Tissues/Membranes PowerPoint
advertisement

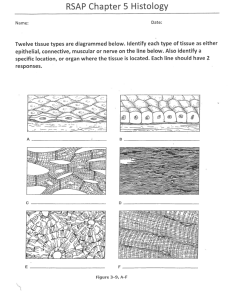
There are four main types of tissues: Epithelial Covers body surfaces and lines inner _____________ Connective Binds and _____________ body parts Muscular ________________ to perform numerous functions Nervous Responds to ______________ and transmits ______________ Functions: Externally, it protects the body from ___________out, injury, and ____________ invasion. Internally, it performs a number of functions, such as ______ ____________ (respiratory tract), ____________ (digestive tract), and absorption (urinary tract) Three main types: Squamous epithelium Locations: walls of _________ vessels, air sacs of ________, lines mouth and ______________, throughout the body Functions: filtration, diffusion of substances, osmosis, friction reduction Cuboidal epithelium Locations: surface of ovaries, lining of glandular ducts, urinary system, eyes, thyroid Functions: ___________ and _____________ Columnar epithelium Locations: reproductive, digestive and respiratory tracts Functions: ______________, absorption, protection Substance? ____________ Name of cell that secretes it? ___________ _______ Described in three ways depending on its layering: Simple – cells exist in a ___________ layer Stratified – cells exist in ____________ layers Pseudostratified – cells ____________ to be layered, but actually _____________ Pseudostratified ciliated A matrix is what makes connective tissue unique. A matrix is a _______________ extracellular substance that surrounds and ______________ cells. The two main components of a matrix are (1) a __________ ________________ and (2) ____________. The ground substance is composed mostly of _______ plus some _____________ and __________________. The fibers are composed mostly of _____________ with some _______________. Matrices vary in consistency from fluid (____________) to squishy (_________) to very hard and tough (____________). Six main types: Loose connective tissue Locations: between muscles, beneath the skin Functions: __________ structures together, fills ____________ between other tissue types, cushions, and protects Adipose connective tissue Locations: beneath the __________, surrounding various organs Functions: ___________ storage, padding for organs, and ________________ Fibrous connective tissue (collagen) Locations: tendons and _________________ Functions: anchors muscles to _________ and bone to ___________ Very __________ tissue Cartilage Three types: hyaline, elastic, fibrocartilage Locations: ends of long _________, nose, rings of ___________, between ribs and sternum, outer ear, pads between ______________ Functions: _____________, protection What is Cartilage? (4:39) Bone Two types: ___________ and _____________ Location: ______________ Functions: _____________, protection, red marrow produces _____________ _________, storage of ______________ salts (Ca and P) Twig video Blood Locations: __________ ________________ Functions: supplies cells with nutrients and _______, removes _____________, fights ______________ Twig videos What is blood? (2:24) Three types: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac Skeletal Locations: attached to ___________ throughout the body Functions: ____________ body parts Striated and ____________ Multinucleated cells Twig video Smooth Locations: ____________ _____________ Functions: s l o w sustained contractions Nonstriated and ________________ Cardiac Location: _________ Function: pump ___________ Striated, ______________, and _________________ Twig video What is the arrow pointing to? Consists of cells called ____________ (neuro = string in Greek) Location: _________, spinal ___________, nerves Function: conduction of nerve _____________ Neurons consist of three main parts: Dendrite: branching extensions that bring in impulses from other ____________ to the _________ ____________ Cell body: contains the nucleus, cytoplasm, and ____________ Axon: conducts impulses ________ from a neuron There are five main types of membranes: Mucous membranes Locations: interior walls of ___________; tubes that lead out of the body (respiratory, digestive, genitourinary tracts) Functions: reduce __________, protection from __________, resist ________ in digestive system Peptic ulcers (1:35) Mucous membrane of stomach (gastric rugae) Serous membranes Locations: line the insides of hollow organs, cover organs Functions: reduce ____________, _____________ internal organs, and compartmentalize the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities Pericardium Dr. Anastasi performing open-heart surgery (bypass and valve replacement) (photos courtesy of Keith Sidehamer, perfusionist) Synovial membranes Locations: line freely movable ___________ _____________ Function: secrete ____________ fluid which greatly reduces ___________ between the bones Arthroscopic image of synovium from a metacarpophalangeal joint Synovial fronds in both images are normal and healthy. Arthroscopic knee surgery (4:01) Meninges Locations: only in the dorsal cavity (surrounds _______ and _________ cord) Function: forms a ___________ covering Dura mater Three layers: _________, ________________, and ___________ maters Meningitis (3:31) Pia mater Arachnoid mater Cutaneous membrane Locations: the _________ Functions: _________ from trauma, _____________ invasion, ___________ loss or gain, and synthesis of vitamin _____