CYP2C19 - PGXL Laboratories
advertisement

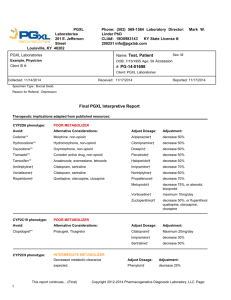
Cardiology Panels Kristen K. Reynolds, PhD VP Laboratory Operations Copyright 2010 PGXL Laboratories, Louisville KY All materials herein are the exclusive property of PGXL Laboratories Panels* Core: Cardio Panel Add-Ons: Thromobophilia: CYP2D6 CYP2C9 CYP2C19 CYP3A4 CYP3A5 CYP1A2 VKORC1 (warfarin) SLCO1B1 (statins) FVL FII MTHFR *All genes always orderable a la carte Cardiology Med List CARDIOLOGY Anti-Arrhythmics, Anti-Hypertensives Amlodipine Norvasc Carvedilol Coreg Diltiazem Cardizem Felodipine Plendil Flecainide Tambocor Lercanidipine Zanidip Losartan Cozaar Metoprolol Toprol-XL Nifedipine Adalat Nisoldipine Sular Nitrendipine Various brands Propafenone Rythmol Propanolol Inderal, various Quinidine Various brands Timolol Blocadren Verapamil Various brands CYP3A4/CYP3A5 CYP2D6 CYP3A4/CYP3A5 CYP3A4/CYP3A5 CYP2D6 CYP3A4/CYP3A5 CYP2C9 CYP2D6 CYP3A4/CYP3A5 CYP3A4/CYP3A5 CYP3A4/CYP3A5 CYP2D6 CYP2D6 CYP3A4/CYP3A5 CYP2D6 CYP3A4/CYP3A5 Antithrombotics Clopidogrel** Rivaroxaban Ticareglor Warfarin Plavix Xarelto Brilinta Coumadin CYP2C19 CYP3A4/CYP3A5 CYP3A4/CYP3A5 CYP2C9 Lipitor, Caduet Lescol Mevacor, Advicor Compactin Crestor Zocor, Vytorin, Simcor CYP3A4/CYP3A5 CYP2C9 CYP3A4/CYP3A5 CYP3A4/CYP3A5 CYP2C9 CYP3A4/CYP3A5 Statins Atorvastatin Fluvastatin Lovastatin Mevastatin Rosuvastatin Simvastatin **indicates prodrug CAD/Stents/TIA: Plavix (2C19) Afib/Valve: Warfarin (2C9+VKORC1) DVT/MI/Ischemic Stroke: thromobophilia risk (FVL, FII, MTHFR) Hypertension/Arrhythmia: Beta blockers, Ca Ch Blockers, ARBs (2D6, 2C9, 3A4/5) Hyperlipidemia: Statins (CYP2C9, CYP3A4, CYP3A5, SLCO1B1) Multi-drug use/ADR/Non-response: 2D6, 2C19, 2C9, VKORC1, 3A4, 3A5, 1A2, SLCO1B1 Genotype Frequency % Gene EM IM PM UM 2D6 53 35 10 2 2C19 36 32 4 28 2C9 57 40 3 NA 3A4 87 12 1 NA 3A5 1 18 81 NA The Problem Reynolds et al. Pers Med 2007;4(1):11-31. 40% 2C9 deficient >70% VKOR sensitivity variant Reynolds et al. Pers Med 2007;4(1):11-31. n i r a . 0 2 . 4 1 . 8 W 0 0 1 . 2 0 0 . 6 0 0 . 0 0 a 3 - r f Warfarin Genotyping C Y P 2 C 9 C Y P 2 C 9 * C Y P 2 C 9 * S CYP2C9 sets the rate, affects time to SS 0 (accumulation and elimination) 0 3 6 9 1 21 T 51 i 82 m 0.8 (predicts warfarin sensitivity) 0.6 42 e 73 ( 6.7 ± 3.3 mg 0.7 S-warfarin VKORC1 sets the target concentration 12 4.2 ± 2.2 mg 2.7 ± 1.2 mg 0.5 0.4 0.3 A/A A/G VKORC1 G/G 0 d a y Warfarin Genotyping Guides dose selection –Estimates Maintenance Dose Requirement Guides optimal INR interpretation –Estimates Time to Reach Steady-State CYP2C9 *2/*3 CYP2C9 Phenotype Poor Metabolizer THERAPEUTIC IMPLICATIONS (adapted from published resources) Decreased metabolic clearance expected. Adjust Dosage Adjustment Phenytoin† decrease 50% Adjust based on multiple factors Warfarin† VKORC1 GA VKORC1 Phenotype THERAPEUTIC IMPLICATIONS (adapted from published resources) Intermediate Average VKORC1 enzyme expression and average warfarin dose requirement expected. warfarin sensitivity WARFARIN DOSE INFORMATION Estimated time to steady-state: Delayed, 16-22 days Estimated warfarin maintenance dose requirement: 3.9 mg/day‡ _ CYP2C9 Poor Metabolizer (PM): This patient’s genotype is consistent with significantly reduced CYP2C9 enzymatic activity. Reduced