Calculating pH
advertisement

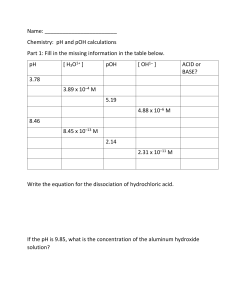
Calculating pH and pOH of Strong Acids and Bases Name: ________________________________ Date: ______________ Block: ______________ 1. Calculate pH and pOH for the following monoprotic strong acids a) 0.006 mol/L HI (aq) b) 0.02 mol/L HNO3 (aq) 2. To clean a clogged drain, 26 g of sodium hydroxide is added to water to make 150 mL of solution. What are the pH and pOH values for this solution? [fist solve for the concentration of NaOH using C = n/V (L) ] 3. Food scienctsists and dieticians measure the pH of foods when they devise recipes. Various measurements related to their acidity are made and recored below. Complete the table below. Food [H+] mol/L [OH-] mol/L pH pOH Oranges 5.5 x 10-3 Asparagus Olives Blackberries 5.6 2.0 x 10-11 10.6 b) Based on pH only and assuming that sour taste is directly proportional to pH, which food listed above would taste most sour? Warner – SCH 4U Calculating pH and pOH of Strong Acids and Bases 4. What mass of potassium hydroxide (KOH) is contained in 500 mL of solution that has a pH of 11.5? Remember mass is calculated by n x MM. 5. Calculate the pH of a 0.032 mol/L Ba(OH)2 (aq) solution. 6. A solution is made by dissolving 0.8 g of Ca(OH)2 in water to makde 100 mL of a final solution. Calculate the pH of the solution. ANSWERS : 1. pH a) 2.2 b) 1.6 pOH 11.8 12.4 2. 14.64 -0.64 4. 0.09 g 5. pH = 12.81 6. pH = 13.33 Warner – SCH 4U 2. oranges asparagus olives blackberry [H+] 5.5 x 10-3 M 3.0 x 10-9 M 5.0 x 10-4 M 4.0 x 10-4 M [OH-] 1.8 x 10-12 M 2.51 x 10-6 M 2.0 x 10-11 M 2.5 x 10-11 M pH 2.26 8.4 3.3 3.4 pOH 11.74 5.6 10.7 10.6