3.6.1 Reproduction of the Flowering Plant * Dormancy and
advertisement

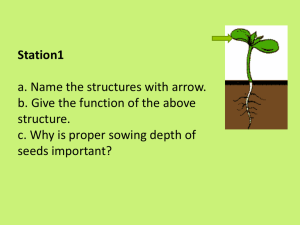
3.6.1 Reproduction of the Flowering Plant – Dormancy and Germination Follow-Me – iQuiz Q. State a difference between the seeds of monocots and dicots other than the number of seed leaves. Aerobic respiration Germination Optimum enzyme activity Anaerobic jar Germination at suitable time; Survival during unfavourable conditions Optimum storage conditions; Optimum sowing time; Maximise the growing season Avoid competition; Avail of suitable conditions Germination; Growth Ovary Ovule Cotyledon; Endosperm Growth of seed or embryo Dormancy Growth regulator; Selective propagation Period of low metabolism; Seed does not germinate despite favourable conditions Enzyme action; Solvent; Transport of materials; Bursting testa; Washing away inhibitors Keep temperature constant; Vary temperature; Heating Petri dish containing a jelly or solid medium Make food soluble and transportable Reproduction; Seed dispersal Milk; Starch Water; Suitable temperature; Oxygen FALSE TRUE Food store as endosperm; No endosperm CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Q. True or False. Light is essential for the germination of seeds. Aerobic respiration Germination Optimum enzyme activity Anaerobic jar Germination at suitable time; Survival during unfavourable conditions Optimum storage conditions; Optimum sowing time; Maximise the growing season Avoid competition; Avail of suitable conditions Germination; Growth Ovary Ovule Cotyledon; Endosperm Growth of seed or embryo Dormancy Growth regulator; Selective propagation Period of low metabolism; Seed does not germinate despite favourable conditions Enzyme action; Solvent; Transport of materials; Bursting testa; Washing away inhibitors Keep temperature constant; Vary temperature; Heating Petri dish containing a jelly or solid medium Make food soluble and transportable Reproduction; Seed dispersal Milk; Starch Water; Suitable temperature; Oxygen FALSE TRUE Food store as endosperm; No endosperm CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Q. What is dormancy? Aerobic respiration Germination Optimum enzyme activity Anaerobic jar Germination at suitable time; Survival during unfavourable conditions Optimum storage conditions; Optimum sowing time; Maximise the growing season Avoid competition; Avail of suitable conditions Germination; Growth Ovary Ovule Cotyledon; Endosperm Growth of seed or embryo Dormancy Growth regulator; Selective propagation Period of low metabolism; Seed does not germinate despite favourable conditions Enzyme action; Solvent; Transport of materials; Bursting testa; Washing away inhibitors Keep temperature constant; Vary temperature; Heating Petri dish containing a jelly or solid medium Make food soluble and transportable Reproduction; Seed dispersal Milk; Starch Water; Suitable temperature; Oxygen FALSE TRUE Food store as endosperm; No endosperm CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Q. What is meant by germination? Aerobic respiration Germination Optimum enzyme activity Anaerobic jar Germination at suitable time; Survival during unfavourable conditions Optimum storage conditions; Optimum sowing time; Maximise the growing season Avoid competition; Avail of suitable conditions Germination; Growth Ovary Ovule Cotyledon; Endosperm Growth of seed or embryo Dormancy Growth regulator; Selective propagation Period of low metabolism; Seed does not germinate despite favourable conditions Enzyme action; Solvent; Transport of materials; Bursting testa; Washing away inhibitors Keep temperature constant; Vary temperature; Heating Petri dish containing a jelly or solid medium Make food soluble and transportable Reproduction; Seed dispersal Milk; Starch Water; Suitable temperature; Oxygen FALSE TRUE Food store as endosperm; No endosperm CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Q. Why is digestion necessary in a germinating seed? Aerobic respiration Germination Optimum enzyme activity Anaerobic jar Germination at suitable time; Survival during unfavourable conditions Optimum storage conditions; Optimum sowing time; Maximise the growing season Avoid competition; Avail of suitable conditions Germination; Growth Ovary Ovule Cotyledon; Endosperm Growth of seed or embryo Dormancy Growth regulator; Selective propagation Period of low metabolism; Seed does not germinate despite favourable conditions Enzyme action; Solvent; Transport of materials; Bursting testa; Washing away inhibitors Keep temperature