CYP2C9 activity leads to lower dose requirement (e.g., warfarin) due to decreased clearance, increased elimination half-life, and increased time to reach steady-state blood concentrations. VKORC1 Intermediate Warfarin Sensitivity: ‡The warfarin maintenance dose estimate was derived using a published formula that accounts for age, gender, weight, and CYP2C9 and VKORC1 genotypes. This estimate should be viewed as an example of how this information can be taken into consideration by the physician as part of the overall patient management strategy. CONFIDENTIAL COPYRIGHT PGXL LABORATORIES 2012 CYP2C9 Celecoxib Celebrex Ibuprofen Advil, Motrin Naproxen Aleve Glyburide Diabeta Glipizide Glucotrol Tolbutamide Orinase Glimepiride Amaryl Phenytoin Dilantin Fluvastatin Lescol Rosuvastatin Crestor Losartan Cozaar CONFIDENTIAL COPYRIGHT PGXL LABORATORIES 2012 Anti-platelet therapy CYP2C19 - Plavix Clopidogrel (Plavix) is a PRODRUG Active metabolite elicits the desired antiplatelet response ~ 30% of patients have deficiency in CYP2C19 – Decreased amount of active metabolite – High on-treatment platelet reactivity Influence of CYP2C19 on Clopidogrel Response Incidence of Adverse events in patients prescribed standard dosages of Clopidogrel by CYP2C19 Phenotype. PHENOTYPE Stent Thrombosis EM CV death, MI, Ischemic Stroke 8% (BASELINE) 8.9% 1.4% IM 10% 2.4% PM 12.7% 5.7% Mega et.al., JAMA. 2010;304(16);1821-1830. 0.9% Gene-Dose dependency of therapeutic platelet inhibition Mega et al. JAMA 2011;23/30; 306(20) Cost-effectiveness • Cost model based on event occurrence in TRITON-TIMI 38 Treatment CV Events Bleed Events ICER Genotype guided 813 340 Clopidogrel 1210 380 $ 6,790 $2.9M Prasugrel 990 500 $ 11,710 $3.9M • Genotype-guided therapy selection may be more cost effective and lead to fewer adverse outcomes Reese, E.S. et. al., Pharmacotherapy 2012;32(4):323–332 2C19 CYP2C19 *2/*2 CYP2C19 Phenotype THERAPEUTIC IMPLICATIONS (adapted from published resources) Poor Metabolizer Avoid Clopidogrel** Alternative Consideration Adjust Dosage Adjustment Prasugrel Imipramine† Sertraline† decrease 30% decrease 50% **Lack of efficacy due to failure to produce active metabolite; †Increased risk of adverse events due to diminished drug clearance. CYP2C19 Poor Metabolizer (PM): This patient’s genotype is consistent with significantly reduced CYP2C19 enzymatic activity. PMs are at increased risk of drug-induced side effects due to diminished drug elimination of active drugs. Patients with no CYP2C19 function (PMs) taking clopidogrel lack adequate antiplatelet response and remain at risk for cardiovascular events, including thrombosis, myocardial infarction, stroke, and death. CONFIDENTIAL COPYRIGHT PGXL LABORATORIES 2012 2C19 all RESULTS Gene THERAPEUTIC IMPLICATIONS (adapted from published resources) Phenotype Avoid Alternative Consideration Adjust Dosage Adjustment † Caution, consider 30% Caution, consider 50% † 30% 50% ! CYP2C19 *1/*2 Intermediate Metabolizer Clopidogrel* Prasugrel Imipramine † Sertraline X CYP2C19 *2/*2 Poor Metabolizer Clopidogrel* Prasugrel Imipramine † Sertraline X CYP2C19 *17/*17 Ultra-Rapid Metabolizer Increased metabolic clearance expected. Possible increased risk of bleeding events with clopidogrel. CYP2C19 *1/*1 Extensive Metabolizer