Acid Base Review Answer Key
advertisement
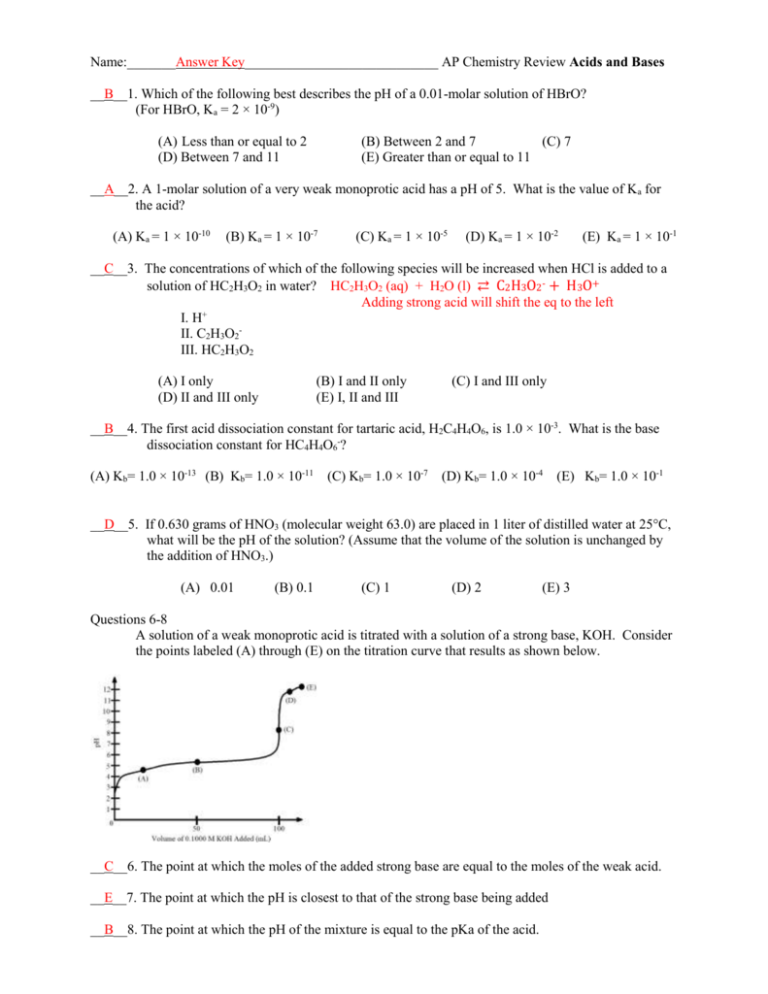
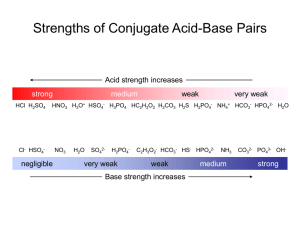
Name:_______Answer Key____________________________ AP Chemistry Review Acids and Bases __B__1. Which of the following best describes the pH of a 0.01-molar solution of HBrO? (For HBrO, Ka = 2 × 10-9) (A) Less than or equal to 2 (D) Between 7 and 11 (B) Between 2 and 7 (C) 7 (E) Greater than or equal to 11 __A__2. A 1-molar solution of a very weak monoprotic acid has a pH of 5. What is the value of Ka for the acid? (A) Ka = 1 × 10-10 (B) Ka = 1 × 10-7 (C) Ka = 1 × 10-5 (D) Ka = 1 × 10-2 (E) Ka = 1 × 10-1 __C__3. The concentrations of which of the following species will be increased when HCl is added to a solution of HC2H3O2 in water? HC2H3O2 (aq) + H2O (l) ⇄ C2H3O2- + H3O+ Adding strong acid will shift the eq to the left I. H+ II. C2H3O2III. HC2H3O2 (A) I only (D) II and III only (B) I and II only (E) I, II and III (C) I and III only __B__4. The first acid dissociation constant for tartaric acid, H2C4H4O6, is 1.0 × 10-3. What is the base dissociation constant for HC4H4O6-? (A) Kb= 1.0 × 10-13 (B) Kb= 1.0 × 10-11 (C) Kb= 1.0 × 10-7 (D) Kb= 1.0 × 10-4 (E) Kb= 1.0 × 10-1 __D__5. If 0.630 grams of HNO3 (molecular weight 63.0) are placed in 1 liter of distilled water at 25°C, what will be the pH of the solution? (Assume that the volume of the solution is unchanged by the addition of HNO3.) (A) 0.01 (B) 0.1 (C) 1 (D) 2 (E) 3 Questions 6-8 A solution of a weak monoprotic acid is titrated with a solution of a strong base, KOH. Consider the points labeled (A) through (E) on the titration curve that results as shown below. __C__6. The point at which the moles of the added strong base are equal to the moles of the weak acid. __E__7. The point at which the pH is closest to that of the strong base being added __B__8. The point at which the pH of the mixture is equal to the pKa of