constant; Vary temperature; Heating Petri dish containing a jelly or solid medium Make food soluble and transportable Reproduction; Seed dispersal Milk; Starch Water; Suitable temperature; Oxygen FALSE TRUE Food store as endosperm; No endosperm CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Q. What is an agar plate? Aerobic respiration Germination Optimum enzyme activity Anaerobic jar Germination at suitable time; Survival during unfavourable conditions Optimum storage conditions; Optimum sowing time; Maximise the growing season Avoid competition; Avail of suitable conditions Germination; Growth Ovary Ovule Cotyledon; Endosperm Growth of seed or embryo Dormancy Growth regulator; Selective propagation Period of low metabolism; Seed does not germinate despite favourable conditions Enzyme action; Solvent; Transport of materials; Bursting testa; Washing away inhibitors Keep temperature constant; Vary temperature; Heating Petri dish containing a jelly or solid medium Make food soluble and transportable Reproduction; Seed dispersal Milk; Starch Water; Suitable temperature; Oxygen FALSE TRUE Food store as endosperm; No endosperm CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Q. Suggest one way in which knowledge of dormancy is useful to farmers and gardeners. Aerobic respiration Germination Optimum enzyme activity Anaerobic jar Germination at suitable time; Survival during unfavourable conditions Optimum storage conditions; Optimum sowing time; Maximise the growing season Avoid competition; Avail of suitable conditions Germination; Growth Ovary Ovule Cotyledon; Endosperm Growth of seed or embryo Dormancy Growth regulator; Selective propagation Period of low metabolism; Seed does not germinate despite favourable conditions Enzyme action; Solvent; Transport of materials; Bursting testa; Washing away inhibitors Keep temperature constant; Vary temperature; Heating Petri dish containing a jelly or solid medium Make food soluble and transportable Reproduction; Seed dispersal Milk; Starch Water; Suitable temperature; Oxygen FALSE TRUE Food store as endosperm; No endosperm CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Q. For what purpose is water needed in germination? Aerobic respiration Germination Optimum enzyme activity Anaerobic jar Germination at suitable time; Survival during unfavourable conditions Optimum storage conditions; Optimum sowing time; Maximise the growing season Avoid competition; Avail of suitable conditions Germination; Growth Ovary Ovule Cotyledon; Endosperm Growth of seed or embryo Dormancy Growth regulator; Selective propagation Period of low metabolism; Seed does not germinate despite favourable conditions Enzyme action; Solvent; Transport of materials; Bursting testa; Washing away inhibitors Keep temperature constant; Vary temperature; Heating Petri dish containing a jelly or solid medium Make food soluble and transportable Reproduction; Seed dispersal Milk; Starch Water; Suitable temperature; Oxygen FALSE TRUE Food store as endosperm; No endosperm CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Q. State a use for a water bath in biological investigations. Aerobic respiration Germination Optimum enzyme activity Anaerobic jar Germination at suitable time; Survival during unfavourable conditions Optimum storage conditions; Optimum sowing time; Maximise the growing season Avoid competition; Avail of suitable conditions Germination; Growth Ovary Ovule Cotyledon; Endosperm Growth of seed or embryo Dormancy Growth regulator; Selective propagation Period of low metabolism; Seed does not germinate despite favourable conditions Enzyme action; Solvent; Transport of materials; Bursting testa; Washing away inhibitors Keep temperature constant; Vary temperature; Heating Petri dish containing a jelly or solid medium Make food soluble and transportable Reproduction; Seed dispersal Milk; Starch Water; Suitable temperature; Oxygen FALSE TRUE Food store as endosperm; No endosperm CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Q. What type of agar plates did you use when investigating the digestive activity of seeds? Aerobic respiration Germination Optimum enzyme activity Anaerobic jar Germination at suitable time; Survival during unfavourable conditions Optimum storage conditions; Optimum sowing time; Maximise the growing season Avoid competition; Avail of suitable conditions Germination; Growth Ovary Ovule Cotyledon; Endosperm Growth of seed or embryo Dormancy Growth regulator; Selective propagation Period of low metabolism; Seed does