Normal metabolic clearance expected. up to 150% Citalopram † up to 150% Escitalopram † 100-200% Omeprazole † 50-100% Esomeprazole † 200% Lansoprazole † 400% Pantoprazole Common CYP2C19 medications next page ! CYP2C19 *2/*17 Or *3/*17 Intermediate ∫ Metabolizer Decreased metabolic clearance expected based on presence of the inactive allele. Imipramine † Sertraline † † Caution, consider 30% Caution, consider 50% CYP2C19 Clopidogrel Citalopram Escitalopram Imipramine Sertraline Diazepam Omeprazole Esomeprazole Pantoprazole Rabeprazole Lansoprazole Nelfinavir Plavix Celexa Lexapro, various Tofranil Zoloft Valium Prilosec Nexium Protonix Aciphex Prevacid Viracept CONFIDENTIAL COPYRIGHT PGXL LABORATORIES 2012 Statin Therapy Statin therapy reduces risk of CV events Statin therapy can lead to muscle weakness – Myalgia – Myopathy – Rhabdomyolysis Genotyping can guide statin choice and dose CYP3A4 and 3A5 Together metabolize 50% of all medications 80% redundancy of function Genetic variants in each – decrease enzyme function (clearance) – Increased risk of dose-dependent adverse events CYP3A4/5 master drug list CYP3A4/CYP3A5 Substrates PSYCHIATRY Benzodiazepines Alprazolam Xanax Midazolam Versed Triazolam Halcion Antipsychotics Quetiapine Seroquel Ziprasidone Geodon Buspirone Buspar Lurasidone Latuda Carbamazepine Various brands Antidepressants Desvenlafaxine Pristiq Vilazodone Viibryd Trazadone Desyrel Nefazadone Serzone Reboxetine Edronax Nortriptyline Pamelor, Aventyl CARDIOLOGY Quinidine Ticareglor Rivaroxaban Statins Atorvastatin Lovastatin Mevastatin Simvastatin Ca Channel Blockers Amlodipine Diltiazem Felodipine Lercanidipine Nifedipine Nisoldipine Nitrendipine Verapamil Various brands Brilinta Xarelto Lipitor, Caduet Mevacor, Advicor Compactin Zocor, Vytorin, Simcor Norvasc Cardizem Plendil Zanidip Adalat Sular Various brands Various brands OTHER Antimicrobials/antivirals Clarithromycin Erythromycin Telithromycin Indinavir Nelfinavir Ritonavir Saquinavir Biaxin E-Mycin Ketek Crixivan Viracept Norvir Fortovase Steroids Estradiol Hydrocortisone Progesterone Testosterone Various brands Various brands Various brands Various brands Chemotherapeutics Vincristine Docetaxel Oncovin Taxotere Pain Management Cyclobenzaprine Fentanyl Alfentanil Flexaril Actiq, Duragesic Alfenta Immunosuppressants Cyclosporine Tacrolimus Gengraf Prograf CYP3A4/5 significant variants CYP3A4*22 – Decreased dose requirements for tacrolimus, cyclosporin, simvastatin, atorvastatin, lovastatin, midazolam – 4-8% frequency CYP3A5*3 – Decreased dose requirements vincristine, tacrolimus, cyclosporin – 90% freq Cauc, 50% AA, 60% Asians 3A4 Interpretation CYP3A4 Phenotype Extensive Metabolizer CYP3A4 Phenotype Partially Decreased Metabolizer CYP3A4 Phenotype Decreased Metabolizer CYP3A4 Phenotype THERAPEUTIC IMPLICATIONS (adapted from published resources) Normal metabolic clearance expected. Common CYP3A4 medications below. THERAPEUTIC IMPLICATIONS (adapted from published resources) Decreased metabolic clearance expected with increased risk of dose-dependent side effects. Common CYP3A4 medications below. THERAPEUTIC IMPLICATIONS (adapted from published resources) Decreased metabolic clearance expected with increased risk of dose-dependent side effects. Common CYP3A4 