Geomorphology
advertisement

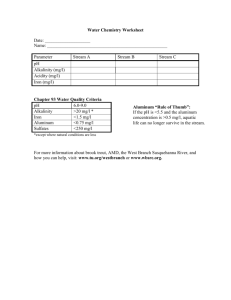
Geomorphology Lake Formation • graben- downfaulted trough; e.g. Lake Tahoe • caldera- subsidence of magma chamber; e.g. Crater Lake, OR • Landslides • glacial activity- e.g. scour, morain dams, & ice melt • solution- CaCO3 (limestone) • Oxbow • wind- playa lakes • humans & beaver Oxbow Lake Fluvial Morphology determined by geology of the site: dendritic- deposits of uniform resistance rectangular- follow faults trellis- flow between parallel ridges Stream Ordering System method of numbering streams as part of a drainage basin network; the smallest unbranched tributary is called 1st order, the stream receiving the tributary is 2nd order, and so on. Stream Ordering Stream Type 1. ephemeral- channels not well defined; flow during and shortly after precipitation events 2. intermittent- generally flow only during the wet season 3. perennial- year round spatial scale in lotic ecosystems World Continent Drainage Watershed Stream Channel Patterns • straight, meandering, & braided • sinuosity- degree of curvature and meandering • pool/riffle sequence; stream energy is lost at the head of the pool causing deposition Braided Stream Sedimentation & Channel Patterns • erosion- chemical and mechanical processes by which stream channels are formed • agrade- increase slope/gradient through deposition. Deposition process where particles that have been entrained and transported are deposited. factors effecting deposition 1. stream gradient 2. flow volume 3. particle size 4. impoundments results of deposition • delta- results when flowing water meets standing water • alluvial fan- sediments are deposited on land after eroding from higher elevation • alluvial flood plain- Delta Alluvial Fan Alluvial Floodplain Flow Classification Sediment Particulate Inorganic Matter (PIM) suspended sediments; primarily silt and clay Dissolved Organic Matter (DOM) decomposed particulate organics (particles < 0.45 um); carbohydrates, humic acids, tannins, proteins, & alcohols Particulate Organic Matter (POM) • larger sized particles; leaves, woody debris, and dead animals • important habitat & nutrients • Fine Particulate Organic Matter (FPOM)- < 1mm- >0.45um • Coarse Particulate Organic Matter (CPOM)- > 1mm