not germinate despite favourable conditions Enzyme action; Solvent; Transport of materials; Bursting testa; Washing away inhibitors Keep temperature constant; Vary temperature; Heating Petri dish containing a jelly or solid medium Make food soluble and transportable Reproduction; Seed dispersal Milk; Starch Water; Suitable temperature; Oxygen FALSE TRUE Food store as endosperm; No endosperm CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Q. How did you demonstrate the requirement for oxygen when investigating the factors necessary for seed germination? Aerobic respiration Germination Optimum enzyme activity Anaerobic jar Germination at suitable time; Survival during unfavourable conditions Optimum storage conditions; Optimum sowing time; Maximise the growing season Avoid competition; Avail of suitable conditions Germination; Growth Ovary Ovule Cotyledon; Endosperm Growth of seed or embryo Dormancy Growth regulator; Selective propagation Period of low metabolism; Seed does not germinate despite favourable conditions Enzyme action; Solvent; Transport of materials; Bursting testa; Washing away inhibitors Keep temperature constant; Vary temperature; Heating Petri dish containing a jelly or solid medium Make food soluble and transportable Reproduction; Seed dispersal Milk; Starch Water; Suitable temperature; Oxygen FALSE TRUE Food store as endosperm; No endosperm CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Q. State three environmental factors that are necessary for germination. Aerobic respiration Germination Optimum enzyme activity Anaerobic jar Germination at suitable time; Survival during unfavourable conditions Optimum storage conditions; Optimum sowing time; Maximise the growing season Avoid competition; Avail of suitable conditions Germination; Growth Ovary Ovule Cotyledon; Endosperm Growth of seed or embryo Dormancy Growth regulator; Selective propagation Period of low metabolism; Seed does not germinate despite favourable conditions Enzyme action; Solvent; Transport of materials; Bursting testa; Washing away inhibitors Keep temperature constant; Vary temperature; Heating Petri dish containing a jelly or solid medium Make food soluble and transportable Reproduction; Seed dispersal Milk; Starch Water; Suitable temperature; Oxygen FALSE TRUE Food store as endosperm; No endosperm CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Q. For what purpose is oxygen needed in germination? Aerobic respiration Germination Optimum enzyme activity Anaerobic jar Germination at suitable time; Survival during unfavourable conditions Optimum storage conditions; Optimum sowing time; Maximise the growing season Avoid competition; Avail of suitable conditions Germination; Growth Ovary Ovule Cotyledon; Endosperm Growth of seed or embryo Dormancy Growth regulator; Selective propagation Period of low metabolism; Seed does not germinate despite favourable conditions Enzyme action; Solvent; Transport of materials; Bursting testa; Washing away inhibitors Keep temperature constant; Vary temperature; Heating Petri dish containing a jelly or solid medium Make food soluble and transportable Reproduction; Seed dispersal Milk; Starch Water; Suitable temperature; Oxygen FALSE TRUE Food store as endosperm; No endosperm CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Q. Seeds may remain inactive for a period before germination. What term is used to describe this period of inactivity? Aerobic respiration Germination Optimum enzyme activity Anaerobic jar Germination at suitable time; Survival during unfavourable conditions Optimum storage conditions; Optimum sowing time; Maximise the growing season Avoid competition; Avail of suitable conditions Germination; Growth Ovary Ovule Cotyledon; Endosperm Growth of seed or embryo Dormancy Growth regulator; Selective propagation Period of low metabolism; Seed does not germinate despite favourable conditions Enzyme action; Solvent; Transport of materials; Bursting testa; Washing away inhibitors Keep temperature constant; Vary temperature; Heating Petri dish containing a jelly or solid medium Make food soluble and transportable Reproduction; Seed dispersal Milk; Starch Water; Suitable temperature; Oxygen FALSE TRUE Food store as endosperm; No endosperm CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Q. What term is given to the growth of an embryo into a plant? Aerobic respiration Germination Optimum enzyme activity Anaerobic jar Germination at suitable time; Survival during unfavourable conditions Optimum storage conditions; Optimum