medications below. THERAPEUTIC IMPLICATIONS (adapted from published resources) Adjust Dosage *22 Decreased metabolic clearance expected Simvastatin Decreased with increased risk of dose-dependent side Atorvastatin Metabolizer effects. Lovastatin Tacrolimus Adjustment max 10-20 mg, or consider alternative statin if also SLCO1B1 *5/*5 genotype max 10-20 mg max 10-20 mg decrease by up to 40% 3A5 Interpretation CYP3A5 Phenotype Extensive Metabolizer CYP3A5 Phenotype Partially Decreased Metabolizer CYP3A5 Phenotype Decreased Metabolizer THERAPEUTIC IMPLICATIONS (adapted from published resources) Genotype consistent with the highest baseline enzymatic activity for CYP3A5. Patients with this genotype represent only 1% of the population. Maintenance dosages for most CYP3A5 drugs may be at the higher end of the typical dose range. Common CYP3A5 medications below. THERAPEUTIC IMPLICATIONS (adapted from published resources) Genotype consistent with intermediate CYP3A5 enzymatic activity and represents approximately 20% of the population. For PDMs, maintenance dosages for most CYP3A5 drugs are lower than extensive metabolizers and are higher than decreased metabolizers. THERAPEUTIC IMPLICATIONS (adapted from published resources) Genotype consistent with reduced CYP3A5 enzymatic activity and represents the majority (60-80%) of the population. For DMs, maintenance dosages for most CYP3A drugs are lower than extensive metabolizers. Common CYP3A5 medications below. SLC01B1 OATP1B1 ~35% of population are carriers of the SLC01B1*5 allele – Myalgia/muscle cramps Myopathy on 40mg/day: – SLCO1B1 *1/*5, OR = 2.6 – SLCO1B1 *5/*5, OR = 5.2 Most frequently associated with simvastatin > atorvastatin > pravastatin Vanderbilt Algorithm Wilke et al. Clin Pharmaco Ther 2012;92(1). Statin Combo Interpretation CYP3A4 Phenotype THERAPEUTIC IMPLICATIONS (adapted from published resources) Adjust Dosage *22 Decreased Decreased metabolic clearance expected with Metabolizer increased risk of dose-dependent side effects. SLCO1B1 Phenotype Simvastatin Atorvastatin Lovastatin Tacrolimus Adjustment max 10-20 mg, or consider alternative statin if also SLCO1B1 *5/*5 genotype max 10-20 mg max 10-20 mg decrease by up to 40% THERAPEUTIC IMPLICATIONS (adapted from published resources) Avoid >5 Fold Increased Simvastatin Myopathy Risk Alternative Consideration pravastatin, lovastatin, fluvastatin, rosuvastatin, mevastatin Adjust Dosage Adjustment Atorvastatin max 10-20 mg Anti-arrhythmics and Anti-hypertensives 3A4: Ca++ Channel Blockers Amlodipine Diltiazem Felodipine Lercanidipine Nifedipine Nisoldipine Nitrendipine Verapamil CYP3A4 Phenotype Extensive Metabolizer CYP3A4 Phenotype Partially Decreased Metabolizer CYP3A4 Phenotype Decreased Metabolizer Norvasc Cardizem Plendil Zanidip Adalat Sular Various brands Various brands THERAPEUTIC IMPLICATIONS (adapted from published resources) Normal metabolic clearance expected. Common CYP3A4 medications below. THERAPEUTIC IMPLICATIONS (adapted from published resources) Decreased metabolic clearance expected with increased risk of dose-dependent side effects. Common CYP3A4 medications below. THERAPEUTIC IMPLICATIONS (adapted from published resources) Decreased metabolic clearance expected with increased risk of dose-dependent side