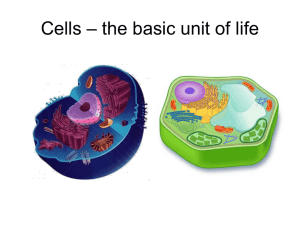
cell membrane.
advertisement

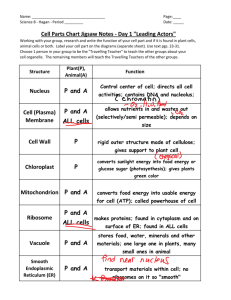
State the three parts of the cell theory. 1 1. 2. 3. What was the name of the scientist that stated that animals are composed of cells? What was the name of the scientist that first coined the word cell? State the three parts of the cell theory. 2 1. Difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. 2. Identify the different types of cells: bacterial, animal, & plant. 3. Identify the key cell parts. 4. Describe the function of the cell parts. 5. Identify structural differences in animal and plant cells. 3 PROKARYOTES No nucleus Not bound by a nuclear membrane Usually contains one circular chromosome composed of DNA with proteins EUKARYOTES Nucleus present Bound by a nuclear membrane Contains one or more paired linear chromosomes • Ex. plants and animals • Ex. bacteria 4 1. 2. 3. 5 Human cells are animal cells which are different depending on their function, but there are similarities. Each cell is specialized and has a different function, but there are similarities. Every cell in our body has the same DNA or genetic material 7 8 9 Can you identify any of the cell parts in the liver sample? 10 FUNCTION: Controls IMAGE: the cell’s activity. Storehouse for genetic information called DNA • Site of DNA replication & its transcription to RNA. Analogy: Like a City Hall 12 Function: Located in the nucleus of cells. Ribosomes are synthesized (made) here, then migrate to the cytoplasm. Image: 13 Image: Function: Protects the cell from the outside environment Selectively Permeable- controls what material moves in and out of the cell • Acts like a gatekeeper Analogy: City Border 15 FUNCTION: IMAGE: Fills the space between the nucleus and the cell membrane. Fluid portion is called the cytosol and is mainly water. Site of most cell activity (transports materials through out the cell). Analogy: Property or City Proper Image: Function: The place where RNA (transcribed from DNA) is translated to produce protein Analogy: Lumber Yard 17 Function: Image: Net work of folded membranes that transport materials (nutrients and waste) through out the cell Two Types: • Rough ER • Smooth ER Analogy: High Way Road System Lacks Ribosomes Acts as a storage area for proteins exiting the cell Smooth ER Contains Ribosomes Transport Proteins in and out of the nucleus. Rough ER 19 Function: Image: Condensed membrane-enclosed spaces that process, sort and deliver proteins created in the ribosomes on the ER Analogy: Post Office or UPS 21 Function: Power house of the cell Converts the nutrients the cell intakes to usable energy It is folded and kidney bean shaped Analogy: Energy Plants or Electrical Plants Image: 23 FUNCTION: in the Golgi Apparatus Breaks down food Recycle older organelles Return digested components to cytoplasm to be reused IMAGE: Form Analogy: Recycling Center Function: Network of proteins that give the cell support Found in the cytoplasm Gives the cell its shape and mobility Image: Analogy: Brick Foundations Image: Function: Small, beating hair-like extensions that are used to create a current to move things away and out of the cell. 26 Function: Image: Whip-like structure used for movement of the cell. 27 Plant cells are found in all plants and they are the building blocks of these living organisms. There are some difference between plant cells and animal cells. 28 29 Can you identify any of the cell parts in the plant sample? 30 Function: Rigid outermost layer of the plant cell, made of cellulose Maintains cell shape and aids in protection Prevents expansion when water enters Image: Analogy: City Limits 31 Function: Storage Image: for water and waste. Analogy: Water Table, Wells, and Sewers 32 Function: Store Image: food pigments. • Ie. Chloroplast- where photosynthesis occurs to form sugars for metabolism. Analogy: Solar Plants 33 34 Plant Cells Animal Cells Chloroplasts • Where sunlight is converted into energy through photosynthesis Cell Wall Mitochondria • Produces cells energy from food No Cell Wall • Presence of a rigid cell wall surrounding the cell membrane Vacuoles • Make up 30% of cell and 90% of cell volume • Space filler in the cell • Can be used as storage for nutrients Lacking Vacuoles What are the key differences between animal cells and plant cells? 36 What is the function of the nucleolus? What is the function of ribosomes? 37 Nucleus Nucleolus Cell membrane Cytoplasm Ribosome Cytoskeleton Vacuole Cell Wall Chloroplast Prokaryote Eukaryote Protein Smooth ER Rough ER Golgi Apparatus Mitochondria Lysosome Cilia Flagella Plastid Cellulose Cytosol Nucleoplasm Nuclear Membrane 38 If you were looking at a specimen underneath the microscope, how would you go about magnifying what you see? 39 40 A light bulb acts like the ______________. A letter acts like the __________________. A brain acts like the __________________. A sweeper acts like the _______________. Arteries A act like the ___________________. battery acts like the __________________. 41 FREE! 42