sowing time; Maximise the growing season Avoid competition; Avail of suitable conditions Germination; Growth Ovary Ovule Cotyledon; Endosperm Growth of seed or embryo Dormancy Growth regulator; Selective propagation Period of low metabolism; Seed does not germinate despite favourable conditions Enzyme action; Solvent; Transport of materials; Bursting testa; Washing away inhibitors Keep temperature constant; Vary temperature; Heating Petri dish containing a jelly or solid medium Make food soluble and transportable Reproduction; Seed dispersal Milk; Starch Water; Suitable temperature; Oxygen FALSE TRUE Food store as endosperm; No endosperm CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Q. Suggest two advantages of dormancy. Aerobic respiration Germination Optimum enzyme activity Anaerobic jar Germination at suitable time; Survival during unfavourable conditions Optimum storage conditions; Optimum sowing time; Maximise the growing season Avoid competition; Avail of suitable conditions Germination; Growth Ovary Ovule Cotyledon; Endosperm Growth of seed or embryo Dormancy Growth regulator; Selective propagation Period of low metabolism; Seed does not germinate despite favourable conditions Enzyme action; Solvent; Transport of materials; Bursting testa; Washing away inhibitors Keep temperature constant; Vary temperature; Heating Petri dish containing a jelly or solid medium Make food soluble and transportable Reproduction; Seed dispersal Milk; Starch Water; Suitable temperature; Oxygen FALSE TRUE Food store as endosperm; No endosperm CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Q. Why is it necessary for plants to disperse their seeds? Aerobic respiration Germination Optimum enzyme activity Anaerobic jar Germination at suitable time; Survival during unfavourable conditions Optimum storage conditions; Optimum sowing time; Maximise the growing season Avoid competition; Avail of suitable conditions Germination; Growth Ovary Ovule Cotyledon; Endosperm Growth of seed or embryo Dormancy Growth regulator; Selective propagation Period of low metabolism; Seed does not germinate despite favourable conditions Enzyme action; Solvent; Transport of materials; Bursting testa; Washing away inhibitors Keep temperature constant; Vary temperature; Heating Petri dish containing a jelly or solid medium Make food soluble and transportable Reproduction; Seed dispersal Milk; Starch Water; Suitable temperature; Oxygen FALSE TRUE Food store as endosperm; No endosperm CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Q. After fertilisation, what part of the flower becomes the fruit? Aerobic respiration Germination Optimum enzyme activity Anaerobic jar Germination at suitable time; Survival during unfavourable conditions Optimum storage conditions; Optimum sowing time; Maximise the growing season Avoid competition; Avail of suitable conditions Germination; Growth Ovary Ovule Cotyledon; Endosperm Growth of seed or embryo Dormancy Growth regulator; Selective propagation Period of low metabolism; Seed does not germinate despite favourable conditions Enzyme action; Solvent; Transport of materials; Bursting testa; Washing away inhibitors Keep temperature constant; Vary temperature; Heating Petri dish containing a jelly or solid medium Make food soluble and transportable Reproduction; Seed dispersal Milk; Starch Water; Suitable temperature; Oxygen FALSE TRUE Food store as endosperm; No endosperm CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Q. Name the stage in the plant’s life cycle that follows dormancy. Aerobic respiration Germination Optimum enzyme activity Anaerobic jar Germination at suitable time; Survival during unfavourable conditions Optimum storage conditions; Optimum sowing time; Maximise the growing season Avoid competition; Avail of suitable conditions Germination; Growth Ovary Ovule Cotyledon; Endosperm Growth of seed or embryo Dormancy Growth regulator; Selective propagation Period of low metabolism; Seed does not germinate despite favourable conditions Enzyme action; Solvent; Transport of materials; Bursting testa; Washing away inhibitors Keep temperature constant; Vary temperature; Heating Petri dish containing a jelly or solid medium Make food soluble and transportable Reproduction; Seed dispersal Milk; Starch Water; Suitable temperature; Oxygen FALSE TRUE Food store as endosperm; No endosperm CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Q. For what purpose is a suitable temperature needed in germination? Aerobic respiration Germination Optimum enzyme