • What is the difference between respiration and cellular respiration? – Respiration is the exchange of gases (oxygen and carbon dioxide) between the body’s cells and the external environment – Cellular respiration is the process used by the body cells for gaining energy through the burning of glucose (C6H12O6) in the presence of oxygen (this is why we need to breath in oxygen) Thought Question • What is the function of the diaphragm? – Functions in breathing – During inhalation, the diaphragm contracts and moves down which creates more space in the thoracic cavity (chest). This creates low pressure inside the cavity and high pressure outside the cavity and air rushes from high pressure (outside body) to the low pressure (inside the body) – During exhalation, the diaphragm relaxes and moves up which creates high pressure inside the chest and causes air to rush out of the body. Thought Question • How do freshwater and marine organisms get their oxygen? – Oxygen is dissolved into water in the form of very tiny bubbles. When organisms with gills like fish breathe, they constantly move water through their gills and tiny capillaries in the gills absorb the tiny dissolved oxygen bubbles into their circulatory systems Thought Question • What organ do marine organisms have as an adaptation rather than lungs? – Gills Thought Question • What cell organelle corresponds most closely to the respiratory system? – The cell membrane is semi-permeable and allows some materials to flow into and out of the cell. The membrane does allow oxygen from the blood into the cell and waste gas (carbon dioxide) to leave the cell and enter the blood. Thought Question • What are some common respiratory disorders? – Respiratory infections (colds, flu) – Pneumonia – Chronic bronchitis – Emphysema – Lung cancer – Asthma Respiratory Disorders Cancerous Lung Name the Organs 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Nose, nasal cavity Mouth Larynx Lung Bronchi Diaphragm Pharynx Trachea Bronchi Bronchiole Alveoli