the acid. 9. a. A 0.100M solution of NH3 is prepared in a 125mL flask. What is the pH of the solution if Kb of ammonia is 1.79 x 10-5? R NH3 (aq) + I 0.100M C -X E 0.100M Kb<<[NH3]i [NH3]E = [NH3]I Kb = H2O (l) ⇄ ------------------------------------- [𝑁𝐻4+ ][𝑂𝐻 − ] [𝑁𝐻3 ] Kb = 𝑋2 0.100𝑀 pOH = - log[OH-] 14 – pOH = pH NH4+ + OH0M 0M +X +X X X = 1.79 x 10-5 X = 0.00134M = [OH-] pOH = - log(0.00134) pOH = 2.87 14 – 2.87 = 11.13 b. A different solution is prepared containing 0.100-molar NH4Cl with 0.200-molar solution of NH3. What is the pH of this new solution ? The value of Kb for ammonia is 1.79 × 10-5. BUFFER!!! pH = pka + log ([A-]/[HA]) Ka • Kb = Kw Ka (1.79 x 10-5) = 1.0 x 10-14 pH = -log(5.59 x 10-10) + log (0.200M/0.100M) Ka = 5.59 x 10-10 pH = 9.55 10. A sample of 40.0 milliliters of a 0.100 molar HC2H3O2 solution is titrated with a 0.150 molar NaOH solution. The Ka value for acetic acid is1.8×10-5. (a) What volume of NaOH is used in the titration in order to reach the equivalence point? MAVA = MBVB MA = 0.100M VA = 40.0 mL MB = 0.150M VB = ? (0.100M)(40.0mL) = (0.150M)(VB) VB = 26.67mL (b) What is the molar concentration of C2H3O2- at the equivalence point? At equivalence all moles of acid have been converted to conjugate base. mol = M(V) mol = (0.100M) ( 0.040L) mol = 0.004 mol HC2H3O2 at equvilance 0.004 mol HC2H3O2 are converted to 0.004 mol C2H3O2[C2H3O2-] = 0.004 mol/(total volume) [C2H3O2-] = 0.004 mol/(0.040L + 0.02667L) = 0.060M (c) What is the pH of the solution at the equivalence point? Ka • Kb = Kw (1.8 x 10-5)Kb = 1.0 x 10-14 R C2H3O2- (aq) + H2O (l) ⇄ I 0.060M ------------C -X ------------E 0.060M ------------Kb<<[C2H3O2 ]i [C2H3O2-]E = [C2H3O2-]I Kb = [HC2H3O2][𝑂𝐻 − ] [C2H3O2− ] pOH = - log[OH-] 14 – pOH = pH Kb = Kb = 5.56 x 10-10 HC2H3O2 (aq) + OH0M 0M +X +X X X 𝑋2 0.060𝑀 = 5.56 x 10-10 pOH = - log(5.78 x 10-6 M) 14 – 5.24 = 8.76 X = 5.78 x 10-6 M= [OH-] pOH = 5.24