How plants reproduce
advertisement

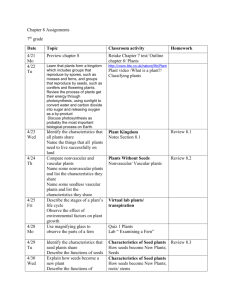
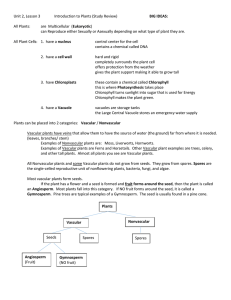
How plants reproduce Different methods of reproduction Nonvascular plants • Nonvascular plants can move water, nutrients, and food only from one cell to the next. • This is why nonvascular plants are so small. • Nonvascular plants do not have flowers so they do not produce seeds. • Instead they reproduce with spores. • Def- spores are single reproductive cells that grow into a new plant. Simple vascular plants • Simple vascular plants reproduce with spores. • Like nonvascular plants they have 2 different stages in their life cycles. • Ferns unite cells from both male and female plant cells. • But the united cell or zygote divides and grows into a separate spore producing plant. Cone bearing vascular plants • Seed bearing plants make less seeds, but the seeds have a better chance of growing into a plant. • It has a better chance because the seed contains food to feed the plant when it is first sprouting. • Most vascular plants reproduce with seeds. • There are two kinds of seed producing plantswith no protections or gymnosperms; or seeds with protection or angiosperms. • Gymnosperm’s seeds do not have much protection. The most common kinds are conifers or cone bearing plants like pine trees. • Most conifers produce male and female cones on the same tree. Male cones contain the pollen and the wind blows the pollen into the female cones and the seeds develop hidden in the cone. When the weather becomes dry and warm, the cones open, releasing the seeds to grow. Flowering vascular plants Plants that produce flowers are those that have fruits. Fruits are the protection for the seeds inside. The fruit’s fleshy part keeps animals from getting the seeds, protects it from harsh weather, and provides food for the growing sprout. Seed dispersal • • • • Seeds can be spread through many ways. Attaching to objects that brush by is one way. Wind blowing them far away is another. Animal droppings after eating them is another way. • Sometimes it just gets knocked and carried away by an animal such as humans. Seed germination • A seed survives inside the seed coat until conditions are right for it to grow. • Conditions like fertile soil, enough rainfall, warm temperatures,