PRODUCTIONS/OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
advertisement

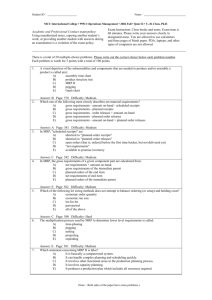
Chapter 14 MRP and ERP 1 Transparency on aggregate to master plan 2 Independent Demand Dependent Demand A C(2) B(4) D(1) E(1) D(3) F(2) Independent demand is uncertain. Dependent demand is certain. 3 Dependant Demand • Dependent demand: Demand for items that are subassemblies or component parts to be used in production of finished goods. • Once the independent demand is known, the dependent demand can be determined. 4 MRP • Material requirements planning (MRP): Computer-based information system that translates master schedule requirements for end items into timephased requirements for subassemblies, components, and raw materials. 5 • Master Production Schedule • Time-phased plan specifying timing and quantity of production for each end item. • Material Requirement Planning Process 6 MRP MRP Inputs MRP Processing MRP Outputs Changes Order releases Master schedule Planned-order schedules Primary reports Bill of materials file Inventory records file MRP computer programs Exception reports Planning reports Secondary reports Performancecontrol reports Inventory transaction 7 Planning Horizon Assembly Subassembly Fabrication Procurement 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Weeks 8 Master Schedule Master schedule: One of three primary inputs in MRP; states which end items are to be produced, when these are needed, and in what quantities. Cumulative lead time: The sum of the lead times that sequential phases of a process require, from ordering of parts or raw materials to completion of final assembly. Time fences: Series of time intervals during which order changes are allowed or restricted. 9 Bill-of-Materials Bill of materials: One of the three primary inputs of MRP; a listing of all of the raw materials, parts, subassemblies, and assemblies needed to produce one unit of a product. Product structure tree: Visual depiction of the requirements in a bill of materials, where all components are listed by levels. 10 Product Structure Tree Level 0 1 Chair Leg Assembly 2 Legs (2) Cross bar Seat Back Assembly Side Cross Back Rails (2) bar Supports (3) 11 Inventory Records • One of the three primary inputs in MRP • Includes information on the status of each item by time period – Gross requirements – Scheduled receipts – Amount on hand – Lead times – Lot sizes – And more … 12 Other Considerations • Safety Stock • Lot sizing 13 MRP Processing • Gross requirements • Schedule requirements • Projected on hand • Net requirements • Planned-order receipts • Planned-order releases 14 MPR Processing • Gross requirements – Total expected demand • Scheduled receipts – Open orders scheduled to arrive • Planned on hand – Expected inventory on hand at the beginning of each time period 15 MPR Processing • Net requirements – Actual amount needed in each time period • Planned-order receipts – Quantity expected to received at the beginning of the period in which it is shown, reflecting the lot size • Planned-order releases – Planned amount to order in each time period; same as Planned-order receipts offset by lead time 16 Inventory Requirements • Net requirements: Net Requirements = Gross Requirements – Available Inventory • Available Inventory: Available Inventory = Projected on hand – Safety stock – Inventory allocated to other items 17 T14-1: MRP - Example Clear Master Schedule Week Number for Shutters: Quantity 1 2 3 Shutters: Gross requirements Scheduled receipts Projected on hand Net requirements Planned-order receipts Planned-order releases 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Gross requirements Scheduled receipts 2 Projected on hand 2 Net requirements 320 Planned-order receipts Planned-order releases 0 Quantity = LT = Lot Size = Frames: Quantity = LT = Lot Size = Wood sections: 1 1 1 Gross requirements Scheduled receipts Quantity = 4 Projected on hand LT = 1 Net requirements Lot Size = 70 Planned-order receipts Planned-order releases Note: Use Lot Size = 1 for lot-for-lot ordering. 4 100 5 6 7 8 150 100 0 0 0 150 0 0 0 100 0 100 100 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 150 0 150 150 0 0 200 0 0 0 300 0 0 0 0 320 0 0 0 0 0 200 320 0 120 0 0 0 120 0 0 320 120 0 0 0 120 180 320 0 140 0 0 0 0 70 70 0 0 0 0 400 0 0 0 600 0 70 0 0 350 70 330 350 0 20 0 0 0 20 0 0 0 20 0 0 630 20 580 630 0 50 0 0 0 18 A Key MRP Output • Planned orders (referring to Planned Order Releases)- schedule indicating the amount and timing of future orders. It tells us how when to order and how much, assuring us a lower level of inventory than if we did not use MRP. 19 Other MRP Outputs (MRP Secondary Reports) • Performance-control reports • Planning reports • Exception reports 20 Capacity Planning Capacity requirements planning: The process of determining short-range capacity requirements. Load reports: Department or work center reports that compare known and expected future capacity requirements with projected capacity availability. 21 Capacity Requirements in MRP Planning Develop a tentative master production schedule Use MRP to simulate material requirements Convert material requirements to resource requirements Revise tentative master production schedule No Is shop capacity adequate? Yes Firm up a portion of the MPS No Can capacity be changed to meet requirements Yes Change capacity 22 Benefits of MRP • Low levels of in-process inventories • Ability to track material requirements • Ability to evaluate capacity requirements • Means of allocating production time 23 Requirements of MRP • Computer and necessary software • Accurate and up-to-date – Master schedules – Bills of materials – Inventory records • Integrity of data 24 MRP II or Manufacturing Resource Planning • Expanded MRP with and emphasis placed on integration – Financial planning – Marketing – Engineering – Purchasing – Manufacturing 25 MRP II Manufacturing Master production schedule Marketing Production plan MRP Rough-cut capacity planning Capacity planning Adjust production plan Yes Problems? No Requirements schedules No Problems? Adjust master schedule Market Demand Finance Yes 26 ERP • Enterprise resource planning (ERP): – Next step in an evolution that began with MPR and evolved into MRPII – Integration of financial, manufacturing, and human resources on a single computer system. 27 ERP Software – ERP software provides a system to capture and make data available in real time to decision makers and other users in the organization – Provides tools for planning and monitoring various business processes – Includes • • • • Production planning and scheduling Inventory management Product costing Distribution 28 MRP in Services • Service applications such as: – Professional services – Postal services – Retail – Banking – Healthcare – Higher education – Engineering – Logistical services – Real estate 29 ERP Strategy Considerations • • • • High initial cost High cost to maintain Future upgrades Training 30 The following slides are from a consultant who markets ERP systems. Please review the slides. As time permits. we can go through them in class. Note the reason for these slides is to illustrate a situation you might find yourself in if you are a manager in a company making a decision to purchase an ERP system. It can be a very intimidating process for your company when the seller has all the information about a complex system, and the buyer is at the mercy of the seller’s knowledge and technical know-how. 31 Basic Definitions 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 End of slides for MRP/ERP 42