effects. Common CYP3A4 medications below. CYP2D6 CYP2D6 *4/*4 CYP2D6 Phenotype THERAPEUTIC IMPLICATIONS (adapted from published resources) Poor Metabolizer Avoid Codeine** Hydrocodone** Oxycodone** Tramadol** Tamoxifen** Amitriptyline † Venlafaxine † Risperidone † Alternative Consideration Adjust Dosage Adjustment Morphine, non-opioid Hydromorphone, non-opioid Oxymorphone, non-opioid Consider active drug, non-opioid Anastrozole, exemestane, letrozole Citalopram, sertraline Citalopram, sertraline Quetiapine, olanzapine, clozapine Aripiprazole † 10 mg/day maximum decrease 50% decrease 60% decrease 50% decrease 50% decrease 70% decrease 60% decrease 70% decrease 75%, or atenolol, bisoprolol, carvedilol decrease 50%, or flupenthixol, quetiapine, olanzapine, clozapine Clomipramine † Doxepin † Flecainide † Haloperidol † Imipramine† Nortriptyline † Propafenone † Metoprolol † Zuclopenthixol † **Lack of efficacy due to failure to produce active metabolite; †Increased risk of adverse events due to diminished drug clearance. CONFIDENTIAL COPYRIGHT PGXL LABORATORIES 2012 RESULTS Gene X CYP2D6 *4/*4 THERAPEUTIC IMPLICATIONS (adapted from published resources) Phenotype Poor Metabolizer Avoid Codeine* Hydrocodone* Oxycodone* Tramadol* Normal metabolic clearance expected. Adjustment 10 mg/day maximum 50% 60% 50% 50% 70% 60% 70% 75%, or atenolol, bisoprolol, carvedilol † Zuclopenthixol 50%, or flupenthixol, quetiapine, olanzapine, clozapine Common CYP2D6 medications next page Oxycodone* Hydrocodone* † Propafenone Oxymorphone, non-opioid Hydromorphone, non-opioid Sotalol, disopyramide, quinidine, amiodarone Quetiapine, olanzapine, clozapine Citalopram, sertraline Codeine* Tramadol* Tamoxifen* Morphine, non-opioid Hydromorphone, non-opioid Oxymorphone, non-opioid Citalopram, sertraline Citalopram, sertraline Citalopram, sertraline Methylphenidate Quetiapine, olanzapine, clozapine Flupenthixol, quetiapine, olanzapine, clozapine Sotalol, disopyramide, quinidine, amiodarone Tramadol* † Imipramine † Nortriptyline † Venlafaxine Tamoxifen* Amitriptyline † Venlafaxine † Risperidone CYP2D6 *1/*1 ! CYP2D6 *1/*4 Extensive Metabolizer Intermediate Metabolizer Risperidone † † † Velafaxine X CYP2D6 *1/*1xN Ultra-Rapid Metabolizer Codeine* Hydrocodone* Oxycodone* † Amitriptyline † Clomipramine † Paroxetine † Atomoxetine † Risperidone Zuclopenthixol Propafenone † † Alternative Consideration Morphine, non-opioid Hydromorphone, non-opioid Oxymorphone, non-opioid Consider active drug, nonopioid Anastrozole, exemestane, letrozole Citalopram, sertraline Citalopram, sertraline Quetiapine, olanzapine, clozapine Adjust Dosage † Aripiprazole † Clomipramine † Doxepin † Flecainide † Haloperidol † Imipramine † Nortriptyline † Propafenone † Metoprolol † Amitriptyline † Imipramine † Nortriptyline † Zuclopenthixol † Doxepin † Flecainide † Metoprolol Haloperidol † † Doxepin † Metoprolol 15-60 mg/hr titrate to pain relief Avoid CYP2D6 inhibitors, e.g. paroxetine, or consider aromatase inhibitor in postmenopausal women 25% 30% 40% 25% 20% 25% 50%, or atenolol, bisoprolol, carvedilol 30% 70% 60% 150%, or citalopram, sertraline based on plasma measurement, or pimozide, flupenthixol, fluphenazine, quetiapine, olanzapine, clozapine 100% up to 250%, or atenolol, bisoprolol, carvedilol CYP2D6 