High School Chemistry Core Concept Cheat Sheet
08: Naming Chemical Compounds
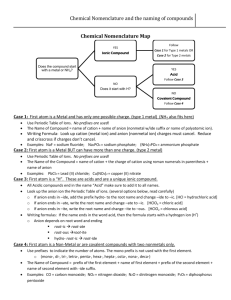
Key Chemistry Terms
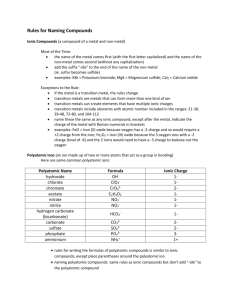
Multivalent Metal Compounds
• Atom: Smallest piece of matter that retains the chemical
properties of the element. Contains protons (+), neutrons
(neutral) and electrons (-). Overall neutral charge
• Ion: Atom with a charge. Charge is determined by ratio of
protons to electrons
• Cation: Positively charged atom (electrons were lost)
• Anion: Negatively charged atom (electrons were gained)
• Polyatomic ion: Group of atoms bonded together that
have a net charge.
• Binary ionic compound: Compound containing two
elements—one metal (cation) and one non-metal (anion)
• Polyatomic ionic compound: Compound containing at
least one polyatomic ion
• Multivalent metal: Metal that can form more than one
charge when forming a cation.
• Binary Covalent compound: Compound containing two
non-metals—ions are not formed.
• Acid (Arrhenius definition): donates H+ to water to form
hydronium ion (H3O+) and anion
Type 1: Binary Ionic Compounds
(Type #1 or #2)
Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, Hg, Pb, Sn
1. Name the cation and anion as for Type #1 or Type #2
2. The compound is neutral. Use the charge of the anion to
determine the charge of the cation.
3. Write the charge of the cation in roman numerals inside
parenthesis
Examples:
CuCl Æ Copper (I) chloride
Fe2(CO3)3 Æ Iron (III) carbonate
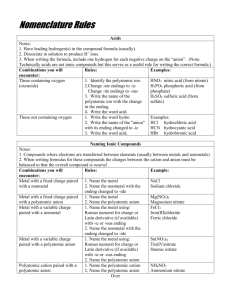
Type 3: Binary Covalent Compounds
Contains two non-metals (which do not form charges when
bonding together).
1.
2.
Contains two elements—one metal & one non-metal
Write the first element’s name with the prefix indicating
the # of molecules (mono- is not used with the first
element)
Write the second element’s name with the prefix
indicating the # of molecules and “-ide”
Example:
P2O5 Æ diphosphorus pentaoxide
SiO2 Æ silicon dioxide
1. Write the name of the first element
2. Write the name of the second element with “-ide”
(subscripts do not matter in this type)
Acids
Examples:
NaCl Æ sodium chloride
K2O Æ potassium oxide
1.
2.
Type #2: Polyatomic Ionic Compounds
Contains at least one polyatomic ion
1.
2.
Write the name of the metal or “ammonium” for NH4
Write the name of the polyatomic anion (do not change
the ending) or the single element with “-ide”
(subscripts within a polyatomic ion must match the name
exactly. If there are parenthesis, the polyatomic ion is inside
the parenthesis)
Compounds with “H+” cations are acids
Look up the anion:
o
No oxygen, a single element: “hydro__ic acid”
o
“__ate” ion: “__ic acid”
o
“__ite” ion: “__ous acid”
Examples:
HCl Æ Hydrochloric acid
H2SO4 Æ sulfuric acid
H3PO3 Æ phosphorous acid
Examples:
NaNO3 Æ sodium nitrate
K2SO4 Æ potassium sulfate
(NH4)2S Æ ammonium sulfide
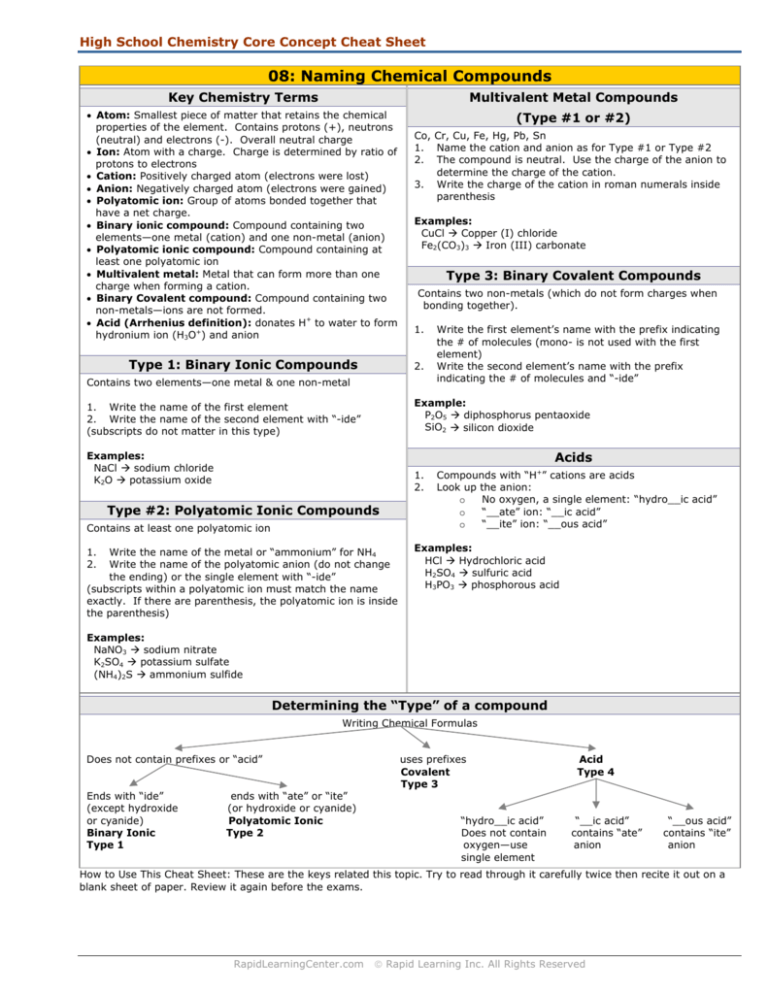
Determining the “Type” of a compound
Writing Chemical Formulas
Does not contain prefixes or “acid”
Ends with “ide”
(except hydroxide
or cyanide)
Binary Ionic
Type 1
ends with “ate” or “ite”
(or hydroxide or cyanide)
Polyatomic Ionic
Type 2
uses prefixes
Covalent
Type 3
“hydro__ic acid”
Does not contain
oxygen—use
single element
Acid
Type 4
“__ic acid”
contains “ate”
anion
“__ous acid”
contains “ite”
anion
How to Use This Cheat Sheet: These are the keys related this topic. Try to read through it carefully twice then recite it out on a
blank sheet of paper. Review it again before the exams.
RapidLearningCenter.com
© Rapid Learning Inc. All Rights Reserved