NamingCompounds.ppt - Ms. Y's Chemistry Class 2011-2012
advertisement

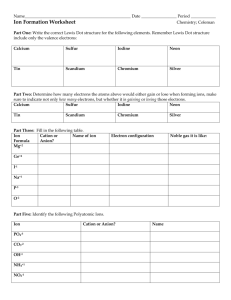
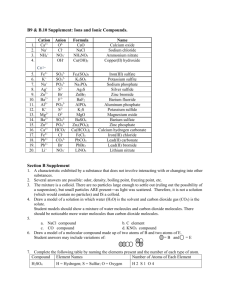
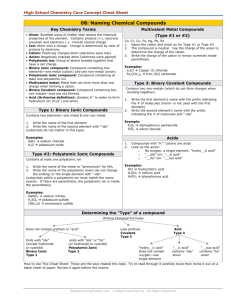
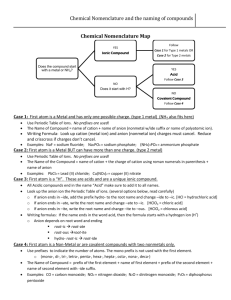
• On the back of your 2. Cr packet: • How much of the packet did you complete? • Label the following as transition metals or regular metals: 3. Co 4. Fe 5. Fr 6. Sn 7. K 8. Mg 1. Ca Thursday ANNOUNCEMENTS! Ms. Y Absent, Projects, Make up work, grades, uniforms, etc! Vocabulary • Cation: Positively charged Ion • Anion: Negatively charged Ion COVALENT COMPOUND NAMING INVESTIGATION Examples of Covalent compound names Covalent Compound names: • PH3 : Phosphorus Trihydride • CO : Carbon Monoxide • N2O3 : Dinitrogen Trioxide • CF4 : Carbon Tetrafluoride PREFIXES! – used for covalent compounds only! • 1 : Mono (only • 6 : Hexa used for the 2nd element!) • 2 : Di • 3 : Tri • 4 : Tetra • 5 : Penta • 7 : Hepta • 8 : Octa • 9: Nona • 10 : Deca Rules • 1. The first element is named first, using the elements name. • 2. Second element is named as an Anion (suffix "-ide") • 3. Prefixes are used to denote the number of atoms • 4. "Mono" is not used to name the first element Practice “-ide” ending • Fluorine • Fluoride • Chlorine • Chloride • Iodine • Iodide • Oxygen • Oxide • Sulfur • Sulfide • Phosphorus • Phosphide • Selenium • Selenide Example: • SiF4 • P2O5 • C 3 H8 • N 2 F6 • NO What is the difference? Ionic Compound names: Covalent Compound names: • PH3 : Phosphorus • CaCl2 : Calcium Chloride • K3N: Potassium Nitride • NaF: Sodium Fluoride Trihydride • CO : Carbon Monoxide • N2O3 : Dinitrogen Trihydride IONIC COMPOUND NAMING INVESTIGATION Rules • 1. The Cation (positive ion) is named first, the Anion second. • 2. Cations take the element name Na+ --> Sodium Ca2+ --> Calcium • 3. Anions take the elements name and ends with "-ide” Cl- --> Chloride DO NOT USE PREFIXES! Name Compound Calcium Elemen Charge Bromide t ? Cation Anion Ca Br +2 -1 CaBr2 LCM 2 How many? 1 2 Name Compound Barium Elemen Charge Sulfide t ? Cation Anion Ba +2 S -2 BaS LCM 2 How many? 1 1 Name Compound Aluminu m Oxide Cation Anion Elemen Charge t ? Al O +3 -2 Al2O3 LCM 6 How many? 2 3 TRANSITION METALS NAMING INVESTIGATION TRANSITION METALS - GREEN: EXCEPTIONS – YELLOW: TRANSITION METALS But Ms. Y…We don’t know the charge!?!?!? Name Compound Iron (III) Charge Chloride ? Cation Anion Fe +3 Cl -1 FeCl3 LCM 3 How many? 1 3 Name Compound Copper Charge (II) ? Oxide Cation Anion TM +2 NonM -2 CuO LCM 2 How many? 1 1 Transition metal naming • CoBr2 = Cobalt (II) Bromide • FeCl3 = Iron (III) Chloride • SnO2 = Tin (IV) Oxide Compound Name Charge MnCl2 ? Cation Anion Mn +2 Cl -1 LCM Manganese (II) Chloride 2 How many? 1 2 Name Compound HgF2 Cation Anion Charge ? Hg +2 F -1 Mercury (II) Fluoride LCM 2 How many? 1 2 Name Compound Charge Mn2O3 ? Cation Anion Mn +3 O -2 LCM 6 Manganese (III) Oxide How many? 2 3 Rules For Compound to name • 1. The Cation (positive ion) is named first, the Anion second. • 2. Cations take the element name then is followed by the roman numeral charge Ag+ --> Silver (I) Co2+ --> Cobalt (II) • 3. Anions take the elements name and ends with "-ide” Cl- --> Chloride DO NOT USE PREFIXES! Catalyst • What is the difference between naming a covalent and ionic compounds? • What is the difference between naming a transition metal and a regular metal? • Name the following compounds: •C2H4 •Na3P •Co2S Monday! Catalyst – Use your flow charts to complete the following: • Write the formula for the following compounds: Tuesday • Calcium Nitride • Iron (III) Chloride • Write the name for the following compounds: • NO2 • NiN After you are finished look over the explosion questions! Name_________________________ __ Period______ Chemistry, Comprehensive Ionic Bonding START: Think about your personality. Do you tend to base your decisions based on how you feel or what seems logical? logic feelings Do you like to come up with very concrete, specific data or do you like to be creative and abstract? Do you like to come up with very concrete, specific data or do you like to be creative and abstract? concret e concret e abstract abstract Do you prefer to work in a group or work individually? Do you prefer to work in a group or work individually? Do you prefer to work in a group or work individually? Do you prefer to work in a group or work individually? Group Group Group Group You are popular, live in the moment, put others first, welldeveloped common sense Individual You are quiet, sensitive, kind, like to serve others, practical, welldeveloped common sense Individual You have great people skills, probably dislike being alone, get excited about new ideas You are quietly sensitive and have a welldeveloped value system. You do the right thing and care about You like to DO, you are active, hardworking, loyal, and have great people skills Individual You are serious and quiet. Usually you can do anything you set your mind to. Very dependable Outspoken and good at leading. Enjoy good conversation and can easily speak in public Individual You are logical, creative, and independent. You have very high standar Directions: Your turn! Now YOU need to come up with a similar “quiz” that you put each compound you are working with through. You will not always be told if a compound contains a covalent compound, transition metal or a regular metal. You will need to determine this on your own. Use the starting of this chart to create a “quiz” to help you do so START: Look at the problem. Are you writing the name or the compound formula? formula name Write the name for a covalent compound: Ex. Write the name for an ionic compounds with regular metals: Ex Write the name for an ionic compound with transition metals: Ex Write the formula for a covalent compound: Ex. Write the formula for an ionic compound regular metals: Ex. Write the formula for an ionic compound with transition metals: Ex Pop Quiz • Determine if each is covalent or ionic, then name each compound. 1. K2O 2. N2F4 3. Fe2O3 • Determine if each is covalent or ionic, then write the formula for each compound. 