Pain Management Codeine** Oxycodone** Hydrocodone** Tramadol** Various brands Oxycontin, various Various brands Ultram, various Cardiology Carvedilol Metoprolol Propanolol Timolol Propafenone Flecainide Coreg Toprol-XL Inderal, various Blocadren Rythmol Tambocor Other Loratadine Donepezil Dextromethorphan Tamoxifen** Claritin Aricept Various brands Various brands Psychiatry Antidepressants Fluoxetine Fluvoxamine Paroxetine Venlafaxine Duloxetine Maprotiline Mirtazapine Amitriptyline Clomipramine Desipramine Doxepin Imipramine Nortriptyline Trimipramine Prozac Luvox Paxil Effexor Cymbalta Ludiomil Remeron Various brands Ananfranil Norpramin Sinequan Tofranil Pamelor, Aventyl Surmontil CONFIDENTIAL COPYRIGHT PGXL LABORATORIES 2012 Antipsychotics Haloperidol Risperidone Aripiprazole Zuclopenthixol Perphenazine Thioridazine Iloperidine Chlorpromazine Atomoxetine Amphetamine Haldol Risperidol Abilify Various brands Trilafon Mellaril Fanapt Thorazine Strattera Adderall Thrombophilia panel Thrombophilia Panel • Factor V Leiden • Factor II (prothrombin) • MTHFR X Factor V Leiden AA >9 fold Increased Thrombosis Risk Female, Positive family history of thrombotic events: avoid estrogen-containing oral contraceptives and consider alternative contraceptive (e.g., IUD or progestin-only contraceptive). ! Factor II GA 2-3 fold Increased Thrombosis Risk X MTHFR 677 TT 1298 AA Increased Risk Negative family history of thrombotic events: avoid additional risk factors (e.g., obesity, smoking). Increased risk of hyperhomocysteinemia, coronary artery disease, and thrombosis when folate deficiency is present. Consider folate supplementation. Factor V Leiden High Thrombosis Risk: This genotype result revealed that the patient is homozygous for (has two copies of) the Factor V Leiden (1691 G>A) variant, which has been associated with an increased risk of thromboembolic events. This variant is found in approximately 4% of individuals in the U.S. Presence of the Factor V Leiden variant increases the risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE) by 3-8 fold in heterozygous carriers and >9 fold in homozygous carriers. Factor II Moderate Thrombosis Risk: This genotype result revealed that the patient is heterozygous for (has one copy of) the Factor II (Prothrombin) 20210 G>A variant, which has been associated with an increased risk of thromboembolic events. This variant is found in approximately 2% of individuals in the U.S. Presence of the Factor II 20210G>A variant increases the risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE) by 2-3 fold in heterozygous carriers and >3 fold in homozygous carriers. MTHFR Increased Risk: Presence of the 677 C>T polymorphism of MTHFR leads to decreased MTHFR enzymatic activity and elevated homocysteine. This patient’s genotype is consistent with an increased risk of hyperhomocysteinemia, atherosclerotic heart disease, myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular disease, and venous thrombosis. Additionally, associations between the 677 C>T polymorphism and increased risk for methotrexate toxicity, increased 5-fluorouracil chemosensitivity, and increased risk of fetal neural tube defects in pregnant women have also been reported in states of folate deficiency. Thank You! kreynolds@pgxlab.com