What is love?

Attraction & Intimacy
Who do you love?
What is love?
Why do fools fall in love?
Will you love me forever?
Let me sleep on it, I’ll give you an answer in the morning (Meatloaf, 1978).
1
What factors predict liking?
Proximity – geographical nearness
mere exposure
anticipation of interaction
Attractiveness – “what is beautiful is good”
Similarity – attitudes, personality.
Reinforcement – liking for a person will result under conditions in which a person experiences positive or negative reinforcement in the presence of that person.
2
What is love?
Types of love:
I. Passionate vs. Companionate love
Companionate love is the strong affection we have for those with whom our lives are deeply involved.
Passionate love is a state of intense absorption in someone. It involves arousal and intense desire and often has a swift onset.
The Bridge Study
3
Types of Love
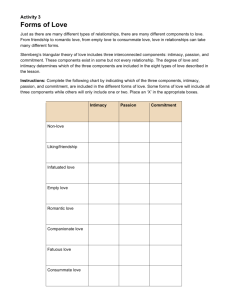
II. Sternberg’s Triangle Model
3 ingredients of consummate love:
Intimacy- feelings of closeness, affection, and connectedness
Passion- motivational drives relating to sex, physical closeness and romance
Decision/commitment- initial thought of love and longterm determination to maintain that love
4
Intimacy (Liking)
Romantic Love
(Intimacy + passion)
Passion
(Infatuation)
Consummate
Love
(Intimacy +
Passion + commitment
Companionate Love
(Intimacy + commitment)
Decision/Commitment
Fatuous Love
(Empty love)
(Passion + commitment)
5
Individual Differences in Relationship
Style
Gender
Women rate financial independence/career as more important in a mate than men; men rate physical attractiveness as more important than women.
Women tend to prefer older men; men tend to prefer younger women.
Women report more emotional jealousy; men report more sexual jealousy
(Buss).
6
Individual Differences in
Relationship Style
Attachment Theory—children learn relationship behaviors that are modeled by parents.
Secure attachment-child learns to nurture intimacy, feels secure in relationships with others.
Avoidant attachment-child learns to starve intimacy by being emotionally distant, avoids commitment and closeness in relationships with others.
Anxious/ambivalent attachment-child learns to smother intimacy by being possessive, jealous, and emotionally demanding.
7
Individual Differences in
Relationship Style
Self-Esteem
In the face of a relationship threat, LSE’s distance themselves from their partner; HSE’s increase closeness.
(Murray & Holmes).
SE is negatively correlated with relationship social comparisons.
(Smith-LeBeau & Buckingham).
8
Will you love me forever?
I. Equity Theory-
Your benefits
Your contributions
= Your Partner’s Benefits
Your Partner’s Contributions
9
Will you love me forever?
II. Investment model-
Satisfaction +
Investment + Commitment Relationship
CLalt Stability
Satisfaction is based on costs and rewards.
CLalt is the comparison level for alternative relationships.
10