1. Zinc (I) Sulfide 2. Barium Chloride 3. Tricarbon Hexahydride Catalyst – use your flashcards! • Write the formula for the following Polyatomic Ions: •Carbonate •Hydroxide •Nitrite • Name the following polyatomic ions AND decide if it is a cation or anion!: •SO32•NH4+ Wednesday •PO43- Pick up paper in front! Keep your HW packet at your desk! Catalyst • Write the formula for the following compounds: • Magnesium Chlorate • Silver (II) Nitrite Friday POLYATOMIC IONS What does Poly mean? What is an atom? What is an ion? So…what is a polyatomic Ion? List of all polyatomic ions… Ammonium NH4+ Hydroxide OH- Hydronium H3 O+ Permanganat e MnO4- Hydrogen Carbonate CO3- Carbonate CO32- Acetate C2H3O2- Sulfate SO42- Cyanide CN- Sulfite SO32- Nitrite NO2- Phosphate PO43- Nitrate NO3- Dichromate Cr2O72- Cyanide CN- Chlorate ClO3- The polyatomics you need to know: Ammonium NH4+ Hydroxide OH- Hydronium H3 O+ Permanganat e MnO4- Hydrogen Carbonate HCO3- Carbonate CO32- Acetate C2H3O2- Sulfate SO42- Cyanide CN- Sulfite SO32- Nitrite NO2- Phosphate PO43- Nitrate NO3- Dichromate Cr2O72- Chlorate ClO3- Circle the polyatomic ion in the compound below: • NaClO3 • KMnO4 • NH4Cl • CaCO3 • Mg(OH)2 • Cs2SO4 Now name the polyatomic ions below • NaClO3 • Chlorate • KMNO4 • Permanganate • NH4Cl • Ammonium • CaCO3 • Carbonate • Mg(OH)2 • Hydroxide • Cs2SO4 • Sulfate LET’S PLAY MEMORY! Look at the names below, what do you notice? • NaClO3 • Sodium Chlorate • KMNO4 • Potassium Permanganate • NH4Cl • Ammonium Chloride • CaCO3 • Calcium Carbonate • Ag(OH)2 • Silver (II) Hydroxide • TiSO4 • Titanium (II) Sulfate Naming polyatomic ions Compound Name 1. Identify the polyatomic ion 2. Determine if the polyatomic ion is a cation or anion A. If Cation: Polyatomic name then nonmetal name ending in –ide a. Ex. NH4Cl – Ammonium Chloride B. If Anion: name metal (if transition metal use roman numeral) then polyatomic ion name a. Ex. MgSO4 – Magnesium Sulfate Catalyst • Name the following Compounds: •KCN •Pb(NO3)2 •NH4F Thursday Compound Name Charge Cu3(PO4)2 ? +2 Cu Cation -3 PO4 Anion LCM How many? 6 Copper (II) Phosphate 3 2 Compound Name Ti2SO4 Cation Anion Charge ? Ti +1 SO4 -2 LCM 2 Titanium (I) Sulfate How many? 2 1 POLYATOMIC IONS NAME COMPOUND Name Compound Sodium Charge Carbonate ? Cation Anion Na +1 CO3 -2 Na2CO3 LCM 2 How many? 2 1 Name Compound Iron (III) Charge Cyanide ? Cation Anion Fe +3 CN -1 LCM Fe(CN)3 3 How many? 1 3 Name Compound Tin (IV) Charge Hydroxide ? Cation Anion Sn +4 OH -1 Sn(OH)4 LCM 4 How many? 1 4 How to draw the transfer of electrons 1. Draw the Lewis Dot Diagram of each element 2. Draw arrows moving electrons from the cation to the anion LEWIS DOT DIAGRAMS! Drawing Covalent Compound movement What is the electron movement like for covalent compounds? They SHARE their electrons! How do we draw the sharing of electrons? 1. Position the atoms (least electronegative 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. atom in the center) Write the other atoms around the central atom Count Total number of valence electrons from the Periodic Table Draw a single bond from the center atom to the each of the outer atoms. Fill in the octets Count the number of electrons and compare to PT count Helpful hints: • Each bond is worth TWO electrons • Hydrogen and Group 17 will NEVER be the center atom Exceptions: • Hydrogen only wants TWO electrons NOT 8! • Boron only wants SIX electrons, NOT 8 Examples: •PCl3 •CH4 •BF3 • I2