Genetics Case Study: The Royal Family
advertisement

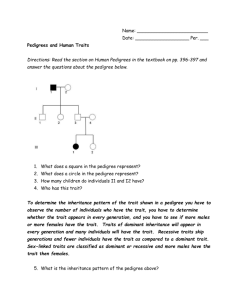
Genetics Case Study: The Royal Family The Romanov Family •Romanov Empire included one-sixth of the globe. •Nicholas II became Czar of Russia in 1896 •Resentment against the Czar and wealthy class begins at end of 19th century. Alexei • Born in 1904, Nicholas’s only son. • Had hemophilia, a bleeding disorder. • Had body guard with him at all times to prevent accidents. • Alexei had several internal bleeding instances. • These bleedings were stopped after the prayers of the healer Rasputin. Rasputin •Healer or Scoundrel???? •Alexandra (Alexei’s mom) called Rasputin in to stop Alexei’s bleeding. •Alexandra took Rasputin in as a relative (which lowered public faith of the Romanov family). His influence on the Czar is arguable by historians. •Assassinated by Russian aristocrats. Rasputin • Rasputin was drugged, poisoned, and shot before he died of drowning in the Neva river End of the Empire •July, 1918: Russian Revolution (Romanov’s assassinated) •Alexei’s body missing from mass grave found in 1990’s. So what does this have to do with Genetics? Learn how to read a PEDIGREE. Learn the inheritance pattern of HEMOPHILIA. Sex-Linkage •Traits controlled by genes located on the sex chromosomes are called sex-linked traits. •The gene for a protein that helps blood clot is on the X chromosome. •If this gene is mutated (deletion, point mutation, etc), it may cause HEMOPHILIA. •Heterozygotes are carriers & may pass trait on to children, but themselves appear normal. •Other sex-linked traits are red-green colorblindness, Duchenne muscular dystrophy, and Fragile X syndrome. Royal Family Pedigree Pedigrees • • • • Each row represents a generation Genders represented by different shapes Affected individuals indicated by shading Carriers indicated by half shading Reading a Pedigree Sometimes, carriers are indicated this way. Pedigree Problems: Tips • Recessive: trait usually skips a generation • Dominant: trait shows up often • Autosomal: trait seen in both genders • Sex-linked: trait seen usually in 1 gender Sample Pedigrees Pedigree Practice Dominant or recessive trait? Autosomal or sex-linked? Pedigree Practice Dominant or recessive trait? Autosomal or sex-linked? Pedigree Practice Dominant or recessive? Autosomal or Sex-linked? Practice Problems • http://www.yhc.edu/external/jasonb/previou s_semesters/Bio103_Su2004/Links_of_Inte rest/links_to_practice_pedigree_probs.htm Create your own pedigree! 1. Draw your family tree like the pedigrees we’ve seen. 2. Decide on a trait, and shade the affected individuals. (see list of traits on next slide) 3. Show the trait through 3 generations in your family (grandparents, parents, and you and your siblings). Dominant Widow’s peak hairline Tongue-rolling Free earlobes Can’t bend back 45° Freckles No chin cleft Bent little finger Oval face Morton’s Toe(2nd toe) Dark hair (brown/black) Not red hair Recessive Straight hairline Can’t roll tongue Attached earlobes Hitchhiker’s thumb No freckles Chin cleft Not bent Square face Big Toe is tallest Blonde Hair Red Hair