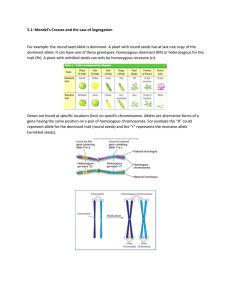
If 81% of a population is homozygous recessive for a given trait.......
advertisement

The DNA sequences of three species were compared. Species 1 is 94% identical to species 2, while only 85% identical to species 3. Species 2 is 89% identical to species three. Create a phylogenetic tree to represent the relationship between these species. Name three ways of dating fossils in a rock layer. What are homologous structures? What do they show about the evolution of the species that have them? How can biogeography be used as evidence of evolution? Define natural selection. What is the main driving force of the natural selection process. List all mechanisms of evolution. Differentiate between the bottleneck effect and the founder effect. Differentiate between genetic drift and gene flow. Give a specific example when mutations became beneficial. What is artificial selection? How can we use it as an evidence of evolution? How did Malthus contribute to Darwin’s theory of evolution? How did Lyell contribute to Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection? 1. Many crustaceans use their tails to swim, but crabs have reduced tails that curl under their shells and are not used in swimming. This is an example of: A. artificial selection B. a homologous structure C. natural selection D. a vestigial trait 2. Scientific theories are A. nearly the same things as hypotheses B. are supported by a large body of evidence C. cannot be tested because the events they describe occurred only once D. are predictions of future events 3. Structures as different as human arms, bat wings, and dolphin flippers contain many of the same bones, which develop from similar embryonic tissues. These structural features are examples of A. homology B. analogy C. Lamarckism D. natural selection 4. A certain population has only one type of allele for a trait. Can natural selection act on that trait? Why? Why not? 5. Who came up with the theory of evolution by natural selection? 6. Name and explain one specific example of evolution occurring in a population. Name 3 scientists who contributed to Darwin’s theory of evolution. Describe their contributions. List 5 evidence of evolution Describe how vestigial organs can be used as evidence of evolution. Describe how comparative embryology can be used as evidence of evolution. List and describe 3 ways of dating fossils. Define natural selection and list its five aspects List all mechanisms of evolution. What is their significance? Define what a scientific theory is. Name the molecules that could be used to determine evolutionary relatedness. Explain how these would be used. Which rock layer is the oldest on the picture below? Name three ways in which you can determine the age of the fossils in layer 2A. State which layers are present in location B but missing in location A. State which layer in location A is the same as the top layer in location B. List the types of natural selection. Represent them with a graph and give specific examples of each. List 4 examples of evolution and describe one. Relate evolution to allele frequency and to the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. List the conditions of the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. Define what a population is. Define the following: Gene pool Allele frequency Phenotype frequency Lets say that brown fur coloring is dominant to gray fur coloring in mice. If you have 168 brown mice in a population of 200 mice........ What is the predicted frequency of heterozygotes? What is the predicted frequency of homozygous dominant? What is the predicted frequency of homozygous recessive? If 81% of a population is homozygous recessive for a given trait.......... What is the predicted frequency of homozygous dominant? What is the predicted frequency of heterozygotes? What is the frequency of the dominant and recessive alleles in the population? If 51% of the population carries at least one copy of the recessive allele....... What is the predicted frequency of individuals in the population that express the dominant phenotype? What is the predicted frequency of individuals in the population that express the recessive phenotype? Within a population of butterflies, the color brown (B) is dominant over the color white (b). And, 40% of all butterflies are white. Given this simple information, which is something that is very likely to be on an exam, calculate the following: The percentage of butterflies in the population that are heterozygous. The percentage of butterflies that are homozygous dominant.