activity Anaerobic jar Germination at suitable time; Survival during unfavourable conditions Optimum storage conditions; Optimum sowing time; Maximise the growing season Avoid competition; Avail of suitable conditions Germination; Growth Ovary Ovule Cotyledon; Endosperm Growth of seed or embryo Dormancy Growth regulator; Selective propagation Period of low metabolism; Seed does not germinate despite favourable conditions Enzyme action; Solvent; Transport of materials; Bursting testa; Washing away inhibitors Keep temperature constant; Vary temperature; Heating Petri dish containing a jelly or solid medium Make food soluble and transportable Reproduction; Seed dispersal Milk; Starch Water; Suitable temperature; Oxygen FALSE TRUE Food store as endosperm; No endosperm CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Q. From what does a seed develop? Aerobic respiration Germination Optimum enzyme activity Anaerobic jar Germination at suitable time; Survival during unfavourable conditions Optimum storage conditions; Optimum sowing time; Maximise the growing season Avoid competition; Avail of suitable conditions Germination; Growth Ovary Ovule Cotyledon; Endosperm Growth of seed or embryo Dormancy Growth regulator; Selective propagation Period of low metabolism; Seed does not germinate despite favourable conditions Enzyme action; Solvent; Transport of materials; Bursting testa; Washing away inhibitors Keep temperature constant; Vary temperature; Heating Petri dish containing a jelly or solid medium Make food soluble and transportable Reproduction; Seed dispersal Milk; Starch Water; Suitable temperature; Oxygen FALSE TRUE Food store as endosperm; No endosperm CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Q. State one method that is used to produce seedless fruits. Aerobic respiration Germination Optimum enzyme activity Anaerobic jar Germination at suitable time; Survival during unfavourable conditions Optimum storage conditions; Optimum sowing time; Maximise the growing season Avoid competition; Avail of suitable conditions Germination; Growth Ovary Ovule Cotyledon; Endosperm Growth of seed or embryo Dormancy Growth regulator; Selective propagation Period of low metabolism; Seed does not germinate despite favourable conditions Enzyme action; Solvent; Transport of materials; Bursting testa; Washing away inhibitors Keep temperature constant; Vary temperature; Heating Petri dish containing a jelly or solid medium Make food soluble and transportable Reproduction; Seed dispersal Milk; Starch Water; Suitable temperature; Oxygen FALSE TRUE Food store as endosperm; No endosperm CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Q. State two locations in the seed where food may be stored. Aerobic respiration Germination Optimum enzyme activity Anaerobic jar Germination at suitable time; Survival during unfavourable conditions Optimum storage conditions; Optimum sowing time; Maximise the growing season Avoid competition; Avail of suitable conditions Germination; Growth Ovary Ovule Cotyledon; Endosperm Growth of seed or embryo Dormancy Growth regulator; Selective propagation Period of low metabolism; Seed does not germinate despite favourable conditions Enzyme action; Solvent; Transport of materials; Bursting testa; Washing away inhibitors Keep temperature constant; Vary temperature; Heating Petri dish containing a jelly or solid medium Make food soluble and transportable Reproduction; Seed dispersal Milk; Starch Water; Suitable temperature; Oxygen FALSE TRUE Food store as endosperm; No endosperm CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Q. What is the role of the fruit? Aerobic respiration Germination Optimum enzyme activity Anaerobic jar Germination at suitable time; Survival during unfavourable conditions Optimum storage conditions; Optimum sowing time; Maximise the growing season Avoid competition; Avail of suitable conditions Germination; Growth Ovary Ovule Cotyledon; Endosperm Growth of seed or embryo Dormancy Growth regulator; Selective propagation Period of low metabolism; Seed does not germinate despite favourable conditions Enzyme action; Solvent; Transport of materials; Bursting testa; Washing away inhibitors Keep temperature constant; Vary temperature; Heating Petri dish containing a jelly or solid medium Make food soluble and transportable Reproduction; Seed dispersal Milk; Starch Water; Suitable temperature; Oxygen FALSE TRUE Food store as endosperm; No endosperm CONGRATULATIONS You’re Brilliant Incorrect Please CLICK on THIS BOX to Try Again